Decorative rats are neat animals for which their owners provide decent living conditions.
Unfortunately, parasites are found in rats even if they are kept comfortably in an apartment, with timely cleaning and regular disinfection of the rodent cage. If your pet rat has become restless, often itches and bites fur with its teeth, scratches, bloody crusts, and areas of baldness appear on its body, then you should suspect that your furry friend has external or subcutaneous parasites. In such cases, it is advisable to immediately take the pet to a veterinary clinic to clarify the diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment, otherwise rat parasites can cause exhaustion and death of the animal.
Where do parasites come from in decorative rats?
Inexperienced rat breeders often ask a similar question when they discover parasitic animals on the body of their beloved pet. A domestic rodent can pick up parasites even with very careful care and maintenance; they can be their sources.
Filler
Often, lice eaters and ticks live in hay and sawdust, which animal owners buy in dubious places and use as filler.
Contact with infected animals
They can be domestic or wild mice and rats.
External environment
Even a loving owner who brings the infection from the street on his hands and clothes can give his pet parasites.
Consequences for animals
The animal becomes lethargic, exhaustion appears, and immunity decreases. As a result, chronic problems worsen, infectious diseases and colds become more common.
Anemia and vitamin deficiency may develop. Another danger of lice eaters is that they themselves are carriers of many diseases and can cause fungal, viral, bacterial, and helminth diseases.
In any case, infestation with parasites undermines the health of the infected animal, causing numerous problems.
Very often, lemon tree owners may notice strange growths on the plant - these are scale insects. Find out how to get rid of it by reading our article.
Rat flea bites are very dangerous, as these parasites carry many diseases. What to do if you find bites of these insects, read the link https://stopvreditel.ru/parazity/perenoschiki/krysinaja-bloha.html.
Major rat parasites
In decorative rats you can find different types of ectoparasites, all of which cause unbearable itching and anxiety to the animal.
lice eaters
Red wingless small insects no larger than 1 mm in size with an oblong elongated body covered with bristles, shaped like cat fleas. In light-colored rodents, adult insects can easily be detected in the fur. Rat pests feed on particles of the epidermis and blood of the rodent.
Infection of domestic rats with lice eaters is accompanied by severe debilitating itching in the rodent; the domestic rat becomes very restless, twitchy, often itches intensely, refuses to eat, and progressive exhaustion is observed. There are numerous wounds, scratches, and bruises on the pet’s body, accompanied by severe swelling and inflammatory processes.
Lice eaters in rats multiply rapidly; an adult female lays more than a hundred nit eggs, which stick to the animal’s fur. The owner can detect light shiny inclusions on the lower back and near the tail, fixed in the pet's hair and reminiscent of ordinary dandruff. It is almost impossible to remove nits from a rat's fur, only by completely removing the animal's hair. A huge number of larvae emerge from the eggs, which within a month become adult, sexually mature individuals.
The parasitism of lice eaters in rats is dangerous due to the death of the pet, so treatment should begin at the first characteristic symptoms of infection.
Lice
Lice in rats cause severe itching and anxiety; these parasitic insects feed only on the blood of a domestic rat; per day, one louse attaches itself more than 10 times to the animal’s skin. Adults can only be seen under a microscope; the body size of the parasites is no more than 0.5 mm.
Rat lice are small red insects with an elongated body, at the head end of which there are hooks for holding on the animal’s body and two sharp stilettos for piercing the skin. The louse cuts through the skin, injects substances that prevent the rodent's blood from clotting, and attaches itself to the animal's body.
Reproduction of lice occurs in the same way as in lice, with the deposition of nit eggs and the hatching of nymphs, which turn into sexually mature individuals. White shiny nits of lice can be found on the fur of a rat; parasitism is accompanied by severe nervousness of the animal, active itching, lethargy and apathy of the pet; the development of anemia, typhus and hemobartonellosis in the rat is possible.
Fleas
Rat fleas are unpleasant blood-sucking insects of a red-brown color with a characteristic body flattened on both sides, the size of the insect is 2-5 mm. The flea is capable of jumping long distances and clinging to the host's fur with tenacious claws, and is capable of migrating between cats, dogs and rats.
When infected, pets constantly scratch itchy areas, become restless, and may develop anemia. Dried burgundy crusts can be found on the animal's body - flea secretions; when bathing a rat, they turn the water pink.
Mites are very common in rats; there are several types of parasites that live on the skin and in the epidermal layer. The rat tick is red-brown in color, 0.1-1 mm in size, has an oblong flat body, feeds on the blood of an animal and carries various serious diseases. With a lack of nutrition, the tick is capable of attacking humans.
IMPORTANT!!! Rat mites are dangerous to humans! People, especially children, have a hard time with eczematous dermatitis, which develops as a result of parasitism by these insects. Ticks infect people with typhus and murine typhus, tularemia, plague, rickettsial infections and Q fever.
Subcutaneous mites live in the upper layer of the epidermis under the skin of a rodent. It is impossible to visually detect these mites; the diagnosis is made only on the basis of examination of skin scrapings under a microscope.
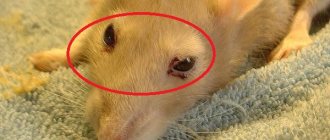
Parasitism of ticks on the body of a rat is manifested by characteristic symptoms: hair loss and the formation of multiple swollen red wounds on the neck, head, spine and shoulders of the rodent.
Ear mites primarily attack the delicate skin of the ear, pinna and nose, which is manifested by the appearance of yellow or red growths on the ears, nose, limbs and genitals.
Bedbugs
Ordinary bed bugs can also drink blood from decorative rats, causing severe itching, scratching, anemia, and infection with blood parasites. Bedbugs attack domestic rodents during periods of food shortage or the absence of a person nearby as a food source.
Description of insects
Adults
They have a flattened body of light yellow color, reaching a length of no more than 1 mm. The head is large, wider than the chest, shaped like a shield. There are no wings.
The oral apparatus has a complex structure and is of the gnawing type. It consists of an upper jaw covered with a chitinous shell, a thick upper lip, and a lower jaw, which, like the upper one, is entirely covered with denticles.
Three pairs of legs ending in claws are attached to the chest. It is they, together with the teeth of the jaws, that help securely attach to the hair of animals.
The abdomen is elongated and consists of segments, each of which is covered with setae. The antennae of lice eaters have three segments.
Larva
It is no different from the imago; its development goes through three instars, ending with molting. The break between them ranges from 2 to 12 days. The entire period of larval development lasts approximately 20 days.
Habitats
Lice eaters settle on the surface of the skin of mammals, localizing in the fur. They feed on epidermal cells, blood, secretions of the sebaceous glands, lymph, and keratinized cells.
Reproduction
Fertilization occurs by mating of a male and a female, after which the female
lays eggs (nits). Caring for the offspring is expressed in the fact that the female firmly attaches the eggs to the hair with the help of quickly hardening cement secreted by the glands of the insect. One adult is capable of producing about 100 eggs.
From the moment the egg is laid until the first instar larva emerges from it, 5–10 days pass.
Treatment of an infected rat
Specifying the type of parasite and prescribing treatment should be carried out by a specialist in a veterinary clinic, since different medications are used to destroy external and subcutaneous parasites. In case of complications, the animal is prescribed anti-inflammatory ointments, immunostimulating drugs and a course of vitamins and antibiotics.
Insecticidal preparations are highly toxic; if handled incorrectly or in excess of the dosage, there is a risk of poisoning a decorative rat. It is advisable that the animal be treated by a veterinarian; it is also permissible to treat a furry pet at home in a well-ventilated area, strictly following the recommendations of a specialist.
At the same time as treating your pet, you need to throw away the bedding, disinfect the cage and all accessories several times, change the filler, and treat the entire room with repellents. It is advisable to throw away all wooden objects from the cage; they can be places where parasites accumulate. The rodent's claws should be trimmed short during treatment to prevent scratching of the skin.
When keeping domestic rats in groups, all rats must be treated repeatedly to avoid re-infection. If a pet is bitten by fleas or bedbugs, it is recommended to treat all pets living in the house with insecticides, as well as the room itself: carpets, upholstered furniture, mattresses, floors, etc.
Prevention
Both external and internal parasites cause a lot of anxiety and trouble for the pet and its owner. In addition, parasitic diseases that are not treated promptly can lead to serious complications for the animal’s health. Therefore, it is better to pay attention to the prevention of all types of parasites. The following measures will help avoid infection:
- Regular cleaning of the cage . You need to wash the tray and change the filler at least 3 times a week. And once a month it is necessary to completely disinfect the cage and everything in it.
- Buying quality filler . Insects are almost never found in products from trusted manufacturers. Additionally, to avoid troubles, it is necessary to store the filler in sealed bags. If this is not possible, it is better to buy filler in small packages that are quickly used up.
- Sending newly acquired rats to quarantine . It is advisable to place purchased animals in a separate cage for the first 2-3 weeks. This time is enough to check your pet for parasites and, if necessary, treat it.
- Fencing a decorative rat from other domestic animals . First of all, from strangers. This applies to those who like to receive guests with their pets.
- Compliance with personal hygiene rules . You should not touch your fluffy immediately after being outside, especially in public places. First you need to change clothes and wash your hands thoroughly with soap. And only after that, start communicating with pets.
- Feeding with quality products . Industrial food for decorative rats usually does not pose any danger. However, during long-term storage, insects may appear in the bag. But natural nutrition can become a potential source of danger. Therefore, before serving to the rat, it is necessary to thoroughly wash fruits and vegetables, and heat treat meat and fish.
Knowing what causes parasites in rats and how to get rid of ticks, lice, fleas and worms, every owner will be able to provide their pet with a healthy and happy life. The main thing is to take precautions in time. And if you still cannot avoid infection, contact a veterinary clinic.
Diseases
The parasite's bites cause an itchy skin irritation in humans called rat mite dermatitis. Children may have an eczematous or vesicular reaction to the sting. Rat mite attacks must be differentiated from other insect bites or skin irritations caused by the body's reaction to an allergen.
Treatment of rat tick-borne dermatitis is symptomatic. To alleviate the condition of the victim, use:
- oral antihistamines;
- topical corticosteroids;
- benzyl benzoate;
- gamma-benzene hexachloride;
- Crotamiton.
But often the irritation goes away on its own or people simply do not react to the saliva of rat bloodsuckers.
Rat mite
The reaction to rat parasites must be separated from the symptoms:
Laboratory studies have also shown that rat mites can carry dangerous diseases:
In unfavorable times, rat ticks, along with fleas, were the main carriers of typhoid and plague from rodents to people.
Infection of residential premises
Unfortunately, situations are possible when rat and mouse parasites infect apartments. This is a truly serious problem that requires the help of specialists. The first thing you need to do is make sure that the room is infested with rat mites. This can be done by a disinfectant. In the event that infection is confirmed, disinsection is carried out.
When carrying out disinfestation, potent drugs are used that are aimed at getting rid of parasites. In this case, it is necessary to treat all possible locations of insects. In cases where pets live in the house, be sure to visit a veterinarian who will recommend a remedy for treatment.
It is very important in this situation to find the cause of the infection; if this happened due to the presence of mice and rats in the basement, then this room must also be treated, since the situation will repeat itself.
Pet treatment
To get rid of fleas faster, you first need to rid your pets of them. This will deprive the insects of food. Shampoo or spray to kill fleas living in the animal’s fur, as well as drops, will help with this. Then you should put a special collar on your pet, which will repel fleas and prevent re-infestation.
Drops
Drops containing an insecticide are applied to the animal’s withers. Drugs produced in this dosage form are safer and more effective.
Before treating your pet, you should not bathe it for 3-4 days so that the fatty film on the skin is not disturbed. If you apply the drops immediately after washing, there is a high probability that the drug will not work. The product protects your pet for 3-4 weeks.
The most effective drugs include:
- Rolf 3D;
- Advantan;
- Hartz;
- Stronghold;
- Frontline;
- "Inspector";
- "Bars".
“Bars” is one of the most effective flea medications.
Rat mite (Ornithonyssus bacoti) – what it looks like, life cycle, habitat, features
This is a small tick, the body length does not exceed 1.44 mm, but individuals with a length of 0.78 mm (females) and 0.53 mm (males) are more common. Offspring parameters:
- eggs – 0.34 mm;
- larvae – 0.3 mm.
Rat mites, like other representatives of the order, are covered with sensitive villi. They have 4 pairs of limbs, but the front 2 legs are longer. The outer covers are transparent light brown. After eating, the tick enlarges several times, and the color changes to dark red.
The parasite climbs onto the host when it needs to get a portion of food. It has a piercing-sucking type of mouthparts, which allows it to pierce the skin and suck out blood at a rapid pace, since the digestive system works on the principle of a pump. It is found in temperate and tropical climates, but does not live in cold regions. The main host is a rat (gray).
In the absence of a food source,
the parasite transfers to the mouse. Less often it bites other rodents.
If there is no suitable food nearby, rat ticks can bite a dog or cat, and sometimes a person. But at this stage of life the pest does not reproduce. For the birth of offspring, the blood of rodents is necessary. Moreover, the life expectancy of a person is 1.5 months. Life cycle of pests:
- egg;
- larva;
- protonymph;
- deutonymph;
- imago.
Moreover, the development cycle is short - about 16 days, sometimes less (from 7 to 12 days), which is determined by the ambient temperature. Most often, such pests live for 2.5 months, but the lifespan of males can be reduced to 45 days. Females, on the contrary, can survive for 9 months. They lay up to 100 eggs during this period, but they do this not at once, but in batches one at a time.
Rat ticks can carry serious diseases
Attack of rat ticks on adults and children - complications
Soon after a bite, people develop dermatitis of unknown etiology. Moreover, they are complicated by severe itching, the formation of papules, vesicles, and rashes over large areas of the skin. Bite marks are found where the fabric of clothing adheres more tightly to the outer skin. At the same time, a hyperemic area appears. Less frequently, the temperature rises and headache appears. This is caused by the body’s reaction to the substance introduced by the rat parasite (in saliva), as well as harmful microorganisms that the pest carries on its body.
Rat mite (Ornithonyssus bacoti)
What medications are used to make you feel better after bites?
When rat mites attack a person in an apartment, you need to use the most effective means with antiseptic, antimicrobial and antiparasitic properties:
- Benzyl benzoate ointment;
- Sulfuric ointment;
- Wilkinson's ointment;
- Bensocryl;
- Salicylic-zinc paste;
- Spregal.
What and with whom can the reaction to rat bites be confused?
When traces of contact with parasites appear, it is important to recognize who exactly attacked. If the tick has already crawled away, you need to be guided by the external signs of bites. A red spot remains with a dark dot in the center. These are nonspecific signs characteristic of most parasites. At the initial stage (during the first day), the bites of the rat parasite resemble traces of contact with mosquitoes and midges. But in the first case, the affected areas of the skin do not change much. In comparison, dermatosis caused by rat pests develops dermatitis later.
Midge bites
more painful, the affected tissues soon swell.
Rat tick bite on a human body
Rat mites can be a carrier of very dangerous diseases for humans.
Such parasites are carriers of pathogenic microorganisms, and they also pose a danger to humans. Diseases spread by such pests:
- rat typhus;
- Q fever;
- Lyme disease;
- icteric leptospirosis;
- smallpox or vesicular rickettsiosis;
- tick-borne encephalitis;
- West Nile fever;
- tularemia;
- plague.