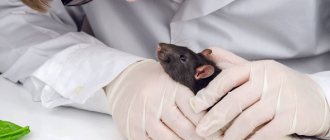
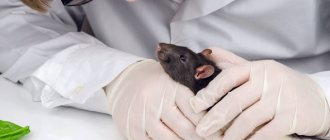
Is a stroke in a rat a death sentence?
Fortunately, medicine does not stand still, and there are many methods of not only treating stroke in rats, but also preventing it. Therefore, today we can say with confidence that the stroke that occurred in a rat is not a death sentence at all. Timely treatment and subsequent preventive actions can prolong the normal life of a rat after a stroke.
If you want your pet to live a full life, it is very important to treat your rodent after a stroke only under the supervision of a veterinarian. Timely detection of a stroke and timely prescribed medications, along with subsequent care, will help cope and return the rodent to normal life.
Important! If you find signs in your rat that indicate a stroke, you should not panic and remember the main points - what to do if your rat has a stroke:
- put the animal on its side;
- check your mouth - free it from vomit/saliva, check if your tongue is stuck;
- go to the veterinary clinic.
You can't do:
- apply cold to the rat's head - cold can provoke spasm of the affected vessels, causing even more harm;
- give medications without instructions from a veterinarian;
- do not give any injections.
When transporting, it is very important not to disturb the animal; it should be in a lying position, there is no need to turn it over or try to revive it.
Definition of stroke - what is it?
To understand how to overcome a disease, you need to know what it is, the reasons for its occurrence and ways to help if you suddenly notice symptoms of a stroke in a rat.
Stroke is an acute disturbance of normal cerebral circulation (CVA), in which typical symptoms appear in a short period of time and persist throughout the day. This disease leads to many neurological disorders and even death.
Symptoms of coronavirus COVID-19
Coronavirus
COVID-19
625 January 27
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Definition
The SARS-CoV-2 virus spreads in microscopic particles of fluid released by a sick person during coughing, sneezing, talking, singing or heavy breathing and gets onto the mucous membranes of the nose, mouth or eyes of another person.
In addition, the virus can also spread through household contact, when particles with the virus located on surfaces or objects enter the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract through the hands.
Aerosol transmission occurs in closed, crowded and poorly ventilated areas.
The airborne dust (aerosol) transmission route is realized through the spread of aerosols (droplet nuclei) suspended in the air, the size of which is <5 microns. Due to their small size, aerosols can be transported over long distances and remain in the air for several hours. It must be remembered that aerosol-producing devices (nebulizers, halochambers, etc.) are prohibited for use in healthcare institutions during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Symptoms of mild COVID-19
Most common symptoms
- The main symptom (80-90%) is any increase in body temperature (even low-grade - 37-37.5°C).
- The cough is dry or with a small amount of sputum (60-80%).
- Increased fatigue (40-50%).
Less common symptoms
- Sudden loss of smell and/or taste (60-80%).
- Nasal congestion or mild rhinorrhea (5%).
- Conjunctivitis or redness of the eyes (1-2%).
- Sore throat (14%).
- Headaches, dizziness (8-14%). Immediately after the end of the incubation period, migraines of varying severity may appear.
- Pain in joints and muscles (11-15%).
- Skin rashes (8%).
- Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting (up to 20%).
- Chills (11-13%).
Those who have had a mild form of COVID-19 infection compare the sensations with the course of a common respiratory disease.
Symptoms of COVID-19 in severe and moderate forms of the disease
Most common symptoms
- Shortness of breath, rapid breathing (55%).
- Increased cough, appearance of sputum (30-35%).
- Hemoptysis (5%).
- Loss of appetite (20%).
- Confusion (9%).
- Sensation of constriction and congestion in the chest (> 20%).
- Body temperature above 38°C (80%) for more than 5 days.
- Blood oxygen saturation according to pulse oximetry (SpO2) ≤ 95% (up to 20%).
Less common symptoms
- tachycardia,
- vitamin D deficiency,
- irritability,
- convulsions,
- anxiety,
- depressed state
- sleep disorders.
Important! Symptoms may not be detected during the incubation period of COVID-19 or may appear in any combination (for example, without fever). The exact diagnosis is determined by the doctor based on the results of examinations.
Patients over 65 years of age may experience an atypical picture of the disease, which includes delirium (cloudedness of consciousness), speech impairment, movement disorders, as well as more severe and rare neurological complications - stroke, inflammatory brain damage, and others.
The majority (about 80%) of patients who develop symptoms recover without hospitalization. Approximately 15% of patients develop a severe form of the disease that requires oxygen therapy, and 5% develop an extremely severe form that requires treatment in an intensive care unit.
Differences between the new coronavirus disease COVID-19 and ARVI and influenza
COVID-19 also refers to ARVI - acute respiratory viral infections characterized by similar symptoms: cough, runny nose, fever, headache, sore throat and sore throat. The most clearly defined clinical picture is caused by influenza viruses, parainfluenza, and adenoviruses. Coronavirus can be more severe than other acute respiratory viral infections, leading to complications and even death. That is why it is extremely important to distinguish the new type of coronavirus from a relatively harmless cold.
What is the difference between coronavirus and ARVI?
- Longer incubation period. For ARVI, 2-3 days are enough to go into the acute phase, but coronavirus takes up to 2 weeks.
- Unlike other acute respiratory diseases, coronavirus causes a low body temperature of 37-37.5°C, which can last a relatively long time (up to 7 days).
- A cough when infected with coronavirus is often long-lasting, dry, painful and may be accompanied by chest pain.
- Coronavirus infection can cause digestive upset (diarrhea, nausea, vomiting); such phenomena are rare with ARVI in adults.
- ARVI is usually cured in 7-10 days, and COVID-19 on the 7-8th day in a certain percentage of people can move to the next stage, when shortness of breath and respiratory failure appear.
Only a laboratory test will help you accurately name the type of pathogen and establish the disease (coronavirus, ARVI, influenza).
What is the difference between coronavirus and flu
It should be noted that COVID-19 and influenza have much in common:
- transmitted by airborne droplets and contact;
- may manifest as aching joints, headache, severe weakness and a general feeling of weakness;
- Intestinal disorders may occur.
Main differences:
- The flu begins acutely with an increase in temperature immediately to febrile values (39-40⁰C). Symptoms of general intoxication come to the fore: headache, weakness, pain in muscles and joints, lacrimation, pain in the eyes.
- Coronavirus develops gradually - from general malaise in the first days to severe symptoms, including a significant increase in body temperature after a week.
It is important that a doctor determine the difference between coronavirus and influenza, since both diseases can lead to dangerous complications, including pneumonia.
If a person has the flu and not coronavirus, he also needs medical care and treatment under the supervision of a therapist. Other diseases with similar symptoms
Pneumonia, including atypical.
Allergies. Shortness of breath, problems with smell, and other symptoms may occur as a result of exposure to allergens. The problem is solved by antihistamines, which are ineffective for viral infections.
Bronchial asthma, which also makes itself felt by difficulty breathing and a painful cough, but is non-infectious in nature.
Are symptoms different in children and adults?
Children make up only about 2% of all COVID-19 cases. At the same time, they tolerate coronavirus infection more easily and are often asymptomatic carriers.
The course of COVID-19 in children of different ages:
From 1 year to 3 years
The infection usually manifests itself as a mild illness. There are no characteristic symptoms of COVID-19. Sometimes there is a loss of appetite, which goes away after 2-3 days and does not affect the baby’s general well-being.
From 3 to 7 years
Children at this age are sick for about seven days and recover without complications. They may experience hoarseness and mild nasal congestion. There is no cough, occasional sneezing is possible.
From 7 to 17 years old
Primary schoolchildren and adolescents may experience a slight increase in body temperature and mild malaise. A dry cough is possible, and even less often - a headache.
According to Rospotrebnadzor, a mild form of the disease is usually due to the patient’s strong immunity.
The immune system of children and adolescents is usually well prepared to fight viruses. They can become infected, but their disease is milder or completely asymptomatic.
Stages of disease development taking into account symptoms
Symptoms of coronavirus in an adult by day
1-3 days. The disease begins with mild malaise, a slight increase in temperature, nasal congestion and muscle pain, as with ARVI or influenza.
3-5th day. Body temperature rises, and a mild, superficial cough is possible. The sense of smell may disappear, and taste sensations may change greatly. Digestive disorders occur, including diarrhea. This period is considered the culmination of a mild form of COVID-19.
5-10th day. An important period for determining the severity of coronavirus infection. 80% of people sick with COVID-19 experience improvements, which can lead to a full recovery in a few days. The second scenario involves a worsening of the condition, which is manifested by an increase in the number and severity of symptoms. With this development of events, the patient develops a severe runny nose, debilitating cough, chills, body pain, and shortness of breath.
10-12th day. This period is characterized by severe shortness of breath, chest pain, progression of weakness, and pallor, which indicates the development of pneumonia. Damage to the lungs leads to oxygen starvation. Hospitalization required. This condition is considered moderate.
12-14th day. With COVID-19, 75% of patients with viral pneumonia begin to recover on average 2 weeks from the onset of the disease. However, those who develop severe disease may require mechanical ventilation.
14-30th day. It takes on average up to two weeks from the onset of a serious complication to recover from a severe form of pneumonia caused by coronavirus.
But even after complete recovery, mild shortness of breath may persist, weakness and malaise may appear for a long time (up to several months).
Clinical variants and manifestations of COVID-19
- Affects only the upper respiratory tract.
- Pneumonia without respiratory failure.
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome (pneumonia with acute respiratory failure).
- Sepsis, septic (infectious-toxic) shock.
- Syndrome of disseminated intravascular coagulation, thrombosis and thromboembolism.
- Blood oxygen saturation is less than 88%.
Patients with critical COVID-19 develop vascular endothelial dysfunction, bleeding disorders, thrombosis, and thrombotic microangiopathy.
A cytokine storm in COVID-19 is the body’s response to an inflammatory process, leading to immune cells attacking not only the virus, but also the tissues of the body’s own. The consequence of this can be the destruction of tissues and organs, and, as a consequence, the death of the body.
It is very important that sometimes COVID-19 is dangerous not only because of pneumonia and its complications, but also because it has a negative effect on blood vessels, the brain and the heart, which increases the risk of stroke. In such cases, the patient experiences dizziness, fainting may occur, the face turns blue and the muscles become numb.
Symptoms indicating the healing process
Attention!
The time intervals for the course of the disease are arbitrary; they depend on the individual characteristics of the organism. COVID-19 in mild form usually lasts no more than 14 days. But only an antibody test can confirm final recovery. Given the severity of the disease, the recovery process can take place in different ways. The criterion for recovery is if two consecutive tests for coronavirus using the PCR method gave a negative result.
Types of stroke
Stroke in pet rats is divided into two types - hemorrhagic and ischemic.
Hemorrhagic stroke is intracerebral hemorrhage. Ischemic stroke is a disorder of cerebral blood circulation that damages brain tissue.
For convenience, consider the table:
| Hemorrhagic | Ischemic | |
| Onset of the disease | Sudden | Gradual |
| External signs | Increased sweating, cramps, hyperemia | Not expressed |
| Motor excitement | Expressed | Not expressed/Rarely |
| Convulsions | Yes | Rarely |
| Breath | Snore | Often no change |
| Impaired consciousness | Swift | Slow |
Based on the above, we can conclude that with a hemorrhagic stroke in an animal due to a rupture of an artery or a traumatic brain injury, the stroke occurs spontaneously, and this type of disease is considered more dangerous, more often leading to death.
Ischemic stroke, which occurs as a result of narrowing or blockage of individual vessels, occurs differently; if the development of this type was rapid and with loss of consciousness, then, most likely, an embolic type occurred.
Causes of stroke. Etiology of the disease
This disease has many causes, including internal and external factors:
- Internal – genetic predisposition, changes associated with the age of the animal, heart/vascular/kidney diseases, brain tumors, thrombosis, embolism.
- External – poor diet, inactive lifestyle, unfavorable living environment, excess weight.
In addition to the main causes, for each type of stroke, separate factors are identified that can trigger the development of the disease.
| Ischemic | Hemorrhagic |
| Hypertension | Poisoning with rat poison |
| Endocrine diseases | Head injuries resulting in brain injuries |
| Kidney/heart/vascular diseases | Autoimmune diseases |
Unfortunately, it is not always possible to perform a CT scan or ultrasound on an animal to determine the exact cause of a stroke; in this case, a diagnosis is made - idiopathic stroke, i.e. It occurs suddenly, without reason, but such an illness always has a trigger factor and for subsequent recovery it is advisable to identify it.
Without stopping the provoking factor, there is a possibility of repeated strokes and subsequent death of the pet.
Stroke in a rat: symptoms and treatment
A stroke in its symptoms may be similar to other diseases or neurological disorders, so in this case it is impossible to do without consulting a doctor; also, along with characteristic manifestations, there may be nonspecific signs of a stroke in a rat, which also complicates the diagnosis.
Treatment involves complex therapy aimed at relieving symptoms and regenerating brain cells.
Symptoms of a stroke in a rat
How severe the symptoms of a stroke will be depends on the degree of damage to brain cells. Typically, signs of a stroke in a rat appear in a fairly short period of time.
Stroke in its symptoms may be similar to other diseases or neurological disorders, so in this case it is impossible to do without consulting a doctor; also, along with characteristic manifestations, there may be nonspecific symptoms, which also complicates the diagnosis. If you notice signs of a stroke in rats, it is very important to remember not only them, but the order, severity and duration with which they appear, this is very important for establishing an accurate diagnosis and subsequent treatment.
Just like with people, the sooner help is provided, the greater the chance of recovery. It is important to remember that when stroke occurs in rats, symptoms affect treatment.
For convenience, consider a table of the main characteristic symptoms of a stroke in a rat:
| Symptoms | Frequency |
| Falls over on its side | Almost always |
| Hard breath | Always |
| Loss of coordination | Always |
| Visual impairment | Almost always |
| Emotional instability | Almost always |
| Convulsions | Rarely |
In addition to the main symptoms, there may be other atypical signs, but if you notice several of the above signs of a stroke, you should immediately seek help from a veterinary clinic.
What are hallucinations, what are they?
Hallucinations are images that appear in a person’s consciousness. Most often these are symptoms of a psychological illness. A person may also experience auditory hallucinations. Healthy people can also experience hallucinations, but as a result of severe overwork of the body. If this condition is not uncommon for you, then you should think about treatment.
Free consultation right now!
Online consultation with a specialist on your issue!
License number: LO-77-01-019036
Clinical signs and diagnosis of stroke in rats
The following symptoms may be noticed:
- Apathy - the animal shows no interest in eating or playing.
- Emotional instability/changes in behavior - the animal may show aggression or frightenedly rush around the cage, thus showing signs of anxiety.
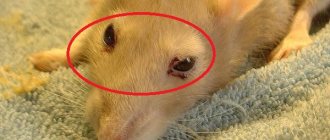
- A characteristic sign of a stroke is redness of the white of the eye or complete blindness - which can also be noticed by the strange behavior of the animal.
- Loss of coordination: the rat will not be able to walk straight, it will fall over on its side, and all its movements become clumsy.
- Tilt of the head to one side - the muscles lose their tone, muscle weakness may persist for several weeks after the attack.
- Spontaneous bowel movements - due to weakness of the abdominal muscles, which can also be affected by a stroke.
- Breathing disorders - breathing becomes shallow and shallow, it is clear that the animal is having difficulty breathing.
- Muscle spasms.
- Paralysis - complete or partial.
It is important to remember that in addition to typical symptoms, there may be signs that are not characteristic of a stroke.
General symptoms
The main symptoms of hyperkinesis include motor acts performed by patients against their will, the so-called violent ones. Patients themselves describe them as the result of an irresistible desire that they cannot resist.
The list of symptoms representing hyperkinesis includes:
- frequent blinking and squinting of the eyes (tics);
- convulsive tilting or turning of the head;
- tremor of various parts of the body, most often the limbs;
- myoclonus – sudden muscle twitching of the arms or neck;
- chorea - arrhythmic movements of facial expressions, involuntary sounds arising from rapid contractions of the muscles of the larynx;
- ballism - sudden rotation of the hip or shoulder;
- Blapharospasm is a pathological closure of the eyelids, as one of the signs of various diseases.
Forms of hyperkinesis can vary from intermittently frequent to constant. Some patients manage to control certain forms of hyperkinesis (for example, tics) by force of will, but after a while the attack of violent movements manifests itself again with even greater force.
Treatment methods
The main goal of drug treatment for stroke in rats is to negate the negative consequences after the stroke has occurred and remove inflammation from the cells. Along with therapy, it is very important that the animal feels comfortable and is surrounded by care and proper care.
There is no single cure for the consequences of a stroke; it is a whole range of measures, including:
- Rehydration of the body - for this, a rehydration solution is administered.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs - to relieve inflammation in brain cells and tissues.
- Antiemetics - if after first aid it does not go away and the animal continues to vomit.
- Sedatives - help cope with disorientation.
- Antibiotics - to prevent the addition of a secondary infection, because The rodent's body is weakened after a stroke.
- Oxygen - to eliminate the effects of brain hypoxia.
- Corticosteroids provide comprehensive treatment to eliminate the severe consequences of a stroke.
- Diuretics - to prevent swelling.
Before starting treatment, the specialist must carry out a number of diagnostic measures that are aimed at establishing a diagnosis and the reasons that led to the disease.
For diagnostic purposes, a CT scan (computed tomography of the head) and an X-ray of the rat’s head can be used; these measures will help identify hematomas and/or tumors. An ophthalmoscopy examination will help identify disorders in the retina and signs of hypertension; these data are necessary for prescribing therapy.
After diagnosis and treatment, the animal is sent home; further care and rehabilitation depends on the owner of the animal.
The attending veterinarian decides how to treat a stroke in a rat; without the necessary knowledge, self-medication can harm the animal even more, which will lead to dire consequences.
How many rats survive after a stroke?
If we recall history, we will notice that rats are quite tenacious creatures; in the wild, these rodents are accustomed to great physical exertion, they have learned to avoid danger, even not to eat food that causes doubts in it or from which its relatives died. Considering this, as well as statistics, 95% of rats not only survive a stroke, but also fully recover! The most important thing is timely provision of assistance. With an accurate diagnosis, correctly prescribed treatment and proper follow-up care, the animal has a favorable prognosis and a high chance of returning to its previous life.
Structure and functions of the cornea of the eye
The cornea looks like a concave-convex natural lens. This section of the eye is up to 10 mm in diameter.
The structure of the cornea is represented by 5 layers:
- anterior (integumentary)
, consisting of epithelial cells, providing protection to this part of the eye from damage; - Bowman's membrane
, which helps the cornea maintain its shape; - stroma
, formed by collagen fibers and leukocytes, making the cornea of the eyes quite strong; - Descemet's
, which increases the cornea's resistance to harmful factors; - posterior (endothelial)
, supplying the cornea with nutrients.
The cornea performs several important functions - it participates in the process of light refraction, protects the eye from injury, and maintains the normal shape of the eyeball. If its transparency deteriorates, a sharp deterioration in vision occurs, requiring immediate eye treatment.
Caring for a Sick Rat
After a stroke in rats, subsequent treatment at home is important, which requires:
- Provide access to food and water.
- Secure your home - remove all gaming accessories for the recovery period;
- Monitor the water balance - check at the drinking bowl whether the rat has been drinking; if not, find out the reasons and eliminate it, for example, help it quench its thirst.
- Massage - the veterinarian will show you how to do it to prevent muscle atrophy.
- Maintain cleanliness and the necessary, comfortable temperature in the rodent’s home.
Regarding the diet during a stroke: no specific diet is required, and if the rat is able to feed itself, its nutrition remains the same, if the animal cannot feed on its own, the owner’s help will be required, then food is supplied through a syringe.
In order to prevent bedsores and ulcers, it is necessary to turn the animal over at regular intervals and change the bedding as it becomes moist, since, most likely, the animal will defecate on itself. During the recovery period, the animal must be under constant supervision and surrounded by care.
If the first necessary assistance is provided on time, then improvements will be noticeable already on the third day; if there is no positive dynamics, then the prognosis of the disease is unfavorable. Along with the treatment provided, it is important how the rat’s body will react to it, and whether it will have a response. If treatment for stroke in rats is carried out correctly and the animal reacts positively to it, then the next day improvements will be noticeable, and after a couple of weeks the animal will fully get back on its feet.
If a rat begins to itch after a stroke , you should seek a second consultation with your doctor; itching may indicate:
- neurological disorders;
- improper care, and subsequently skin pathologies arose;
- allergies to medications.
After the examination, the doctor will determine the cause of the itching and suggest treatment options. The main rule in caring for a sick animal is peace, comfort and care.
What to do if you have hallucinations?
Today, there are a huge number of methods for treating hallucinations, and different methods are aimed at eliminating different types of hallucinations. It must be said that therapy is often aimed at treating the cause of hallucinations. But, unfortunately, it is not always possible to eliminate the cause of the disease. It is necessary that hallucinations or the disease that caused them be diagnosed by an experienced specialist. Do not be shy or wait for an exacerbation; you should consult a doctor immediately.
Get a consultation at the psychiatric department of the KORSAKOV clinic.
How to identify hallucinations?
Diagnostics involves determining whether there is a difference from the illusory deception that a healthy person may have. It is necessary to look at the general condition and behavior of the patient, check whether he has delusions or other mental illnesses. Analyze his facial expressions, gestures, check whether he has a feeling of anxiety, and based on the overall picture, draw a conclusion about the person’s condition. This way you can understand whether a disease exists, and if so, determine the degree.
How to deal with hallucinations?
The first step is to diagnose the cause of the hallucination and possible diseases. Next, you need to prescribe a course of appropriate treatment.
At the diagnostic stage, an anamnesis is collected, it is clarified what exactly the patient sees, hears and feels. A thorough examination of what is visible, audible, and felt is carried out, an examination is carried out and a method of treatment is selected. The method of monitoring and caring for the patient is also selected.
Online consultation with a specialist
regarding your question!
License number: LO-77-01-019036
Stroke in a rat: disease prevention
Stroke prevention is important not only for a healthy animal, as a preventive measure, but also for those who have already suffered a stroke, in order to prevent repeated attacks.
According to veterinarians, nutrition is not an unimportant part; to prevent this serious disease, it is necessary to include in the rodent’s diet foods rich in Omega-3 acids and other antioxidants; these components are the prevention of many cardiovascular diseases, including stroke.
In addition to nutrition, it is necessary to contact the clinic at the first signs of any disease. This will prevent the development of serious illnesses that can subsequently cause a stroke.
It is easier to treat any illness at the initial stage than to deal with the negative consequences in an advanced case.
Experts have identified a number of preventive tips that, if followed, can prevent the development of a stroke:
- balancing nutrition;
- monitor weight - prevent your pet from becoming overweight
- treatment of diseases in a timely manner - responsibility for the life and health of the pet lies with the owner;
- active lifestyle - having gaming accessories will help avoid physical inactivity;
- eliminating possible stress.
By following these simple tips, you will extend the life of your pet, making it full and happy, and getting a reliable friend in return.
Diagnosis of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve
Depending on the affected area and the set of symptoms, the strategy for diagnosing the disease is determined. To determine the location of nerve damage, the severity and dynamics of recovery, doctors prescribe a hardware diagnostic method, for example, electromyography. MRI and CT scans are used to determine the presence of tumors in the brain.
The patient may also be referred for a general or biochemical blood test, x-ray of the lungs, ultrasound of soft tissues or ophthalmoscopy.
You can be confident in the quality of the procedures performed in the clinic and the high accuracy of the results of MRI, CT and other methods of diagnosing various diseases. Medunion performs magnetic resonance imaging of all types: head, spine, abdominal cavity and joints using modern equipment.