IMPORTANT!!! A specialist must diagnose the pathology, identify the cause and treat the rat! If a domestic rat is sick, it is advisable for the owner to urgently contact a veterinary clinic; some diseases of rats are very dangerous for humans: mycoplasmosis, rabies, tuberculosis, toxoplasmosis, tularemia, toxocariasis, rickettsiosis, leptospirosis, hemorrhagic fever, typhus, plague, sodoku, listeriosis.
How to tell if a rat is sick
Diseases of domestic rats often arise due to violations of feeding and maintenance standards; hypothermia, overheating or drafts cause colds and inflammatory diseases in smart animals; unbalanced diet and abuse of harmful treats cause obesity, allergies, vitamin deficiencies or intestinal pathologies in pets.
Infectious diseases of rats are also common; domestic rodents can become infected with viral, fungal and parasitic diseases through care items, food or through contact with infected relatives.
Owners of furry rodents often wonder whether a rat can get a virus or a cold from a person. Decorative rats are bred in laboratory conditions, have reduced immunity and are susceptible to human respiratory viral infections. During the acute period of the disease, the owner needs to limit communication with pets, cancel walks and games, leaving only feeding and changing water for the animal.
Diseases of domestic rats can be caused by various causes and pathogens, as a result of which a different clinical picture will be observed. The owner can understand that a pet rat is sick if his beloved rodent exhibits characteristic symptoms common to many pathologies:
- change in appetite or complete refusal of food;
- lethargy, excessive sleepiness, reluctance to play with the owner or other rats;
- changes in the color and odor of urine and feces;
- dirty genitals, the pet stops licking itself;
- dull and tousled coat, formation of bald areas;
- the appearance of causeless aggression, anxiety, nervousness;
- slowness, difficulty moving;
- breathing problems;
- unnatural poses;
- the formation of growths, bumps, swellings on the animal’s body;
- discharge from the nose, eyes, vagina, anus.
Using the method of repelling rats in Rostov-on-Don
You can scare away rats using 2 methods: 1) strong unpleasant odors. These include acetone, kerosene, gasoline. Chamomile is a suitable herb. This method is not suitable for residential premises, since the persistent smell of these substances will cause discomfort to household members; 2) repelling using ultrasound. This is a safer and more humane remedy, since it only affects rodents, which will be forced to look for a new habitat. It does not cause any harm to humans or pets. The downside is that if you turn it off, the risk of rodents coming back will increase.
Diseases of decorative rats and their treatment
Diseases in rats can be divided into two large groups, within which several subgroups are distinguished.
Contagious diseases
They are caused by various biological pathogens (pathogenic microflora, viruses, fungi) and are divided into:
- Infectious diseases of rats;
The causative agents are bacteria, viruses, fungi, rickettsia: listeriosis, ectromelia, salmonellosis, pasteurellosis, infectious pneumonia, tularemia, rabies, tuberculosis, encephalomyelitis.
- Invasive (parasitic diseases).
Caused by infection of the domestic rat's body with ticks, insects, helminths and protozoa: syphaciosis, aspiculuriosis, rodentolepiasis, hymenolepiasis, coccidiosis, demodicosis, pediculosis, fleas, scabies.
Non-communicable diseases
Decorative rats develop as a result of violation of the conditions of feeding and keeping the animal and are divided into:
- Internal;
Diseases of internal organs, blood and metabolic disorders: gastritis, enterocolitis, rhinitis, bronchitis, pneumonia, pyelonephritis, vitamin deficiencies, oncology, allergies, anemia, cardiovascular failure, ischemia, porphyrin.
- External;
Diseases of the limbs, head, neck, skin, tail - wounds, pododermatitis, injuries, skin abscesses, burns, bruises, frostbite, eczema, diseases of the eyes, ears and teeth.
- Diseases of the genital area.
Endometritis, vaginitis, pyometra, miscarriage, spirochetosis.
Treatment of pathologies of ornamental rats is carried out by a veterinarian after determining the diagnosis and determining the cause of the disease; many diseases require specific therapy or euthanasia of the infected animal.
Fighting rats at the dacha in Rostov-on-Don
With the arrival of a cold cyclone, the rats look for shelter for the winter. This is a very important aspect! Therefore, it is advisable to increase vigilance and control at this time of year. If at least one individual is detected on the territory, it is necessary to take appropriate measures. Methods of fighting in the country can be very radical, but at the same time highly effective. It is advisable to carry out a complex for the destruction of rodents together with the special services. Professionals know the habits of pests, and with the help of special-purpose devices they will eliminate pests in a short time and for a long time.
Contagious diseases of domestic rats
Infectious diseases often found in decorative rats include: mycoplasmosis, listeriosis, tuberculosis, infectious pneumonia, parasitic diseases.
Infectious diseases of rats
Domestic rodents often become infected with infectious diseases; sources of pathogens can be contaminated food, water, litter, insects, or sick animals. These pathologies are characterized by a severe course with serious damage to the vital organs of the animal, often leading to the death of the pet. Many infectious diseases of rodents are dangerous to humans; self-treatment of rats is unacceptable and can lead to dire consequences. A timely visit to a specialist can save the life of a small animal and protect the animal owner’s family from infection.
Mycoplasmosis
Most decorative rats are carriers of the causative agent of mycoplasmosis, but infection and the development of characteristic pathological changes are observed only as a result of contact with a sick animal, in violation of feeding and maintenance conditions, hypovitaminosis and weakened immunity, in elderly individuals. Pathogenic microorganisms infect the upper and lower parts of the rodent's lungs, forming numerous abscesses and causing the development of pneumonia, sometimes the inflammatory process affects the animal's genitals.
Symptoms characteristic of rats: sneezing, red discharge from the nose and eyes (porphyrin), wheezing and whistling when breathing, blue discoloration of the mucous membranes and skin, the rat has become lethargic and lies down a lot. Treatment includes a course of antibiotics, hormones, vitamins and anti-inflammatory drugs; in advanced cases, it is impossible to save a furry rodent.
Rabies
Rabies in ornamental rats is quite rare, it is very dangerous for humans, a pet becomes infected through saliva when bitten by a sick animal, especially while walking on the street, the most severe course of the disease is observed when bitten on the head or area of the nerve nodes.
The disease can occur in violent, paralytic and abortive forms; the incubation period in bitten people and decorative rats ranges from 2 weeks to three months.
Signs of rabies in rats develop gradually, in several stages:
- the first stage - apathy and photophobia are observed, followed by aggressiveness, sudden jumps around the cage, and characteristic attempts to catch non-existent flies. The rodent refuses food, salivation, vomiting, shortness of breath appear, and the pet cannot swallow due to paralysis of the lower jaw. Similar symptoms of rabies in rats against the background of recent bites should alert the owner of the rodent; it is necessary to urgently contact a veterinary clinic;
- the second stage - rabies in rats manifests itself in increased aggression, the rodent bites people, animals, cages, profuse salivation appears, paralysis of the hind limbs and pharynx, a drooping jaw, drooping head and tail are characteristic. Outbursts of excessive aggression are followed by periods of calm. The rabies virus penetrates the brain and the rat dies within 5-10 days. If a disease is detected in a decorative rat, the animal is euthanized, and the room where the pet was kept is disinfected using ultraviolet rays and alcohol.
Infectious pneumonia
The causative agents of the disease are specific viruses; domestic rodents become infected by airborne droplets; the pathological process occurs in the upper parts of the lung of a domestic rat. The pathology is manifested by characteristic symptoms: sneezing, red and mucopurulent discharge from the nose and eyes, hunched back, wheezing and whistling, the rodent breathes heavily on its sides, refuses food, the rat is lethargic, apathetic, sleeps more than usual. Sometimes a rapid course of the disease is observed, due to the increased level of metabolism in rats; in advanced cases, the animal cannot be saved. Treatment is carried out using antibiotics, hormones, vitamins and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Papillomas in rats
The papilloma virus in rats is manifested by the formation of small skin growths on the skin, which can degenerate into malignant neoplasms. Infection occurs through contact with a sick animal through damaged areas of the skin (wounds, cracks, scratches); the disease manifests itself only in emaciated, weakened or elderly individuals. If papillomas are detected, they must be surgically removed.
Parasitic diseases of rats
Most often, decorative rats are affected by ectoparasites - parasitic insects, infection occurs through food, filler, clothing and hands of the owner, upon contact with sick animals, characteristic symptoms of the disease are severe anxiety of the animal, sores on the neck of the rat, scratching and wounds on the head and shoulders fluffy rodent. To treat a pet, treat it with insecticidal sprays.
Lice and lice
Small insects, you can find adult red-brown insects or nit eggs in the form of white dandruff attached to the rodent's fur. Lice feed on the blood of a domestic rat, lice eaters feed on skin flakes and blood; parasitism is accompanied by severe itching and can cause the death of the animal.
Fleas
Small blood-sucking insects that can migrate between rats, dogs and cats; a sick rodent itches intensely, bites fur with its teeth, and worries. If a rat has bloody crusts on its back, this indicates that the pet is infected with fleas and requires immediate treatment.
Ticks
Rat mites live on the skin of healthy animals, exhausted and weakened animals become ill, parasitism is accompanied by itching, the rat has sores on the neck and face or red-yellow growths on the ears and genitals. Some types of rat mites are dangerous to humans.
Worms
Parasites are localized in the internal organs of rats: intestines, kidneys, liver, lungs; migration of larvae causes inflammatory processes in the affected organs; worms produce poisons that cause exhaustion and intoxication of the rodent. The owner may notice intestinal disorders in the pet, lethargy, progressive weight loss, and detection of parasites in the feces. Treatment includes the use of deworming medications.
Professional deratization of premises
In solving this problem, it is quite possible to rely on the professional services of the Operational Pest Control Service, whose employees operate throughout Rostov-on-Don and in adjacent settlements.
The personal experience of each of the specialists, modern equipment and knowledge of professional technology are complemented here by the use of exclusively certified products for deratization of premises with a valid shelf life and 100% effectiveness of use.
The combination of all these factors ensures the complete extermination of mice, rats and other rodents to a single individual. Both adult representatives of the colony and recently born rodents are subject to destruction - professional technology works flawlessly along with effective means of fighting rats, regardless of how securely the rodents are hiding.
If you need additional information about the services of the Operational Disinfestation Service or if you intend to call a pest control team, please contact customer support at the phone number indicated on this catalog page.
Common non-contagious diseases of domestic rats
Among non-communicable diseases in domestic rodents, the following are common: cancer, dental pathologies, urolithiasis, intestinal disorders, obesity, allergies, coronary heart and brain disease, heart and kidney failure.
Tumors
Oncological diseases often affect adult ornamental rats over two years of age, mainly females, and cause the death of their beloved pet.
Benign neoplasms are subject to surgical removal with a favorable prognosis; rat cancer is not treated due to the formation of metastases and the germination of malignant tumors into healthy tissues of the animal. The following types of tumors are often found in decorative rats:
- a tumor of the mammary glands is detected as a mobile lump on the abdomen or fused with the skin;
- a tumor on the neck, on the side, under the paw or under the tail feels like a rolling ball under the skin on a leg;
- the swelling on the face looks like a pet's swollen cheek;
- brain tumor (BTU) is a common benign tumor with a characteristic clinical picture: the rat’s front and hind legs have failed, the rodent lies with outstretched limbs, the joints cannot be bent;
- bone tumors are manifested by thickening of the bones of the limbs, ribs and skull, the animal is not able to move independently.
Allergy
Allergies in rats occur quite often to the action of external irritants, which can be litter, food and water. Allergies in domestic rats are accompanied by itching and manifested by characteristic symptoms: active scratching of the skin, the appearance of wounds and scabs on the paws and neck, swelling of the limbs and skin behind the ears. Signs of allergies in rodents are similar to symptoms of insect parasitism; diagnosis of the disease and examination of the animal should be carried out by a veterinarian. Treatment of allergies in rats involves the use of antihistamines, anti-inflammatory ointments and eliminating the source of the allergen: changing the filler and feed.
Rhinitis
Rhinitis in rats occurs through contact with infected animals or people (infectious rhinitis) or when the conditions of detention are violated (non-infectious rhinitis). Symptoms of infectious rhinitis in rats develop rapidly, the disease is transmitted by airborne droplets, and in weakened, emaciated and elderly animals, the pathology can be fatal. If a rat has a cold, non-contagious rhinitis occurs.
Infectious runny nose in a rat is manifested by mucopurulent discharge from the nose, sneezing, grunting, red discharge from the nose and eyes, lethargy, increased general body temperature of the animal, shortness of breath, heavy breathing and wheezing. Rhinitis should be treated by a veterinarian using antibacterial, hormonal and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Colds in rats occur when the animal is in a draft, hypothermia, or sudden changes in temperature in the room; contributing factors are insufficient feeding and unsanitary conditions for keeping the rodent. If a decorative rat has a cold, the runny nose will be mucous, there is grunting, sneezing, and the animal rubs its nose with its paws. Treatment of a runny nose must begin at the first symptoms of the disease; sick pets are prescribed inhalations and antibacterial drugs; non-contagious rhinitis can cause pneumonia in a domestic rat.
Diarrhea
Diarrhea in a rat occurs as a result of violation of the conditions of keeping and feeding the pet, against a background of stress, and diarrhea can also be caused by the development of an inflammatory process in the animal’s intestines due to infectious and parasitic diseases. The disease manifests itself in the frequent discharge of light, watery feces with an unpleasant odor; mucus and streaks of blood may be present in the feces.
The owner of a rat needs to know what to do if a rat has diarrhea in order to prevent dehydration and exhaustion of the animal. If your animal has soft stool with mucus, you can give your pet rice water and diluted smecta 3 times a day for three days, and also exclude prohibited foods. If there is no improvement, or the animal’s diarrhea initially occurs with the release of a large amount of liquid foamy mass with blood and mucus, it is necessary to urgently contact a specialist.
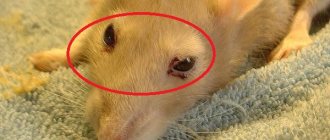
Conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis is an inflammatory disease of the mucous membrane of the eye caused by microtrauma or viral infection. The disease is manifested by purulent discharge from the lacrimal canal, the animal's eyes, and dried crusts of pus are found on the eyelids. If a rodent's eye is inflamed, it is necessary to urgently take the pet to a specialist; the animal needs to wash the conjunctival sac with antiseptic solutions and place hormonal and anti-inflammatory ointments under the eyelid.
Corns (pododermatitis in rats)
Pododermatitis in elderly or overly well-fed rats occurs when animals are kept on hard, dry litter or in cages with slatted floors; the dry skin of the feet is damaged and rounded calluses are formed in rats, reminiscent of human calluses. Subsequently, periodic opening and suppuration of these swellings occurs, lameness and chronic irreversible processes occur in the ligamentous apparatus of the pet’s limbs. Treatment of pododermatitis must begin immediately when the feet become red; therapy consists of moisturizing the skin with oils and creams, and the corns are lubricated with wound-healing ointments. An important preventative step is changing the conditions of keeping and feeding.
Periodontitis
Periodontitis in rats is an inflammatory disease of the supporting-retaining apparatus of the tooth, manifested by refusal of food, bad breath, redness and bleeding of the gums, yellowing of the teeth, excessive salivation, sometimes with blood, loosening and loss of teeth, swelling of the muzzle. The disease develops when the rules of feeding and maintenance are violated, or an unbalanced diet using predominantly soft feed. If a rat's teeth have turned yellow, it is necessary to urgently review the diet; solid food removes tartar well, preventing the development of periodontitis. Treatment of the disease in advanced cases includes removal of diseased teeth and tissues under local anesthesia.
Porphyrin
Porphyrin in decorative rats manifests itself as burgundy-red secretions of the Harderian gland from the nose and eyes, resembling dried blood in appearance. Porphyrin occurs independently due to injuries, stress, violation of feeding and maintenance conditions, or signals serious pathological conditions in the body: pneumonia, mycoplasmosis, oncology, tuberculosis. Treatment of porphyrin comes down to improving feeding conditions, housing, eliminating stress and symptomatic therapy.
Stroke
Stroke is a common pathology in decorative rats, characterized by impaired cerebral circulation as a result of rupture or blockage of blood vessels in the brain. Individuals suffering from obesity, heart and kidney disease, diabetes mellitus, and oncology are predisposed to the disease. A stroke manifests itself as loss of coordination, paralysis of the limbs, blindness, breathing problems, eye hemorrhages, the rat walks sideways, and the rodent may become apathetic or aggressive. Treatment is effective in the first hours after the onset of the disease; the animal is prescribed oxygen, diuretics and antiepileptic drugs.
Abscess
An abscess is a focal inflammation of tissue, a fairly common pathology in domestic rats, which occurs when the integrity of the skin is damaged against the background of reduced immunity. An abscess is characterized by the formation of a swelling filled with pus. Treatment of the disease is carried out only by a veterinarian using surgical dissection using local anesthesia. Treatment at home can cause infection of healthy tissue, sepsis and death of the pet.
Physical methods of rat control in Rostov-on-Don
This method involves blocking holes and exits. Barriers are placed for rats on the way to food products and the rodent, having no food and no way out, dies in its own burrows. It is advisable not to use this method at home, as hungry rats will make heart-rending sounds. The time for physical death cannot be determined, since they may have food reserves in their burrows. It is also worth noting that it is not known when the rat died and it is impossible to determine the time to prevent the corpse from decomposing indoors. If this time interval is missed, then the whole house will be filled with a terrible putrid smell.
Ask yourself: “Is your pet healthy?”
Balanced diet. Rats should have a nutritious and balanced diet. They should not be given fatty foods. Do you feed your rat the foods it needs for proper development: fresh fruits, vegetables, seeds, grains? Does she have fresh water?
Correct content. The rat cage should always be clean. The house must be dry. The cage should be placed away from direct sunlight or air conditioning. It should not be in a smoky room. Are you keeping your pet correctly?
Regular examination of the animal. Your pet should have his ears, teeth and eyes examined regularly. Do you conduct such medical examinations?
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
What measures should be taken afterwards to avoid a re-invasion?
Treat all surfaces with a special compound after treatment a week later; Follow a set of preventive measures. It is advisable to leave the poison for another week after removal. Use ultrasonic repellers, ensure regular garbage removal, and clear favorite habitats (attics, basements, garages) of trash. Such preventive measures will allow you to protect your home from re-entry and maintain sanitary cleanliness in your area. However, if tailed animals reappear, you should contact the city service, which is responsible for elimination and extermination. You can call a specialist by phone.