Ornamental rats kept as pets are very prolific. But owners are not always ready to breed, raise and accommodate numerous offspring.
In addition, some rats show aggression during the heat period, biting and scratching. Therefore, the only way to solve reproductive and behavioral problems is castration.
Pros of castration
- Easier to maintain. Castrated males are much calmer and do not bite their relatives. Nulliparous females get sick less, so their life expectancy is longer.
- You don’t have to worry about an unplanned pregnancy or the problem of settling unwanted rat pups.
- You can easily put opposite-sex and same-sex animals in the same cage; they will not compete and cause injury to their relatives. There will be no unwanted babies, although the animals will be able to breed.
- The appearance of animals will improve due to the normalization of the function of the sebaceous glands.
- Males will not mark the home, and the nasty smell will disappear.
Advantages and disadvantages
Castration of rats has positive and negative sides and can be carried out at the request of the owner, except in cases where the operation was prescribed for medical reasons.
Among the advantages, the following should be noted:
- the possibility of keeping opposite-sex couples in the same cage;
- prevention of many deadly diseases;
- increasing the lifespan of a pet;
- possible reduction in animal aggression;
- improving the appearance of the rodent due to the normalization of the functioning of the sebaceous glands.
We recommend learning how to properly bathe a rat at home.
Therefore, the number of positive effects is large.
However, they face disadvantages such as:
- the need to carefully monitor your pet’s diet due to metabolic disorders;
- the inability to accurately predict the complete decrease in the animal’s aggressiveness;
- poor tolerance of painkillers and anesthesia by rodents.
The last point is the most unpleasant: due to the small size of decorative rats, it is very easy to make mistakes in medication dosages. It is for this reason that you cannot contact an untested and inexperienced veterinarian to castrate an animal. An error in the amount and strength of anesthesia can cause death.
Types and methods of castration
Surgical intervention is performed in three different ways.
- Closed with 2 slits . This option is the most traumatic. The wounds heal within two weeks.
- Open - the method reduces the healing time of the wound to a week. The risk of complications is even greater than with the previous method. Intestinal prolapse is especially dangerous due to an enlarged inguinal ring.
- Closed with one incision is the most optimal method, surgical intervention takes place to the least extent, wounds heal promptly, and the risk of complications is low.
Points for and against
There are constant discussions around the issue of castration of rats between opponents of the operation and those who consider its implementation necessary and justified. The main argument against sterilization is the rat's short lifespan. Many people believe that an animal that will live only 2-3 years should not be subjected to a rather dangerous operation. In addition, uncontrolled behavior and the appearance of strong-smelling discharge at certain periods are not so pronounced in rats, which reduces the motivation for surgical intervention. Another reason for disapproving of castration of rodents is that they do not tolerate the effects of painkillers. In some cases, animals do not recover from general anesthesia after the procedure is completed. This problem has recently become less acute due to the advent of safer inhalation anesthesia.
Intervention is advocated by many veterinarians, breeders and nursery owners who are constantly faced with the need to treat adult animals for various pathologies. Castration is especially important for females, in whom the production of sex hormones very often causes pituitary tumors and rapidly growing neoplasms of the mammary glands. Neutering rats is also the most effective way to control your pet's reproduction.
Before making a decision, it is necessary not only to weigh all the arguments for and against, but also to evaluate the conditions in which the rat will live: whether it will be kept alone or in a group, with individuals of what sex it will be in the same cage, etc.
pros
The positive consequences of castrating a rat include reducing the risk of developing dangerous pathologies and increasing its life expectancy. After the procedure, it is possible for both same-sex and opposite-sex individuals to live together without negative consequences.
Minuses
Removal of the reproductive organs does not have the same effect on the rat as on other animals. Many owners are interested in the question: does castration lead to obesity, and will the pet become less active? Removing the testes or ovaries will not cause weight gain or cause drastic changes in behavior other than eliminating episodes of aggression.
The disadvantages of castration are the anesthetic risk and the cost of the intervention, comparable to performing the same manipulations on a cat or dog.
How rats are castrated
The choice of anesthesia is made by the doctor, usually by injecting the drug into a vein near the tail or gas administration of anesthesia.
Intramuscular administration is less commonly used. When the patient falls asleep, he is fixed in a supine position, the fur is removed and the operation is performed.
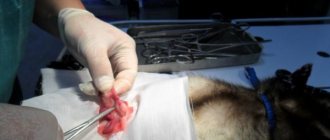
The veterinarian makes a 1.5 cm incision on the scrotum for males and 5 cm on the abdomen for females. The surgeon amputates the testicles, ovaries, uterus and sutures.
Modern suture materials do not need to be removed; they dissolve on their own.
If another suture material is used, the sutures are removed within one to one and a half weeks.
The operation lasts no more than half an hour.
Sterilizing rats has a number of positive aspects
- Unspayed females have a 75% chance of developing one or more mammary tumors. These tumors can grow to enormous sizes in a short period of time. Removal of the ovaries virtually eliminates the possibility of the development of such neoplasms in rats.
- Neutering female rats reduces the likelihood of pituitary tumors, which are also common in rats. Pituitary tumors are neoplasms of the brain. They lead to impaired coordination of movements and the inability to eat food. Ultimately, such tumors lead to the death of the rat. Diagnosis and treatment of such tumors are very complex and expensive.
- Sterilization of rats completely eliminates future diseases of the ovaries and uterus.
- Neutered rats can be kept together with males. Without the risk of the rat becoming pregnant.
Postoperative care
The pet needs comfort after waking up so that the body does not experience shock. A clean fabric ironed with a hot iron is laid on the bottom of the enclosure.
It is advisable to place the patient in a place familiar to him. Anesthesia reduces normal body temperature, so place a heating pad or a bottle of warm water nearby, then the person undergoing surgery will recover faster.
The owner will have to regularly inspect and treat the seam for some time.
The rat's cage and bed must be kept clean and the animal must not be allowed to chew or lick the seam.
To prevent this, you can wear a special blanket. If the seam becomes inflamed or pus appears, consult a doctor immediately.
When the rat wakes up, you can pipet the saline solution.
You can give puree, porridge, and other soft foods. Solid food is indicated no earlier than after 24 hours.
Optimal age
There is no consensus regarding the timing of castration. Most veterinarians believe that the optimal age for a rat is 3 to 4 months. By this point, all organs of the genitourinary system have already been formed, and the growth and development of the rodent has stopped. At the same time, at this age the rat is still young enough to tolerate anesthesia and surgery well, and also to recover quickly in the postoperative period.
Some experts believe that it is possible to operate on a rat almost immediately after puberty, which usually occurs by 40-50 days of life. A specialist will help you correctly determine the recommended age for castration of a particular individual after examining the rodent.
Character of a rat after castration
- A neutered pet does not lose activity and curiosity.
- If the rat was not fat before castration, it will not gain weight.
- The animal will guard the territory as before. Therefore, you need to add relatives according to the usual rules.
- Animals of different sexes are sociable and mate as before, but there will be no offspring.
- Under severe stress, castrated males sometimes begin to mark their territory.
- Operated pets are practically no different from full-fledged animals, but keeping them at home is much easier.
The need for such an operation
In all rodents, the main reproductive feature is high reproduction rates. The age of puberty in ornamental rats is 4 months, while pregnancy lasts 3 weeks.
Did you know? Many species of rodents appeared on the planet long before humans. Rats as a species formed about 60 million years ago at the beginning of the Paleogene period.
In one litter, up to 20 small rodents can be born. If you are the owner of a mixed pair of rats, spaying and neutering is truly necessary to avoid a sharp increase in the number of pets. In the case where two males are kept, this procedure is also necessary to reduce the aggressiveness of rodents.
When it is necessary to do it
Castration is mandatory in cases where it was prescribed by a veterinarian. Doctors usually recommend this operation in cases where the rat’s illness affects the reproductive system, surgical intervention of which will relieve the animal of the disease.
Commonly encountered diseases include:
- inflammation;
- cyst;
- tumors.
Important! Keeping rats in the same room but in different cages can cause severe stress for your pets. This is due to the fact that rodents are school animals and need to communicate with other members of their species.
The latter should be treated with the greatest caution, since decorative rats often suffer from cancer that affects the reproductive system of both females and males. The former may develop malignant tumors in the area of the uterus, ovaries and mammary glands. Males often suffer from tumors on the testes.
Castration and sterilization can act as preventive measures for these diseases. If the operation is performed at a young age, the animal’s body will experience significantly less stress. For females, sterilization, among other things, has a preventive effect on pituitary gland diseases.
Advantages of castration at home
In a modern city, veterinarians operate in clinics and at home. Castration for an experienced surgeon is an elementary procedure; it is successfully performed at home.
For owners and their pets, castration at home is more convenient due to a number of advantages.
- The pet is at home, in peace and comfort. The owner is nearby and will support the pet.
- The animal will not have to be taken to the hospital and back, subjecting it to psychological and physical tests.
- Choose a convenient time, including nights and weekends. The doctor will arrive at the agreed time.
- There is no risk to have surgery at home. The veterinarian will tell you in advance how to prepare the rat and how to care for it after the procedure.
- The price of the service does not differ from a similar procedure in the clinic.
- If complications occur, a doctor will definitely arrive to provide assistance. You can also get advice over the phone.
The veterinarian, when going on call, will take with him the necessary instruments and medications.
The operation lasts no longer than half an hour, and often half as long. After the veterinarian leaves, the owner needs to stay with the pet for several hours until he wakes up from the anesthesia.
After waking up, the patient must be carefully given water, warmed and calmed.
General services
| Prices for services in our clinic | In the clinic and at home |
| Ratologist visiting your home | from 500 |
| Clinical examination, preliminary diagnosis, consultation | from 500 |
| Telephone consultation | for free |
| Therapy | from 150 |
| Surgery | from 150 |
| Ambulance at home (within an hour) | from 1000 |
Therapy
| Prices for services in our clinic | In the clinic and at home |
| Subcutaneous administration of drugs to rodents | from 150 |
| Intramuscular administration of drugs to rodents | from 200 |
| Intravenous (into a catheter, through a needle) | from 200 |
| Dropper for rodents | from 1000 |
| Placement of an intravenous catheter | from 300 |
| Removing the IV catheter | 200 |
| Tube feeding of rodents | from 300 |
| Taking blood samples | from 300 |
| Novocaine blockade | from 200 |
| Reduction of the cheek pouch | from 200 |
| A haircut | |
| Nail trimming | from 300 |
| Haircutting mats | from 1000 |
| Ear treatment | from 300 |
Surgery and Traumatology
| Prices for services in our clinic | In the clinic and at home |
| Surgery | |
| Surgery of the genitourinary organs in rodents: | |
| Castration | from 2000 |
| Sterilization | from 2500 |
| Surgical procedures | from 400 |
| Surgical treatment of wounds | from 300 |
| Application of musculocutaneous sutures | from 200 |
| Applying a bandage | from 100 |
| Applying a plaster cast | from 1000 |
| Removing the plaster cast | from 300 |
| Surgery for skin, soft tissue and tumor infections | |
| Opening abscesses, hematomas | from 400 |
| Treatment of purulent wounds | from 700 |
| Drainage installation | from 500 |
| Flushing the drainage | 350 |
| Treatment of auricular hematoma | from 1500 |
| Unilateral mastectomy | from 4000 |
| Regional mastectomy | from 5000 |
| Removal of tumors | from 2000 |
| Abdominal surgery | |
| Obstetrics in rodents | from 1000 |
| Animation of newborns | from 300 |
| C-section | from 3000 |
| Pyometra | from 1500 |
Anesthesiology for rodents
| Prices for services in our clinic | In the clinic and at home |
| Anesthesia | from 500 |
Ophthalmology
| Prices for services in our clinic | In the clinic and at home |
| Eyelid surgery for inversion, eversion | from 2000 |
| Exenteration of the eyeball | from 3000 |
Dentistry
| Prices for services in our clinic | In the clinic and at home |
| Removal of incisors | from 500 |
| Trimming and correction of teeth in rodents | from 1500 |
Laboratory diagnostics
| Prices for services in our clinic | In the clinic and at home |
| Blood analysis: | |
| General clinical blood test | 900 |
| Blood cytology | 1000 |
| Biochemical analysis for 1 sample indicator | 300 |
| Biochemical blood test for 6 indicators | 1500 |
| Biochemical blood test for 12 indicators | 2500 |
| Additional biochemical indicators for pancreatic amylase, rheumatoid factor, c-reactive protein | from 300 |
| Analysis of urine: | |
| General clinical urine analysis | 400 |
| Express urine glucose test | 200 |
| Express urine test | 300 |
| Biochemistry of urine 1 indicator | 100 |
| Stool examinations | |
| General stool analysis | 500 |
| Stool culture for pathogens | 1500 |
| Stool analysis for dysbacteriosis | 2000 |
| Stool analysis for protozoa and helminth eggs | 500 |
| Bacteriology | |
| Bacteriological screening | 2000 |
| Microbiological screening | 2000 |
| Full microbiological screening (no subtitration) | 1500 |
| Skin studies | |
| Skin biopsy | 1700 |
| Skin smear | 1000 |
| Dermatophytes and ectoparasites | 1000 |
| Pathomorphology | 1500 |
| Histology of neoplasms, cystic contents | 2000 |
| Cytology of neoplasms, cystic contents | 1500 |
Contraindications
Castration of rats is associated with certain risks for the animal. It is not recommended to perform the procedure on individuals older than 1 year, since the body’s response to anesthesia worsens with age. Limitations include some comorbidities. A ratologist, a veterinary specialist who treats rodents, will help eliminate possible contraindications. You can make a decision to castrate a rat after a preliminary examination by a specialist.
An operation in the presence of contraindications is possible when the obvious risks from the identified disease exceed the risk of possible complications during the intervention.
Complications
Castration of rats is associated with the risk of developing surgical and postoperative complications. Incorrect calculation of the dose of anesthetic can cause death or disruption of the functioning of internal organs, primarily the kidneys.
Complications after castration of rats can be caused by wound infection or self-removal of sutures. The penetration of infection is indicated by redness and swelling of the skin around the incision, and the appearance of purulent discharge. In case of any deviations from the normal state, it is necessary to show the rat to a veterinarian as soon as possible.