Skin and parasitic diseases are common problems in guinea pigs. Young and weakened individuals are especially susceptible to them, but an adult animal can also become ill, and even infect a person.
We will learn how to identify the disease at an early stage, and which drugs are effective against various types of pathogens.
What is lichen and why is it dangerous?
“Ringworm” is a common term. In fact, this disease should be called “dermatomycosis”. To be even more precise, this is not one disease, but a whole group of infectious pathologies of fungal origin that affect the skin and coat of animals. Ringworms are considered one of the most dangerous diseases due to their high contagiousness and virulence (in other words, they are highly contagious).
Like any other fungal pathology, lichen greatly suppresses the immune system of a sick pet. There are also many cases where in healthy and young animals some types of lichen can go away on their own (but this happens rarely). Dermatomycosis is dangerous due to its rapid spread in the external environment.
Important! Many varieties are dangerous not only for pigs, but also for other domestic animals, as well as for humans. Because of this, a sick pet must be isolated; it is especially important not to let children and the elderly play with it. Their immunity is too weak, and therefore the likelihood of infection is very high.
In pigs, the disease is most often caused by representatives of two genera of pathogens:
- Microsporum (cause microsporia).
- Trichophyton (pathogens of trichophytosis).
Zhiroviki
A wen most often results from the removal of a lipoma, an abscess, or appears due to infection entering a small wound. If over time the wen does not grow and does not cause any discomfort to the animal, then it does not need to be removed. However, if the wen is painful and significantly increases in size, you should immediately consult a doctor.
The wen can break out on its own and this can lead to not the most pleasant consequences - the formation of tumors under the wen, incomplete release of pus, blood poisoning.
The veterinarian removes not only the wen itself, but also the fat sac. It is this that most often becomes the cause of the recurrence of the wen and the development of tumors. Typically, after surgery, the veterinarian will prescribe a course of antibiotics and complete rest. The wound should be lubricated with ointment and washed with a solution of hydrogen peroxide.
The main types of lichen in guinea pigs
Most often, either microsporia or trichophytosis is detected in animals. Both types of dermatomycosis, by the way, are dangerous for people.
They can be distinguished by the following characteristics:
- Microsporia is characterized by the appearance of ring-shaped bald patches. The skin in these places peels off, in some cases the pet experiences quite severe itching. The development of inflammation is characteristic. The fur over the lesions becomes dull. In addition, with microsporia, the hairs break at a height of approximately 4-6 mm from the skin.
- Trichophytosis is characterized by hair loss. More precisely, they break off flush with the skin, leaving behind a very short “fluff”. Unlike microsporia, there is usually no itching, and the skin is also rarely inflamed. But with trichophytosis, the skin in the affected areas is often covered with multiple pustules.
Diagnostic measures
Diagnosis and treatment of ringworm are carried out by a dermatologist. The doctor examines the patient and identifies typical manifestations of microsporia. Examination of skin scrapings under a microscope reveals fungal mycelium and changes in the structure of hair and skin. Differential diagnosis makes it possible to exclude trichophytosis from the patient’s history, which has similar manifestations upon microscopy of the patient’s biomaterials.
Microflora culture appears to be a more informative diagnostic technique. Laboratory staff determine the type and genus of fungi. Based on the laboratory report, the dermatologist selects drugs that will cure the patient.
Luminescent examination makes it possible to identify pathological lesions on the skin of the patient and those living with him. This diagnostic method is based on the green glow of the fungal mycelium under the influence of a gas-discharge light source.
Routes of transmission of lichen in guinea pigs
In most cases, infection occurs through direct contact between a sick and healthy animal, but the infection can reach a pet in other ways:
- Each hair inside is “eaten away” by fungi and filled with their spores. Accordingly, upon contact with such fur, the animal has an almost 100% chance of getting sick.
- The spores do not remain in the fallen hairs, but scatter, seeding areas of the environment. They can end up anywhere. Thus, infection can occur through contact of a “pig” with contaminated care items, bedding, hay, etc. The situation is aggravated by the fact that mice are frequent carriers of dermatophyte spores. And they, in turn, often live in the hay... which is fed to the pigs.
Prevention
It is important to note that lichen is contagious to humans, so you need to be careful with sick animals. All manipulations with them must be carried out exclusively with gloves.
The cage in which the animal was kept and other objects must be treated with disinfectants. For wet disinfection, a 3% formaldehyde solution is suitable. You need to add a little 1% sodium hydroxide to the composition. A bleach solution can be used to kill ringworm spores. The product must be diluted with water in a ratio of 1:10.
Carpets and upholstered furniture must be steamed and also wiped with disinfectants. It is also necessary to regularly clean the premises and introduce fortified food into the pet’s diet, which will strengthen its immunity. If there are other animals in the house, contact with them should be limited.
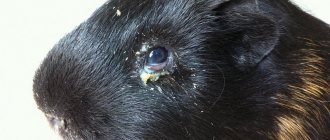
Symptoms and signs of lichen in a guinea pig
Regardless of the specific type of pathogen, the first sign of the disease will be the appearance of areas of mycelium growth on the pet’s skin. In most cases, these will be round, hairless areas with rough and thickened skin in the center.
These areas often become scaly as the skin flakes off and falls off. Multiple ulcers often appear in these same places. Itching does not happen in all cases, but if it does, the pig may lose sleep and rest while trying to scratch itself. The first lesions are found near the eyes, ears, and sometimes on the stomach.
Treatment
The combination of drugs prescribed to the patient depends on the severity of damage to the skin, nail plates and hair follicles. Antifungal therapy may be local or general. In the first case, a child or adult needs to use creams and ointments that suppress the activity of the microsporia pathogen. Drugs in this group are not recommended for use by girls during pregnancy and lactation. Topical sprays are effective in treating large areas of ringworm. Modern formulations do not leave stains on the skin and are not absorbed into the fabric of clothing.
A severe inflammatory reaction is treated with a combination of antifungal and hormonal drugs. Patients will have to apply ointment applications to the affected areas. After this, the skin is treated with iodine solutions. The oral tablet intake schedule is formed by a dermatologist based on the clinical picture of the pathology.
The addition of a secondary infection to microsporia involves the use of drugs based on betamethasone, gentamicin or clotrimazole.
Treatment of lichen in guinea pigs at home
Let us immediately warn you that treatment of lichen in guinea pigs at home is possible only with prior consultation with a veterinarian and subsequent prescription of specific therapy. We will describe basic recommendations for preparing for treatment.
The main condition for successful therapy is good access to the areas of the pet’s skin affected by the fungus. To fulfill this condition, it is necessary to carefully cut the hair near the inflammation.
All fur must be collected and burned. An important element of treatment is bathing with medicated shampoos. After each wash, the sores must be lubricated with ointments.
Skin diseases caused by parasites
Lice and lice eaters
These parasites are especially common in guinea pigs. The first symptoms are severe itching. To detect lice and lice, it is worth examining the skin and fur of the animal under a magnifying glass. If your guinea pig is infested with lice, you will see larvae among the hairs. Nits have a pear-shaped body and measure half a centimeter. Lice eaters are much smaller - the length of an adult insect is about a millimeter. They feed not only on skin scales, but also on the blood of the animal.
It is impossible to comb out insects with a regular brush.
Insecticides are a good way to control parasites. The guinea pig should be placed in a 1% netritonate solution or in a 0.5% bromocyclene solution for several minutes. The procedure should be repeated every seven days for three weeks. Before the procedure, you should also treat the cage with a bromocyclene solution and change all the bedding.
Fungal diseases
Fungus in guinea pigs can often be observed on the face. The first symptoms are hair loss, itching, peeling of the skin. After the muzzle, the fungus affects the paws, ears, chest, and neck. The first type of fungus is dermatophyte. It affects the nails, hair and the stratum corneum of the epidermis of the skin.
Weakened animals, as well as pregnant and lactating females and young individuals are susceptible to infection.
Prevention of the disease includes:
- regular cleaning of the cage and change of bedding (the fungus actively multiplies in a dirty environment),
- high-quality and clean feed,
- low humidity in the room where the animal is kept,
- regular treatment for internal parasites.
If the veterinarian has determined the presence of a fungus - dermatophyte, then the sick animal must be transplanted into a separate cage (it is better to use a terrarium or an aquarium to avoid the spread of spores). The cage where the guinea pig was kept must be thoroughly washed with any chlorine-containing solution. For treatment, you can use Nizoral shampoo, which is sold in pharmacies. It has a good antifungal effect, reduces itching and eliminates skin flaking. Apply the shampoo to the fungus-affected areas of the body for a few minutes, then rinse with warm running water.
Fungoterbin 1% cream, as well as Termikon 1% cream, also help fight fungus well. The cream should be applied to the affected area of the body. Repeat the procedure twice a day until complete recovery.
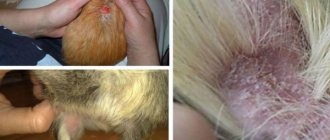
Lichen
Ringworm in guinea pigs is caused by several types of fungus, the spores of which can be carried not only by people, but also by pets and poor-quality food. A guinea pig can become infected with lichen while walking - very often fungal spores are found in the soil and on the grass. Most often, weakened animals and animals kept in poor conditions are susceptible to the disease. The first symptoms are hair loss. Bare areas of skin are red, dry and with noticeable peeling, covered with a dry crust. Ringworm first affects the muzzle and ears, front and hind legs, and then spreads throughout the body. A sick animal experiences severe itching, loses rest and appetite. Through open scratched wounds, various pathogenic bacteria can enter the bloodstream.
Lichen can only be determined by scraping the skin in the laboratory.
A sick guinea pig should be immediately isolated from other animals. The fur around the affected areas should be shaved. The cage where the pig was kept, as well as all feeders, houses and other items, must be thoroughly washed with any chlorine-containing composition. Guinea pigs are treated for shingles with antifungal drugs (clotrimazole or miconazole), as well as frequent washing with a keratolytic shampoo. The danger of deprivation is that it can be transmitted to people. Children, as well as pregnant women and people with weakened immune systems are most vulnerable. Their contact with the sick animal should be completely excluded.
Pododermatitis
Pododermatitis or corns are a consequence of improper care of animals. Dirty bedding, excessively long nails of an animal, or the use of wood pellets for bedding can lead to the formation of painful tumors on the paws and the appearance of purulent wounds. The cause of corns can be the obesity of the animal, as well as diseases of the internal organs. To determine the exact cause, it is recommended to consult a veterinarian and take a blood test. Pododermatitis can only be cured if treatment is started on time. Typically, in the normal course of the disease, the treatment period takes up to two months.
Treatment of pododermatitis consists of daily treatment of the wounds with chlorhexidine, cleansing the wounds of pus and lubricating the affected areas with Levomekol ointment in the morning and Solcoseryl in the evening. When the wounds have completely healed and the discharge of pus has stopped, it is good to lubricate the skin with zinc ointment. If the disease is in a severe stage, then antibacterial drugs should be used and tissue x-rays should be taken. Pododermatitis can lead to bone deformation.
Pododermatitis requires not only drug treatment, but also a complete change in the animal’s diet, as well as living conditions. It is necessary to carefully monitor the weight of the animal, the length of its claws and teeth.
The guinea pig should be kept in a cage with soft bedding, and if the wounds bleed, use any soft cloth as bedding.
Pharmacy products used
Please note that many pharmaceutical products used may be unsafe for the health of the animal (especially antifungal medications). Therefore, they must be used only with the knowledge and approval of the veterinarian!
Ointments
The following ointments can be used in the treatment of lichen:
- Salicylic. It has a double effect: it is not only an excellent antiseptic, but also a means that accelerates the regeneration process of damaged skin. The duration of treatment is at least 10 days, the drug is applied three times a day. When processing, it is necessary to apply the ointment in broad strokes, covering the inflamed areas and areas of healthy skin around them.
- Sulfuric. This simple and cheap drug has a good antifungal effect. The duration of treatment is at least three weeks, the frequency of application is three times a day. To achieve the best effect, the ointment is best used in the form of applications. To do this, a gauze swab is thickly impregnated with the product and glued with a band-aid to the most noticeable lesions. The bandage is changed at least once every two days.
- Ichthyol. A good auxiliary agent with a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect. The frequency of treatment is twice a day throughout the entire treatment period.
- Ointment Yam. It has a very specific smell and an equally distinctive consistency. Despite the “aroma,” when applied to the fungal lesions up to three times a day for two weeks, it often helps to cure the animal without resorting to the use of more serious (and very toxic) drugs.
Routes of infection
The causative agent of microsporia enters the body when a healthy person comes into contact with a carrier of the disease. An alternative way is to interact with objects covered with fungal spores. Ringworm is most often detected in children aged 5-10 years; in boys, microsporia is diagnosed five times more often than in girls. The pathology almost does not affect adults due to the presence of organic acids in their hair structure, which suppress the growth of fungal mycelium.
The reasons for the development of ringworm are microtraumas of the skin and its dryness. Spores get into cracks, scratches or open calluses. Healthy skin becomes an insurmountable barrier to fungus. The pathogen does not survive contact with personal hygiene products - thorough hand washing after contact with spore carriers eliminates the possibility of infection.
The risk group includes people who regularly come into contact with the ground and wild animals. The active growth of the fungus is facilitated by disturbances in the functioning of the sebaceous glands due to changes in the chemical composition of their secretions. Microsporum spores can remain viable for three months when left in open ground.
Folk remedies
Some folk remedies cannot be called “original folk”, but official veterinary medicine does not use them. Despite this, some breeders achieve very good results with their help:
- Simple greenery helps a lot. Apply to areas of inflammation once a day. Treatment period is up to one and a half weeks.
- Alcohol tincture of iodine works similarly. It is used in the same way. Remember that excess iodine can cause chemical burns!
- Birch tar. They lubricate the “mushroom” areas no more than twice a day. Treatment period is up to one week.
Causes
Why does this disease occur? Most often, the fungus appears when:
- weak immunity;
- stress;
- improper diet;
- poor quality care.
The cause of the disease can be either one or several. Fungal spores multiply on dirty litter because it is favorable soil for them. If animals are kept in close quarters, skin fungus can appear in all animals.
The disease manifests itself in the form of thinning hair, bald spots, flaking, dandruff, and white skin plaque. Guinea pigs with fungus suffer from itching and the affected areas itch. This can cause a secondary infection as bacteria enter such areas. In this case, treatment becomes more complicated.
Types of lice
Oddly enough, the varieties of lice in pigs are quite numerous. In practice, in almost 99% of cases, only two types are found, and another one is diagnosed much less frequently:
- Typically, “pigs” are parasitized by two types of lice: Gliricola porcelli and Gyropus ovalis.
- In extremely rare cases, parasites of the species Trimenopon hispidium can be found on the body of an animal.
G. Ovalis are more compact in shape (as their name suggests), but in all other respects they are very similar to the previous variety.
Trimenopon hispidium, then this type of lice is extremely small and most often they are simply not noticed. However, in cases of severe infestations, you can see large accumulations of these parasites, vaguely reminiscent of tiny spiders.
Summing up
Thus, there are many ways to treat shingles. However, for their comprehensive use, not to mention a qualified diagnosis, you should definitely consult a specialist. Treating your guinea pig on your own can only make the problem worse.
In any case, it is worth remembering about preventive measures. The best way to preserve the mood, time and money, as well as the health of your beloved pet, is to simply prevent him from getting sick.
Source
Lichen. Types, symptoms, treatment. Article
Since the 18th century, the term “lichen” (“lichen”, “infection” in Greek) has been used to describe most skin diseases, which at certain stages of their development were accompanied by itchy small nodules.
Currently, the lichen group includes 3 diseases:
- lichen planus;
- ringworm;
- lichen linear.
The term “lichen” is so rooted in the dermatological classification that it has become integral in the definition of such completely different dermatoses as lichen rosea of Zhibera, pityriasis versicolor, lichen simplex vesicularis, lichen herpes, lichen white atrophic Tsumbusha, lichen planus or psoriasis, ringworm or microsporia and others. Thus, the causes of the development of “lichen” can be either viral or fungal agents, or genetic factors, endocrine or neurological disorders. And many fairly well-known and common diseases, such as psoriasis and lichen planus, are currently not fully understood.
Let's look at typical representatives of the lichen group:
Lichen red flat is a common skin disease that affects the skin and mucous membranes, and less often the nails. The most common theories are the infectious and neurogenic origin of the disease. It occurs in adults, more often in women aged 30-60 years. The rashes are located mainly on the flexor surfaces of the forearms, abdomen, and lower back. The rash is characteristic in the form of small 1-3mm polygonal reddish-violet nodules with a flat shiny surface and an umbilical depression in the center. On the surface of larger elements, a whitish mesh pattern is revealed - Wickham's mesh, which is very typical for this disease. Papules can merge into small plaques or form linear or ring-shaped figures, fresh rashes appear at the site of injury (Koebner phenomenon). Severe itching is characteristic. The duration of the disease ranges from several months to several years. Damage to the mucous membranes of the oral cavity or genital organs can be either isolated or combined with the skin. On the inner surface of the cheeks, the red border of the lips, the lateral surfaces of the tongue, on the vulva or head of the penis, there are small whitish shiny papules that form a “fern” or “mesh” pattern.
There are several clinical forms of lichen planus:
- hypertrophic form (in the form of dense warty plaques of a stagnant red or bluish tint);
- atrophic form (rash in the form of spots with a characteristic purple color);
- cystic form (vesicles or blisters with serous contents appear on the surface of the nodules, and erosive and ulcerative defects appear in places of friction);
The erosive-ulcerative form often develops in patients with diabetes mellitus and hypertension (erosions and small ulcers are surrounded by typical papules). Follicular form (small nodules at the mouths of hair follicles). Pigmented form (pigmentation precedes the formation of papules, limited lesions in the abdomen, buttocks, lower extremities).
Lichen (lichen) shiny is a dermatosis characterized by the presence of small papules, reminiscent of papules in lichen planus, the development of which is based on a granulomatous reaction. It is generally accepted that lichen planus is a kind of lichenoid reaction to parasitosis, chronic diseases of the ENT organs and gastrointestinal tract. The disease occurs mainly in children, more often in boys.
Papules are located on the skin of the penis, in the area of the knee and elbow joints, and the rash may spread. Lichen brilliant papules are small 1-2 mm, flat, with a smooth surface, round or polygonal, flesh-colored or pale pink with a pearlescent tint. The rashes are multiple, but never merge and may be at the site of injury. Itching doesn't bother me. The course of the disease is long, sometimes reaching 15-20 years, and can resolve spontaneously.
Lichen (lichen) linear - dermatosis,
characterized by the presence of papular rashes that have a linear arrangement.
Since the rashes are located linearly, usually along the extremities, the background for the development of dermatosis can be damage to the peripheral nerves. The disease occurs in all age groups, more often in women. The upper and lower extremities are affected, rashes in the form of small papules up to 2 mm in color, pale pink or reddish-brown, slightly rising above the surface of healthy skin, closely adjacent to each other and form linear lesions up to 2 cm wide and up to several tens of centimeters long. On the surface of the plaques, peeling from minor to severe psoriasiform itching is possible. The duration of the disease usually does not exceed several months, although sometimes it can last for several years. The diagnosis of lichen is made clinically and can be confirmed by histological examination of the skin. Treatment of “lichen” is predominantly outpatient, taking into account the provoking and concomitant pathologies in a particular patient. Since the course of the disease is often long-term, the patient is recommended to undergo clinical observation by a dermatologist, examination, treatment, including pure sanatorium-resort rehabilitation. The sooner the correct diagnosis is made to the patient, the more effective the treatment methods used will be and the desired result will be achieved!
What it is
Ringworm is a disease of a viral nature and dermatological nature, the source of which is a fungus that affects the skin. In the absence of measures to prevent its development, it quickly covers the entire body of the rodent. It is contagious and poses a threat to other animals, as well as the owners of a sick pet. Transmitted through direct contact.
The fungus is very tenacious. Its elements and spores remain in the pet’s fur and surrounding area for one and a half years. In this case, the body carrying the disease can remain healthy and not show symptoms of infection. Activation of the disease is facilitated by environmental pollution or weak immunity of a particular individual.
The disease manifests itself at any time of the year, but is more common in the spring-summer and autumn seasons.