Guinea pigs are very friendly and affectionate, ideal pets for a child. However, we must remember that they are also susceptible to disease, like any other living creature. Every happy owner of this cute creature must know all the symptoms of diseases to which guinea pigs are susceptible. We hope that after reading this article you will know more about the ailments that can befall such a fragile and cute guinea pig. Let your pets avoid guinea pig diseases
Sleep disturbance and hiccups
Guinea pigs are very active animals. They sleep several times a day and little by little, and in case of danger or in an alarming situation, the guinea pig sleeps with its eyes open. Young animals spend less time sleeping, but older animals spend much more time sleeping. If your guinea pig lives alone, it may also sleep longer. Sleep disturbances are usually caused by a nervous state, problems with skin parasites and improper feeding. You can identify problems with sleep in an animal by changing behavior - the guinea pig becomes more active, loses appetite, may show aggression and refuse offered treats. It is not the effect that should be treated, but the cause - examine the animal, donate blood for analysis and scrape the skin to identify skin parasites.
Sleep problems sometimes cause your guinea pig to hiccup.
Another cause of hiccups is a cold. Signs of a cold include lethargy, decreased appetite, elevated body temperature and heavy breathing. Purulent and mucous discharge is possible from the eyes and nose. Colds are treated with Sulfazine or Sulfadimezine 0.1 mg per kilogram of guinea pig weight three times a day.
Allergies also cause hiccups. Allergies are most often caused by dust contained in sawdust or hay, or too sweet or sour foods. In addition to allergies, problems with clean drinking water can also cause hiccups. The daily amount of water consumed by a pig is approximately 100 ml. However, if yesterday a guinea pig drank more than normal, and today it hardly comes to the drinking bowl, this is not a sign of concern. Sometimes the difference in water consumption can be explained by changes in weather and temperature, changes in mood and the abundance of succulent food in the feeder. But if the animal is thirsty and the drinking bowl is empty, then hiccups may occur.
Rickets
This disease is formed when the working pace of the secretion glands is disrupted, as well as in the absence of the required amount of mineral salts in the animal’s body.
Pigs can get rickets in the winter . It is observed in young individuals.
Symptoms:
- curvature of limbs;
- thickening of joints;
- The pig's back sags.
Pigs suffering from rickets experience stunted growth.
Treatment
and 2-3 drops of trivitamin are added to the pig’s drinking water every day .
For treatment, the use of a quartz lamp is recommended . Radiation of a rodent can be carried out after receiving a recommendation from a veterinarian.
Injuries
If your guinea pig falls on the floor or the soft surface of a chair or sofa, it can cause injury. The animal should be examined immediately for bleeding, lameness, or swelling of the legs. Sometimes it takes a few minutes for the animal to realize that there is a problem, so the breeder should watch the guinea pig for a while. If an animal falls from a height (escapes from the hands and falls to the floor), this can lead to broken limbs. Sometimes the fall ends more sadly: the guinea pig's hind legs give out or it cannot lean on its front legs. This indicates a spinal fracture. The animal must be taken to a veterinarian immediately and x-rayed.
If after the fall the pig does not limp, but slight swelling appears, it is removed with injections:
- Cerebrolysin,
- Mexidol,
- Prednisone.
The drugs are administered 0.1 ml per kilogram of the animal’s weight intramuscularly for a week. In addition to medications, it is necessary to massage the injured limbs.
Pasteurellosis
The main symptom of this disease is a runny nose.
Symptoms
Primary – the hairs around the nostrils are moisturized.
Secondary – sneezing appears.
The animal sneezes and rubs its nose area with its front paws.
The condition of the respiratory system is severe, with wheezing.
Over time, mucus and pus are released from the nose.
The duration of the illness is several months. It may subside for a while and worsen.
A guinea pig in a severe stage of pasteurellosis will have to be euthanized .
Treatment
There is no specific disease; pasteurellosis is practically incurable .
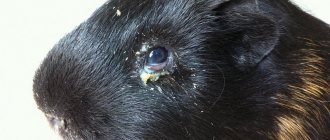
Eye diseases
One of the most common diseases is conjunctivitis. Conjunctivitis in guinea pigs is caused by infection, chemical irritants and physical injury. The disease can affect one eye or both at once. The disease has three stages, each of which has its own symptoms:
- First stage. Swelling, redness of the eyes, sticking of eyelashes,
- Second phase. Discharge of pus from the eyes, the eyes stop opening,
- Third stage. Clouding of the cornea and loss of vision.
If a guinea pig gets sick with conjunctivitis, then first aid will be provided by Albucid solution, which removes mucous and purulent discharge from the eyes. After the eyes have been washed, it is necessary to put Tetracycline or Hydrocortisone ointment under the eyelid. The area around the eyes should also be lubricated with the same ointment. If clouding of the cornea is observed, Calomel should be injected into the affected eye, after mixing it in equal proportions with powdered sugar. The procedure is repeated twice a day.
Eye diseases also include keratitis. It causes a violation of the integrity of the cornea of the eye, and the cause is damage to the mucous membrane by prickly grass or twigs. Keratitis is treated with Fluorescein solution and eye drops. Additionally, you can use any glucose-containing eye ointment.
Diseases of the eyes and ears
Eye diseases can be caused by various reasons, for example, an injury occurred, an allergic reaction developed, or an infection occurred. The most common is conjunctivitis, in which the mucous membranes become inflamed.
Be sure to pay attention to the following signs:
- Photophobia.
- Redness of the sclera.
- Purulent discharge.
- Tearing.
- Swelling of the eyelids.
Around the eyes, the fur clumps together, crusts appear, and bald patches appear. When no treatment is applied, conjunctivitis becomes severe, which is complicated by keratitis.
Treatment is carried out with a 3% solution of albucid; be sure to wash the eyes with disinfectants and anti-inflammatory agents, for example, furatsilin, chamomile decoction, potassium permanganate solution, only weak.
Tetracycline or chloramphenicol ointment is applied to the eyes, or hydrocortisone in severe cases. Often conjunctivitis is complicated by an infection, which also needs to be treated.
Guinea pigs face other eye diseases:
- Cataract. Most often caused by diabetes mellitus, if left untreated it leads to blindness.
- Calcinosis. It is also called ossification of the eyes. Occurs due to injury. It may develop due to disturbances in metabolic processes when bone formations appear.
There may be congenital abnormalities such as a bulging eyelid, as well as microophthalmia, when the eyes are small.
Otitis
If bacterial flora appears in the ears, an inflammatory process develops - otitis media. Manifested by the following symptoms:
- The animal is very restless and can show aggression.
- It scratches his ears.
- Shakes his head.
- Weight loss.
When examining the ears, dried crusts and blood are visible. It is necessary to wash the ears with chlorhexidine, miramistin, and also instill surolan.
Kidney diseases
Kidney stones are a fairly common condition in guinea pigs. And the first symptom is frequent urination. Treatment of urolithiasis is impossible without surgery. Another kidney disease is crystalluria. It is provoked by the peculiarity of the guinea pig's metabolism, when calcium is washed out of the body by urine. When the disease occurs, the urine turns white and becomes very cloudy.
Changes in the color of urine in a guinea pig can be caused not only by diseases, but also by changes in diet.
Some vegetables and fruits contain coloring pigments that can turn urine pinkish or dark yellow. Individual droplets of blood contained in the urine should cause alarm. If blood is noticed in the urine, the animal must be taken to a veterinarian to determine the exact cause. This could be an infection in the urinary canal or in the uterus, stones or sand in the bladder, or a problem with the intestines.
You should consult a doctor immediately if you notice the following symptoms:
- The appearance of mucus in the urine,
- The pig stopped urinating
- The animal's urine smells like silt,
- The pig urinates frequently and little by little.
Constant thirst is also a dangerous symptom. If the feeding diet has not changed, and the animal drinks a lot, then you should also consult a doctor.
Self-treatment of these diseases at home can lead to serious complications and death of the animal.
Can a person become infected from a sick pet?
Unfortunately, there are quite a lot of diseases that can be transmitted from animals to humans, including:
- Worm infestation.
- Giardiasis.
- Microsporia.
- Ringworm.
- Flu.
If there are any changes in behavior, appearance, or the manifestation of any symptoms, be sure to consult a doctor as soon as possible. The sooner the diagnosis is made, the easier it will be to treat the animal and prevent complications.
Features of estrus in guinea pigs
Estrus in guinea pigs is not accompanied by discharge, and their presence indicates inflammatory processes or a possible miscarriage. The first heat in female guinea pigs occurs at approximately five to six weeks and repeats every 21-25 days. The duration of estrus is two days, but the most favorable period for fertilization is the first 10 - 12 hours. Estrus can be determined by the changed behavior of the female, as well as by the absence of a film covering the entrance to the vagina.
Bloating in Guinea Pigs
Flatulence or bloating is caused by gases accumulated in the animal's tummy. Symptoms of the disease:
- Swollen sides
- Hard tummy
- Apathy,
- Loss of appetite and refusal of treats,
- Salivation,
- The guinea pig is breathing heavily
- Wheezing,
- Heartbeat disturbance.
Flatulence can be caused by a sudden change in the animal’s diet, as well as the inclusion in the daily diet of a large number of cabbage leaves and peas, dry food and a lack of hay. Often, flatulence is caused by the fact that the guinea pig drank dirty and stale water. Excess weight, a sedentary lifestyle, dental diseases, various infections and fungal infection lead to the disease. If treatment is not treated in time, flatulence can lead to cardiac arrest of the animal. Flatulence can be cured with Espumisan or any similar drug. 0.5 ml or 1 ml of medication is given to the guinea pig once a day, and if flatulence is profuse, then every two to three hours until visible improvement occurs. Massaging the tummy helps a lot.
During the treatment period, it is important to provide the animal with constant access to fresh and clean water, limit hay and dry food, and completely exclude any vegetables or fruits from the diet.
Digestive system
Symptoms
With digestive diseases, there is a clear decrease in appetite and increased thirst.
Treatment
Before treating constipation, it is necessary to cleanse the gastrointestinal tract - a spoonful of Vaseline or castor oil.
one of the drugs to take orally : “Syntomycin”, “Biomycin”, “Phthalazol”, “Enterosperol” or “Levomycetin”.
to add strong tea to the animal's drinking bowl .
If you are absolutely sure that your pet does not have terrible diarrhea due to feeding errors, let him chew on pomegranate peel or galangal root.
Seizures in guinea pigs
Paralysis is a dangerous and serious disease that can be caused by both infections and injuries. The first symptoms of paralysis are refusal to eat, severe fever, and apathy. The guinea pig is breathing very heavily, trembling and lying on his side. The disease is often accompanied by convulsions and limb failure. If the breeder notices dangerous symptoms in an animal, it should be immediately separated from the other animals and shown to a veterinarian to establish an accurate diagnosis.
Convulsions can be caused not only by paralysis, but also by a more dangerous disease - pestilence.
If a guinea pig's cage was exposed to direct sunlight for a long time, the animal could overheat and suffer heatstroke. In this case, seizures are one of the most important and first symptoms. The cage with the animal must be moved to a cool place and the animal must be provided with sufficient water. You can also cover your guinea pig with a damp, cold towel for a short time. In more rare cases, seizures may accompany heart and lung problems.
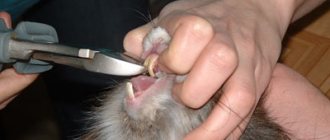
Diseases of the teeth and oral cavity
It is very important to prepare the animal’s diet correctly so that it contains a sufficient amount of solid food, since it is necessary for the animal’s teeth to be properly ground, for this purpose special mineral stones are installed.
If the teeth are long, they interfere with food intake, injure the oral cavity, which means the gnawer cannot eat fully, which is why he loses weight and develops vitamin deficiency. Dental correction is required, which is carried out by a veterinarian.
Guinea pigs can also develop cheilitis, in which the mucous membrane of the lips becomes inflamed. There are several reasons, for example, infection as a consequence of vitamin deficiency, as well as the presence of parasites that live on the upper part of the palate. Cracks, crusts, ulcers appear on the lips and in the oral cavity, and a strong plaque appears on the teeth, which has a greenish tint.
Abscess in guinea pigs
The abscess most often appears on the back, sides and tummy, and takes the form of a hard lump covered with hair and can reach two or more centimeters in size. When pressing, you can feel the liquid, but the animal does not show any signs of pain or anxiety. An abscess is a capsule filled with pus. Pus may break out if the capsule is completely ripe. The opened wound must be washed with hydrogen peroxide and thoroughly cleaned of pus. Most often, the wound heals the very next day. The cause of an abscess can be a bruise or an injection from a sharp twig, or a fight with another guinea pig. To speed up the maturation of the abscess, it is good to make lotions with Vishnevsky ointment or ichthyol ointment, and also increase foods containing vitamin C in the diet.
Tumors in guinea pigs
All types of tumors that occur in animals are divided into two groups: benign and malignant.
Benign tumors are not dangerous for the animal. Malignant tumors can affect all organs in a few days and cause death. Skin cancer is most common in guinea pigs. This type of disease affects the hind legs, less often the back and sides. If you remove this tumor from a guinea pig in the initial stages, the disease may recede. The danger lies in the fact that the symptoms are very similar to an abscess and the owners begin independent and incorrect treatment. As a result, the initial stage of the disease is skipped, during which treatment is most effective and safe.
Lung cancer also occurs in guinea pigs. Even a very attentive breeder is unable to notice the early stages of the disease and most often goes to the veterinary clinic in the later stages. Lung cancer can be identified by difficulty breathing, increased chest volume, apathy of the animal and periodic coughing. However, these symptoms are very similar to colds, so not all breeders immediately consult a doctor. Cancer can only be detected using x-rays. In the later stages, treatment does not bring any results, and it is not possible to remove an overgrown tumor from the lungs.
The appearance of a malignant tumor is preceded by a significant enlargement of the lymph nodes. The lymph nodes in the neck become inflamed first, then in the armpits and groin. Next, the animal’s liver and spleen enlarge, leukemia may begin, which means the chances of saving the animal are zero. Malignant tumors usually run in families and are called lymphosarcoma.
It is important to remember that the type of tumor, exact diagnosis and treatment can only be determined by a doctor after the necessary pictures and tests. Self-treatment will only worsen the course of the disease and the condition of the animal. Breeders also need to remember that in 80% of cases, cancer in guinea pigs leads to death.
Infectious pathologies
Plague
A particularly dangerous viral disease of guinea pigs, characterized by high contagiousness and lethality. After infection, the incubation period usually does not exceed 3 weeks. Clinical signs:
- general weakness;
- convulsions;
- apathy;
- lack of coordination;
- paralysis of the hind limbs.
The diagnosis is confirmed by laboratory testing, and the sick pig is immediately euthanized. No treatment has been developed.
Pseudotuberculosis
A common pathology with high mortality and the main symptom is diarrhea. The disease has nothing in common with real tuberculosis - the name is given due to the discovery of nodules in organs during autopsy, reminiscent of tuberculous tubercles. The main difference from true tuberculosis is the absence of lung damage.
Clinical manifestations:
- watery stool mixed with mucus and blood;
- loss of appetite;
- conjunctivitis is often observed;
- palpation reveals an enlargement of the mesenteric lymph nodes;
- in the terminal stage, convulsions are observed.
A test with pseudotuberculin is used as a laboratory diagnosis, but at the moment this option is available in a small number of clinics.
Treatment is also difficult - most often pseudotuberculosis in guinea pigs occurs in a fulminant and acute form. Therapy is reduced to the administration of antibiotics (tetracycline) in a loading dose, as well as the use of sulfonamides.
Paratyphoid
A common infectious disease of guinea pigs. Damage to the digestive system is noted: debilitating foul green diarrhea, suppressed appetite, tympany. A sick pet is characterized by general lethargy, tousled fur, and constant inactivity.
For treatment use:
- tetracycline antibiotics;
- sulfadimezine;
- antityphoid serum.
Improvements in content are also being monitored. Due to diarrhea in a guinea pig, you should clean the cage more often, provide the animal with easily digestible food, and do not limit drinking.
Pasteurellosis
A bacterial disease of guinea pigs and other animals, the pathology is also dangerous for humans. In pets it manifests itself as a respiratory infection:
- profuse catarrhal-purulent discharge from the nasal passages;
- guinea pigs sneeze and rub their nose;
- hard breath;
- wheezing sounds.
With complications, diarrhea, pustular and erythematous skin lesions develop. In the terminal stage, convulsions are observed. The disease is characterized by high mortality, especially among young animals.
On large guinea pig farms, any stock showing obvious clinical signs should be separated immediately. It is recommended to destroy animals in serious condition and dead. All livestock, including clinically healthy ones, are prescribed a course of antibiotics and sulfa drugs. Therapeutic and quarantine measures are lifted a week after the last case of clinical manifestation of the disease, and all premises and equipment are disinfected.
Lymphocytic choriomeningitis
A viral disease of guinea pigs, characterized by high mortality. The infection spreads with mice; other animals can also pose a danger, so before adding a new pig to an existing one, a month-long quarantine should be carried out.
Pets experience high fever and general weakness. The diagnosis is confirmed by laboratory tests, in which case the guinea pig should be euthanized. No treatment has been developed, and the virus is also dangerous for people.
Bordetellosis
Previously, the disease was registered exclusively in dogs as “kennel cough”; later cases of infection in cats, farm animals, and rodents, including guinea pigs, were identified. The wide range of susceptible animals makes the disease dangerous for pets. In guinea pigs it often appears after contact with other animals. Therefore, the main preventive measure is to prevent contact and timely therapy, vaccination and diagnosis of dogs, cats and other animals. Vaccine prevention of bordetellosis has also been developed in guinea pigs, but it shows little effectiveness and only reduces the severity of the pathology.
Pets experience characteristic changes in the respiratory system:
- sneezing;
- labored breathing;
- catarrhal-purulent discharge from the nasal passages;
- temperature increase;
- inflammation of the conjunctiva;
- the head is often turned to one side - otitis media develops;
- appetite is reduced or absent;
- general lethargy.
Treatment is complex; the best results are achieved with the combined use of antibiotics and sulfonamide drugs:
- subcutaneous injections of baytril, intramuscular injections of gentamicin;
- sulfadimethoxine.
Specific therapy in the form of menthol inhalations and eucalyptus decoctions is difficult, so sodium bicarbonate in an amount of 0.1-0.2 g/kg, thermopsis or pectusin should be added to the feed. To support the heart, injections of sulfocamphocaine or caffeine, carboxylase are prescribed. Complex vitamin supplements are recommended.
Skin diseases
Skin diseases of guinea pigs are most often associated with improper housing and feeding conditions and are provoked by various skin parasites: mites, lice, lice, as well as fungi and allergies. The first signs are itching and the appearance of lumps on the skin, ulcers, most often purulent, scratching and hair loss. Skin diseases are not as safe as many people think.
Severe itching can lead an animal to exhaustion, heart attack and death.
It is possible to determine exactly why a guinea pig is itching and what type of parasite is causing the itching only in a veterinary clinic using skin scrapings. Most often, treatment consists of treating the animal with special shampoos. However, in case of severe damage, antibiotics and probiotics may be prescribed.
Pseudotuberculosis
Pseudotuberculosis is a chronic disease.
It is characterized by the appearance of nodular formations on the diseased organs and tissues.
An animal is infected through food: pseudotuberculosis is caused by a bacillus called bact. pseudotuberculosis rodentium .
Symptoms:
- decreased appetite;
- exhaustion;
- diarrhea;
- paralysis.
Treatment
Be sure to hospitalize your mumps. Treatment is strictly inpatient .
Diseases dangerous to people
Guinea pigs can be a source or carrier of diseases that are dangerous to humans. You can become infected with skin or intestinal parasites from an animal. Roundworms cause strongyloidiasis, and giardia causes giardiasis. Liver fluke can cause severe liver disease, which in most cases is fatal. From a guinea pig, a breeder can acquire diseases caused by bacteria and viruses: salmonellosis, tuberculosis and leptospirosis. The most commonly transmitted skin disease is lichen. Regular flu can be transmitted both from the breeder to the animal, and from the animal to the breeder. Avoiding infection is not difficult: you need to keep the cages clean, wash your hands after each cage cleaning, as well as after interacting with the animal, and avoid getting saliva or animal hair in your mouth. Any illness in an animal - use a disposable medical mask.