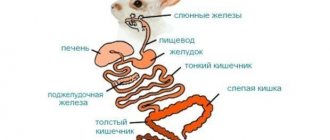
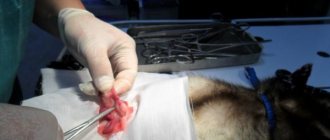
Castration and sterilization of animals is one of the most popular and sought-after veterinary services, the purpose of which is to suppress sexual desire and the reproductive instinct.
This operation not only regulates the number of animals, especially stray ones, but is also a necessary measure for a number of diseases of the reproductive system.
The procedure for removing the reproductive organs is also indicated for breeding animals after they are removed from breeding. This will help avoid a number of diseases, especially cancer, which will increase life expectancy.
Why is chinchilla castration necessary?
This surgical operation has the following advantages:
The level of aggressiveness of the rodent decreases - since it no longer feels the desire to reproduce.
It becomes possible to control reproduction - there is no need to care for the born offspring.
The animal stops marking territories with its urine - you can forever forget about the unpleasant smell from the cage.
The risk of developing pathologies of the genitourinary system is reduced.
A pet lives much longer.
In addition, after castration, you can keep a large number of pets of different sexes in one cage.
Why is the operation performed?
Many pet owners fear for their health, and therefore ask whether it is possible to castrate a chinchilla. In fact, with proper preparation and conduct of the operation, the likelihood of complications is minimal, and the animal recovers quickly.
Castration is carried out on the following grounds:
- The need to improve chinchilla behavior. Often, in an effort to mate, animals begin to show excessive aggressiveness. This leads to frequent conflicts with other animals; chinchillas can attack their owner.
- To exclude uncontrolled reproduction process. With regular mating, the likelihood of offspring is high, and therefore the owner will have to think about where to place the cubs.
- In order to eliminate animal urine marks from cages and surrounding objects. To prevent an unpleasant odor in the apartment, a castration procedure is carried out.
- To reduce the risk of progression of diseases in the reproductive system.
- In order to increase the lifespan of the animal.
- The need to ensure peaceful living in a cage for different-sex individuals without the risk of producing young.
Basic methods of castration
Currently, such procedures can be carried out both in clinical and at home settings.
Typically, such surgical operations are performed in several ways:
Closed bloody - during such an operation, 2 incisions are made on the animal’s body, which provides unhindered access to its reproductive organs.
The main disadvantage of this method is its increased traumatism, which significantly complicates wound healing (more than 14 days).
Open bloody - during the castration process there is no severe injury to the rodent, and the wounds heal within a week.
The main disadvantage of this procedure is the high risk associated with prolapse of the omentum and intestines.
During the operation, only one incision is made, which ensures a high rate of wound healing and eliminates the possibility of complications.
Which animals should be spayed and neutered:
- cats (cat castration, cat sterilization)
- dogs (castration of a male, sterilization of a female)
- ferrets (ferret castration, ferret sterilization)
- mini pigs (boar castration, pig sterilization)
- rabbits (castration of a rabbit, sterilization of a female rabbit)
- rats
Rodents such as chinchilla, guinea pig, degu, rat, hamster are operated on only if there are life-threatening indications (pyometra, pathological childbirth, diseases of the gonads).
Sterilization and castration are effects on the reproductive organs, as a result of which the animal becomes infertile.
The chemical method is the administration of a drug that causes the cessation of the production of sex hormones and the onset of estrus in females, as a result of which she is unable to conceive for some time. Although this is considered a more gentle method of getting rid of an unwanted pregnancy, it has serious consequences in the form of the formation of cysts and tumors of the genital organs and mammary glands, which in the future will lead the animal to the operating table.
The physical method is the use of certain doses of radiation to obtain temporary or permanent infertility. This type of sterilization is contraindicated in animals with weakened immune systems and blood diseases. In addition, an incorrectly selected radiation dose can cause burns and radiation sickness.
Ligation of the fallopian tubes in females is the imposition of a ligature between the ovary and the horns of the uterus (a mechanical barrier to the passage of the egg into the uterus). This type is unreliable and in 40% of cases an unwanted pregnancy occurs, because due to the hormones produced and entering the blood, the animal remains in estrus and sexual desire.
Ligation of the vas deferens in males is a mechanical elimination of the entry of germ cells into the seminal fluid. Animals sterilized in this way are susceptible to the same diseases of the reproductive system as those that are not sterilized.
Removing the ovaries while preserving the uterus is the least recommended way to eliminate a cycle in animals. If the uterus is preserved, endometrial diseases and inflammatory processes may occur, which can lead to the death of the animal.
Complete removal of the ovaries and uterus (total ovariohysterectomy) is the most reliable and favorable type of sterilization of animals. The operated female is forever freed from the possibility of unwanted pregnancy, inflammatory and hormonal diseases of the reproductive organs and mammary glands, as well as the serious consequences that arise from other types of this operation.
For cats, horichs and rabbits, ovariohysterectomy is performed laparoscopically, through a puncture in the abdominal wall. This type of operation is less traumatic than an incision along the white line of the abdomen, which has a beneficial effect on the recovery period.
For dogs and mini pigs, removal of the uterus and ovaries is carried out only through laparotomy, since physiological characteristics (large uterine horns and a developed circulatory system) do not allow the operation to be performed through a puncture.
Removal of the testes in males - the testicles (testicles) are removed through an incision in the scrotum, and excess skin may be excised. It is especially important to promptly castrate hypersexual animals that obsessively demonstrate sexual desire for everything that seems attractive to them.
This operation is also indicated for cryptorchids - those males in whom one of the testicles (or both) has not descended from the abdominal cavity into the scrotum. Otherwise, inflammation of the undescended testis or malignant tissue degeneration may occur.
All these operations can be performed at home. Modern equipment (coagulator, ultrasound), sterile instruments and disposable dressings, gentle anesthesia - all this allows you to perform the operation at the highest level without any complications.
An undoubted advantage of carrying out these surgical procedures at home is that the owner no longer has to transport the operated animal, which has a beneficial effect on the recovery process.
Features of the surgical operation
During the castration process, intramuscular or gas anesthesia is used. Usually this procedure takes no more than half an hour.
After anesthesia is administered, the pet is fixed in a supine position and then the hair is removed from the desired area.
Next, the surgeon makes a small incision on the scrotum of the male, about 1.5 cm, and about 5 cm on the abdomen of the female.
Then the doctor removes the testicles in males and the uterus and ovaries in females.
Finally, sutures are placed at the incision site, which are removed by a veterinarian after the wound has healed (about 10 days). Moreover, sutures applied with self-absorbing threads do not need to be removed at all.
Rehabilitation after castration
In order for your pet to recover from anesthesia as quickly as possible, it is necessary to create extremely comfortable conditions for it.
In particular, you will need to place a soft diaper and a warm heating pad in the rodent's cage. Such measures are necessary to warm the animal after anesthesia.
It is also necessary to treat the seam especially carefully, otherwise inflammation and suppuration will inevitably occur in this place, which can significantly increase the healing time of the wound.
In addition, to prevent your pet from becoming infected, you should clean its cage as often as possible. After the chinchilla recovers from anesthesia, you can begin to feed and water it.
Until the rodent's swallowing reflex is completely restored, it is necessary to drink water and feed boiled vegetables in the form of a puree from a pipette.
After 2 days, the animal can be given the usual solid food.
It is worth noting that, unlike other rodents, chinchillas recover well and quickly from anesthesia, so their rehabilitation process proceeds without any special problems.
Behavior change
After castration, chinchillas become more balanced, calm and friendly. Their mood stabilizes and their mental state normalizes.
They get along well with new cagemates and can reproduce without the risk of unwanted offspring.
Contrary to popular belief, animals do not experience an increase in body weight after surgery; on the contrary, weight normalization is noted.
Most breeders claim that after this procedure, the dental condition of furry pets improves, and it is also much easier to care for them.
Preparing an animal for castration
Any surgical intervention requires preliminary preparation. First, a specialist examines the animal to determine whether it has any contraindications for surgery. One of them may be animal intolerance to anesthesia.
If no such contraindications are found, the specialist will set a time and day for the operation. The animal is not given food for several hours before surgery.
If the animal has not received certain vaccinations, then they must be done in advance of the operation.
If the need arises, antiparasitic treatment must be carried out.
The main advantages of surgery at home
Such simple operations can be carried out both in the clinic and directly at the pet owner’s home.
Castration at home is currently considered one of the most popular services for the following reasons:
- Carrying out the operation at home provides the most comfortable conditions for the animal and significantly shortens the rehabilitation period.
- There is no need to transport the animal to the veterinary hospital and back, which will not only save on transportation costs, but also protect it from unnecessary stress.
- The veterinarian has the opportunity to perform the operation at any time, both on weekdays and on weekends.
- There is no need to stand in long lines at the veterinary hospital, risking contracting some infectious disease.
- The specialist brings with him all the tools and medications needed for castration.
- The cost of this procedure, performed at home, is practically no different from a similar operation performed in a clinic.
- A specialist can give a lot of useful advice related to caring for an animal during the postoperative period.
The veterinarian leaves full contact information to the breeder, so if any problems arise, just call the doctor by phone, and he will arrive at any time of the day.
General services
| Prices for services in our clinic | In the clinic and at home |
| Ratologist visiting your home | from 500 |
| Clinical examination, preliminary diagnosis, consultation | from 500 |
| Telephone consultation | for free |
| Therapy | from 150 |
| Surgery | from 150 |
| Ambulance at home (within an hour) | from 1000 |
Therapy
| Prices for services in our clinic | In the clinic and at home |
| Subcutaneous administration of drugs to rodents | from 150 |
| Intramuscular administration of drugs to rodents | from 200 |
| Intravenous (into a catheter, through a needle) | from 200 |
| Dropper for rodents | from 1000 |
| Placement of an intravenous catheter | from 300 |
| Removing the IV catheter | 200 |
| Tube feeding of rodents | from 300 |
| Taking blood samples | from 300 |
| Novocaine blockade | from 200 |
| Reduction of the cheek pouch | from 200 |
| A haircut | |
| Nail trimming | from 300 |
| Haircutting mats | from 1000 |
| Ear treatment | from 300 |
Surgery and Traumatology
| Prices for services in our clinic | In the clinic and at home |
| Surgery | |
| Surgery of the genitourinary organs in rodents: | |
| Castration | from 2000 |
| Sterilization | from 2500 |
| Surgical procedures | from 400 |
| Surgical treatment of wounds | from 300 |
| Application of musculocutaneous sutures | from 200 |
| Applying a bandage | from 100 |
| Applying a plaster cast | from 1000 |
| Removing the plaster cast | from 300 |
| Surgery for skin, soft tissue and tumor infections | |
| Opening abscesses, hematomas | from 400 |
| Treatment of purulent wounds | from 700 |
| Drainage installation | from 500 |
| Flushing the drainage | 350 |
| Treatment of auricular hematoma | from 1500 |
| Unilateral mastectomy | from 4000 |
| Regional mastectomy | from 5000 |
| Removal of tumors | from 2000 |
| Abdominal surgery | |
| Obstetrics in rodents | from 1000 |
| Animation of newborns | from 300 |
| C-section | from 3000 |
| Pyometra | from 1500 |
Anesthesiology for rodents
| Prices for services in our clinic | In the clinic and at home |
| Anesthesia | from 500 |
Ophthalmology
| Prices for services in our clinic | In the clinic and at home |
| Eyelid surgery for inversion, eversion | from 2000 |
| Exenteration of the eyeball | from 3000 |
Dentistry
| Prices for services in our clinic | In the clinic and at home |
| Removal of incisors | from 500 |
| Trimming and correction of teeth in rodents | from 1500 |
Laboratory diagnostics
| Prices for services in our clinic | In the clinic and at home |
| Blood analysis: | |
| General clinical blood test | 900 |
| Blood cytology | 1000 |
| Biochemical analysis for 1 sample indicator | 300 |
| Biochemical blood test for 6 indicators | 1500 |
| Biochemical blood test for 12 indicators | 2500 |
| Additional biochemical indicators for pancreatic amylase, rheumatoid factor, c-reactive protein | from 300 |
| Analysis of urine: | |
| General clinical urine analysis | 400 |
| Express urine glucose test | 200 |
| Express urine test | 300 |
| Biochemistry of urine 1 indicator | 100 |
| Stool examinations | |
| General stool analysis | 500 |
| Stool culture for pathogens | 1500 |
| Stool analysis for dysbacteriosis | 2000 |
| Stool analysis for protozoa and helminth eggs | 500 |
| Bacteriology | |
| Bacteriological screening | 2000 |
| Microbiological screening | 2000 |
| Full microbiological screening (no subtitration) | 1500 |
| Skin studies | |
| Skin biopsy | 1700 |
| Skin smear | 1000 |
| Dermatophytes and ectoparasites | 1000 |
| Pathomorphology | 1500 |
| Histology of neoplasms, cystic contents | 2000 |
| Cytology of neoplasms, cystic contents | 1500 |
Conditions for sterilization and castration:
- the animal must be clinically healthy (if the operation is not performed in an emergency mode)
- Vaccinations (not required)
- therapist consultation
- appropriate age
Operations to remove the reproductive organs must be done after the onset of puberty, otherwise the animal will not have time to form a skeleton and the urethra in males, which will subsequently lead to its obstruction.
It is also undesirable to carry out these manipulations on old animals, unless there is a threat to life, when surgery is the only salvation.
If you have questions, you can get more detailed information by calling our advisory center at the numbers listed on the website. Doctors will give you detailed answers, preparation instructions and fill out an application for the operation at a time convenient for you.