Guinea pigs are animals that were bred by the Inca tribes living in South America in the territory of modern Peru and Bolivia. They still exist there in the wild. Selection work has made it possible to obtain many decorative breeds of guinea pigs that live with people and require care and attention. If your guinea pig gets sick, your veterinarian will help you understand the cause of the disease and provide treatment.
Guinea pigs are animals that were bred by the Inca tribes living in South America in the territory of modern Peru and Bolivia. They still exist there in the wild. Selection work has made it possible to obtain many decorative breeds of guinea pigs that live with people and require care and attention. If your guinea pig gets sick, your veterinarian will help you understand the cause of the disease and provide treatment.
Why do guinea pigs get sick?
Diseases in guinea pigs are associated with poor diet, infections and lack of vitamins. These can be infectious diseases that affect the animal’s body, getting to it with food and water. Another cause of disease lies in improper feeding. Some foods can cause intestinal upset, and its long-term manifestations result in the death of the animal. The third reason is the structural features of her body, which should be taken into account during care. Treatment by a veterinarian prolongs the life of your pet.
The peculiarity of these rodents is their long intestines, which become upset after a change in diet, and teeth, which grow throughout their lives and require constant grinding. They need to be fed hay every day to keep their teeth and intestines normal. The body of these animals does not absorb vitamins well, so special attention should be paid to the food. These ancient animals cannot tolerate penicillin, which becomes a deadly poison for them. Therefore, moldy food is not suitable for them. Guinea pigs need to chew something constantly to keep their digestive system healthy. These rodents live up to seven years, and those who live in a pack live longer than solitary individuals.
Treatment Options - Nutrition
Depending on the severity and causes of the disease, treatment may vary. First of all, you need to take care of your diet. You should temporarily exclude juicy sour and sweet and sour vegetables and fruits. Their juice will further injure the inflamed mucous tissue. An important element of nutrition remains not juicy vegetables, a variety of herbs, twigs, and hay.
To replenish vitamins, fats, micro- and macroelements, you should add 3-4 pieces of peeled sunflower seeds throughout the week. They are healthy thanks to Omega-6 fatty acids.
You should give your pet flax seeds in a volume of 1/2 teaspoon for a week. They contain Omega-3 fatty acids, so the seeds will provide the necessary amount of nutrients.
It is also permissible to moisten the food with drops of sesame or flax oils.
We wrote in more detail about proper nutrition for guinea pigs in this article.
What to feed your guinea pig?
The problem of feeding a guinea pig worries everyone who brings the animal home. Guinea pigs eat constantly in small portions, so the food should be available to them constantly, but it needs to be refreshed 3 times a day. Grain feeds increase excess weight and lead to obesity, so they are limited to the norm. Be sure to have a piece of well-dried dry grass, branches of fruit trees, and willow in the cage. A guinea pig's teeth grow throughout their life, and hard foods help to wear them down in captivity. To prevent the pig from getting sick, there should always be food in the cage.
Give succulent food to pigs in the morning. You should not give potatoes that the body cannot digest. Carrots, celery, cabbage, beets, pumpkin, and sweet peppers should be given by cutting them into pieces. The norm is 160 grams. For pregnant, lactating and Skinny women, the dose is doubled and divided into two doses: one in the morning, the other in the evening.
The volume of the animal's drinking bowl should be 250 ml. Vitamin C is added to the water in an amount of 2.5-5 mg per glass of water. In summer a minimal dose is sufficient, in winter a larger dose is sufficient. If the animal receives a premix of vitamins in the finished feed, then this is enough.
Berries and fruits are given as a treat in small quantities in the first half of the day. These could be apples, pears, dry rose hips.
Herbs such as red clover, dandelion, plantain, nettle, chamomile, and yarrow are very beneficial for the animal and can be dried for the winter. Parsley, dill, leaf celery - these herbs are not given to pregnant animals. Spinach and lettuce are only those that grew in the open ground in the summer. An excess of fertilizers in greenhouses leads to the accumulation of harmful substances in plants, which can poison the animal. Salt is given to young animals per 1 animal 0.5 g, to adults - 1 - 2 g.
Main symptoms of cheilitis
Forms of cheilitis may differ in symptoms, but there are a number of symptoms that are characteristic of the disease as a whole:
- Formation of cracks and reddish or brown crusts on the lips,
- The appearance of yellow plaque on the teeth,
- The appearance of dark and hard deposits at the roots of teeth,
- Teeth moving in different directions
- The appearance of dark plaque between the teeth,
- Change in tooth enamel color
- Puffiness and swelling of the lips,
- Loss of appetite.
- Formation of ulcers on the lips.
- If the disease is advanced, ulcers and cracks may appear all over the face and nose.
The first signs of the disease
Sick animals huddle in a corner or sit in a house and don’t go out anywhere. Lethargy, watery eyes, refusal to eat, intestinal upset are signs that require attention from the owner. Heavy or fast breathing, slow tousled fur, elevated body temperature over 39.6 indicate that the rodent is sick. If a guinea pig is sick, the owner can provide first aid to it, and then show the animal to a doctor. To provide first aid you must have: hydrogen peroxide, potassium permanganate, activated carbon. It is also good to have a transport cage for carrying the animal. It is better not to give her dosage forms yourself, because the dose calculation depends on the weight of the animal and is carried out according to special tables that are known to specialists. It is not possible to calculate the drug yourself. The pig can die from an overdose. Entrust treatment to a veterinarian.
We measure the temperature
The guinea pig does not like to be forced and tries to escape. To hold her during inspection, you need to turn her paws up and hold her by the fur on the back of her head. In this position, her temperature is measured with a special veterinary or an ordinary thermometer in the anus. To measure it, the pig is placed with its back on the palm of the left hand or on a surface. Press the thumb of the left hand on the groin. With the right hand, a thermometer, disinfected and lubricated with Vaseline, is inserted into the rectum. It is introduced in two stages: first almost vertically, and then in a horizontal position so as to completely hide the thermometer nose. Hold the animal tightly during the entire temperature measurement procedure, which lasts about a minute.
Fungal, viral and oncological diseases
“Pigs” also suffer from fungal, viral and oncological diseases. All of them can be the root cause of pathologies of the kidneys, liver, heart and other systems mentioned above.
Tumors
In most cases, tumors develop in older pets. Their diversity is extremely large, but all neoplasms can be divided into two large types: benign and malignant. The following benign neoplasms are encountered in veterinary practice:
- Lipomas (from adipose tissue).
- Myomas (from muscle tissue).
- Adenomas (develop in the glands).
- In addition, fibroids are quite common in pigs (they grow from connective tissue).
Independent initial examination of the mumps
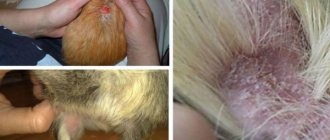
- Lice and lice that infect the skin cause the rodent to itch. Scratching and wounds on the body are also a reason to consult a veterinarian.
- The fur near the anus can only be dirty due to an intestinal disorder.
- The nasal mucosa of a healthy pig is clean, but a sick pig has discharge, both fresh and dried.
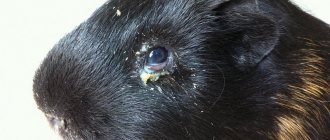
- A healthy guinea pig's eyes are clear and shiny. If there is pus and inflammation, then this is evidence of illness.
- The ear openings show signs of inflammation - you should consult a doctor.
Diseases caused by vitamin deficiency and viruses
- Vitamin deficiency in guinea pigs causes diseases such as scurvy, focal baldness, allergic reaction, itchy skin, decreased immunity and colds.
- Conjunctivitis is a purulent inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eyelids, which often accompanies excessive growth of molars, keeping the animal in a dusty room, due to chemical irritants. First, the animal's eyes become swollen and red, then the appearance of pus causes the eyelashes to stick together and tearing increases. Then the eyelids completely stick together from pus and if the disease is not treated, the mumps will go blind. It is advisable not to self-medicate for conjunctivitis because it may be an indirect sign of a cold that will turn into pneumonia or an indirect sign of overgrown teeth. Remember to practice good personal hygiene and wash your hands after treating your pet.
- Rickets occurs due to a lack of calcium and vitamin D. It usually occurs in young pigs in winter. They recommend a trivitamin, irradiation with a quartz lamp, and adding salt to the diet. With rickets, the limbs are twisted, the joints are thickened, the animal is depressed and stunted.
- Paratyphoid fever is an infectious disease that begins due to damage to the pig's body by microorganisms that enter with drinking water and feed. A sick animal refuses food, its fur becomes sticky, and its eyes become dull. Antibiotic treatment is prescribed only by a doctor.
- Pasteurellosis causes a runny nose. The disease begins with moistening of the hairs around the nostrils, then sneezing appears. The nose itches and the animal rubs it with its paws. Then mucus appears from the nose, turning into pus. The pig's breathing becomes heavy and wheezing. All this is accompanied by decreased appetite and lethargy. The disease is chronic and lasts a long time. During an exacerbation, ulcers appear on the body, high fever and convulsions rise. Pasteurellosis cannot be cured. Animals with severe symptoms of the disease are euthanized. At the beginning of the disease, when the symptoms are not clear, they are treated with antibiotics and sulfa drugs.
- Wounds can occur in the event of a fight with a relative or an attack on an animal by a cat or dog. The hair around the wounds is cut off, the wound is washed and dried using hydrogen peroxide or a solution of potassium permanganate in a ratio of 1:1000. Then it is lubricated with Levomekol, synthomycin or streptocyte ointment until it is completely cured.
- Fractures and cracks in bones occur during a fall. Swelling occurs at the site of injury, and there may be muscle damage with an open fracture. There is always severe pain. The animal will limp for the rest of its life. The fracture must be treated in a clinic.
- Diseases of the digestive system are associated with the structural features of the intestines. In rodents it is very long, and food takes a long time to digest in it. Changing feeds and an excess of juicy vegetables leads to intestinal upset and diarrhea. The owner of a rodent should know that the introduction of new food should begin with minimal portions, in the morning, with a gradual increase and replacement of the usual diet. This is done when absolutely necessary. Or with the change of season, when you need to introduce fresh grass into your diet. To correct nutritional errors, give activated carbon and a weak pink solution of potassium permanganate instead of drinking.
- Flatulence requires examination by a veterinarian. The formation of gases in the colon area often causes disturbances in the functioning of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems. In rodents, this disease leads to death from suffocation or cardiac arrest. You can relieve flatulence with massage or gymnastics. The animal must be released to run around.
- Infection of the salivary gland with cytomegalovirus and herpes virus occurs through water. In some cases, guinea pigs develop a fever and increased drooling. After some time, the immune system expels the virus and the disease goes away. Re-infection is excluded, since antibodies against these viruses have appeared in the body.
- Enteritis is accompanied by diarrhea, bloating and loud rumbling in the intestines; with these signs, the rodent should be urgently taken to the veterinarian. The cause may be moldy feed. A urine test is taken, which shows the presence of ketone bodies. Treatment of enterocolitis involves restoring the intestinal microflora. To do this, exclude all feed except high-quality hay. In summer, you can collect yarrow, chamomile, red clover, plantain, nettle, dry the herbs on an iron tray and feed this to the animal for 3 days. Glucose is added to the water, dissolved feces from healthy pigs are given, which improves the intestinal microflora. It is diluted in water and injected into the oral cavity through a syringe once a day. There is no need to prevent pigs from eating their own droppings. This will only benefit them. The list of diseases can be kept endlessly, but only a veterinarian can make the correct diagnosis.
Any disease with fever, accompanied by pain and discharge requires the attention of a veterinarian. Call the phone number listed on the website and ask all your questions.
Manifestations and stages
Cheilosis is a common inflammatory problem. When the lip tissue is damaged, signs such as increased dryness and redness, the development of wounds and ulcers, and pain appear. Often develops due to poor ecology, irritation caused by food or chemicals. In some cases, it is caused by other diseases, that is, it acts as a symptom.
The following types of lesions are observed in children:
- traumatic;
- exfoliative;
- contact;
- meteorological;
- grandular and angular cheilitis in children;
- microbial.
The traumatic form occurs due to mechanical, chemical and other influences, after which infection develops. Swelling appears, the mucous membrane becomes tense, and lip movements become limited. In some cases, this type of cheilitis is caused by herpes in the acute stage. For treatment, antibiotics, antiseptics or anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed.
The exfoliative type of the disease is accompanied by increased dryness and peeling. The reason is a lack of vitamin B, ascorbic or nicotinic acid. The problem arises with dysfunction of the endocrine or nervous system, impaired lip closure, or mouth breathing. Therapy is prescribed depending on the cause of the lesion; multivitamins and softening creams are often used.
Allergic, or contact, cheilitis in most cases develops in adolescents. The causes are chemicals and other external factors. Manifestations of the disease include itching or burning, blisters on the surface, and dryness. To eliminate the problem, you need to avoid contact with the substance that caused the allergy and take antihistamines.
In addition, there are:
- atopic cheilitis in children, which is accompanied by peeling, swelling, erythema and edema;
- hypovitaminosis, characterized by cracks, soreness, the causes are bad habits, for example, frequent licking of lips;
- Eczematous cheilitis is not an independent disease, but one of the symptoms of an inflammatory process affecting the skin.