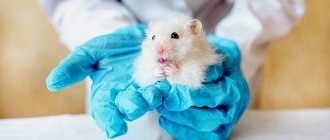
In the wild, the colors of hamsters are not particularly varied. And in captivity, pets were bred with fur of brown, black, gray, cream, and peach shades. And not the least popular among owners are white hamsters, which are not suitable for survival in natural conditions. Let's find out what colors are typical for different breeds of these rodents.
Origin and habitat
The first mention of Djungarians dates back to the end of the 18th century. The German scientist and traveler Pallas described the animal that he encountered on the territory of the Dzungarian region (modern eastern Kazakhstan), initially calling it the Zungarian mouse due to its small size.
In the wild, hamsters prefer to live in deserts, dry steppes, and much less often in forest-steppes.
Their habitat is:
- Western Siberia.
- Northeast of Kazakhstan.
- Steppes of Mongolia, Korea and China.
- Central Asia and Altai.
The domestication of wild hamsters occurred in the 20th century. People fell in love with tiny pets, thanks to which the dwarfs spread throughout Eurasia. They can be found much less often in America.
Colors of Djungarian hamsters
Domesticated rodents, as a result of selection, have acquired a variety of colors, the features of which are a dark stripe and interspersed with light spots on the back, an almost white abdomen and paws. There are main types of colors of Djungarian hamsters.
Standard
The standard color resembles nature. In the wild, it helps animals camouflage against the background of sand and steppe plants. The standard calls for brownish-gray fur on the back and a dark or black stripe from head to tail. The abdomen and paws are white or light gray.
The standard color of the Djungarian hamster is natural.
Albino
Albinos have white fur and pink skin. They have red or pink eyes.
Sapphire
This coloration is characterized by a gray-blue back and a much lighter, to white, belly and paws.
The sapphire-colored hamster has a characteristic gray-blue back.
Pearl
Pearl hamsters have matte white fur with gray patches. Among them there are individuals with a uniform milky color without a stripe on the back.
Mandarin
It is a red color with a brown stripe on the back, with lighter legs and belly.
Mandarin is a red color with light legs and belly.
Features of white color
White dzhungarikas are no different from their relatives, except for their pearl coloring. Often there is no stripe at all on the back of these hamsters. In such cases, the animal is completely dull and milky. Pearly white hamsters are bred by breeders and are loved by breeders.
Albinos, due to a gene mutation, lack the pigment melanin, which is responsible for the color of their skin and coat. Their eyes are red because, in the absence of pigment, the blood vessels in the cornea become clearly visible. The lack of melanin negatively affects the health of hamsters.
The main problems of albinos:
- Skin diseases: lichen, dermatophytosis, tumors and papillomas.
- Vision problems: long-term exposure to sunlight on unprotected eyes can lead to blindness of the animal.
- Lack of melanin: reduces stress resistance of albinos.
The pet must be protected from contact with sunlight.
The cage with a special pet should be placed in a shaded place, protecting the animal as much as possible from contact with direct sunlight.
Communication
Djungarians have an independent character and are not too eager to communicate. To wean the animal from biting and fearlessly picking it up, it will have to be patiently tamed day after day. It will not be possible to raise a hamster once and for the rest of its life: if you do not have contact with it for 1-2 weeks, the pet will run wild again, and hand training begins all over again.
Keeping an animal with a nocturnal lifestyle means not disturbing it during daytime sleep, being content with communicating and observing it in the evening hours. You will have to endure noise at night: the hamster will run in a wheel, chew the bars of the cage and toys, dig for litter, rustle with paper in the house.
Taking care of dzhungarikas is not difficult; the chores even become pleasant for the owner, who is sincerely attached to his pet. Its cute habits and appearance make this variety of dwarf hamster the most common pet. With proper care, the animal will live 2 years or more. Although this period seems sadly short for humans, in captivity hamsters live much longer than their wild counterparts.
If you are considering a Djungarian hamster as your pet, then before making a choice, we recommend that you also get to know the Syrian hamster. The Syrian hamster is almost as popular as the dwarf hamster, but differs significantly from its brother.
>Sungur hamsters.
Lifestyle of Djungarian hamsters
Adult Djungarians prefer to live alone. They are characterized by territorial division.
Hamsters' burrows are spacious, up to 1 m deep, with many branches and chambers. Separate rooms are equipped for sleeping, storing supplies, and toilets.
Hamsters sleep during the day and forage for food at dusk and at night.
The basis of the diet is:
- seeds, grains, leaves and roots of plants;
- small insects and worms;
- young shoots, berries and vegetables.
A hamster can walk several kilometers in search of food, and stores about 20 kg of food for the winter. Djungarians carry food in subcutaneous bags on the sides of the body.
Adult dwarfs live alone.
This species of the hamster family does not hibernate. In winter, the coat color becomes lighter and blends into the snowy landscape. By cold weather, the hamster's body acquires subcutaneous fat.
If the cold continues for a long time down to -10 °C or the animal experiences stress, then it falls into torpor, a state close to death when the body temperature drops to +20 °C. This is how hamsters minimize energy expenditure and survive.
Rodent character
Djungarian hamsters are militant introverts. They are sensitive to the protection of personal space. These cute rodents fiercely fight the enemy if he encroaches on their territory. They use teeth and claws, causing terrible wounds. Male Djungarians warn their relatives about the invasion of aliens with sharp sounds, standing on their hind legs.
Domesticated animals also like to live alone. Hamsters quickly get used to people, they willingly allow themselves to be picked up, they like gentle stroking and calm speech. They are inquisitive and nimble. If you make sudden movements and make frightening sounds, the hamster may scratch and bite.
Reproduction of dzhungariks
Physically, Djungarian hamsters are capable of breeding already at the age of 4-5 weeks, as soon as the females begin to estrus. But if you plan to breed pets at home, you should not breed before 4-5 months of age. A pregnant female bears offspring for 18-22 days and gives birth to 4-6 Djungarian babies.
The mother feeds the offspring with milk for up to a month, then they are completely independent. The female is ready for a new pregnancy within a day after giving birth (at home, do not breed more often than once every 2-3 months).
In queue! The mother is not rubber.
Have you decided to get a dzhungarika?
If you decide to get a Djungarian animal or you already have a pet, be sure to read about the rules for caring for a Djungarian animal here.
Briefly about caring for dzhungarika
In the wild, hamsters of this species live on average 1 year. If you follow simple rules for keeping dwarfs, their life expectancy in captivity can be on average 2 years, sometimes 3 and very rarely 4 years.
Selecting a cage and accessories
When choosing a cage, you should consider that:
- its area should not be less than 30x50 cm: the hamster needs enough space for an active life;
- high cages are dangerous for hamsters: the animals love to climb the bars, and falling from a height often leads to injury and death;
- It is not advisable to buy a multi-tiered cage with complex staircase structures: for Dzungarians such a home is dangerous for injury.
The hamster cage should have a large area.
The bottom of the cage is lined with special filler from a pet store. You can use sawdust from fruit trees and finely torn paper napkins and towels as available materials.
Pieces of fabric, cotton wool and hay should not be allowed to get into the cage.
The main accessories for arranging the cage are a running wheel and a rest house. The size of the wheel should be at least 18 cm in diameter to prevent curvature of the hamster's spine during running. It’s better to buy a house without windows - animals often get stuck in them.
Nutrition and diet
The basis of nutrition for domestic hamsters is balanced dry food from a pet store. As wet additives, you can offer your pet lettuce, parsley, cucumbers, and zucchini. If you are deficient in protein, lean pieces of boiled chicken help well.
Vegetables and fruits containing a lot of sugar are contraindicated for hamsters due to their predisposition to diabetes. Also, you should not treat your hamster to insects from the street, so as not to infect him with parasites.
The domestic hamster eats balanced dry food.
There should always be enough fresh water in a special drinking bowl. You cannot put a bowl of water in the cage. A wet hamster may get sick.
Necessary socializing and play time
Evening is the best time to communicate with pets. During the day you should not disturb hamsters - this is a time for rest and recuperation. Half an hour is enough to pamper your pet in your hands, clean the cage, and change the water. Then all that remains is to observe the behavior of the dwarf in the active phase of the day.
Number of individuals in one cell
Only one individual will live comfortably in one cage. If you house at least two, then both hamsters will constantly experience stress and fight, which will negatively affect their health and life expectancy.
The female is placed with the male only for mating, after which she goes to her cage.
Health and hygiene
A healthy hamster looks beautiful, behaves actively, communicates willingly, and has a good appetite.
There are not many conditions sufficient to keep a pet in good shape:
- fresh food and water;
- conditions for sufficient physical activity;
- purity;
- sole ownership of the cage;
- absence of sharp and loud sounds;
- location of the cage out of direct sunlight.
Djungarians clean themselves using their paws and tongue. You can pour fine sand from a pet store into a separate container. In such a “bath” hamsters love to tumble for a long time. The procedure helps them clean the body more thoroughly.
LiveInternetLiveInternet
There are many funny animals in the world, watching which brings an involuntary smile and even children's delight. Dwarf hamsters can easily be considered one of these wonderful animals.
Dwarf hamsters are very small, nimble animals that are often mistaken for mice in pet stores. Indeed, small beady eyes, gray antennae and brownish coloring make dwarf hamsters look like mice.
Of course, a normal hamster can reach more than 20 cm in length. Dwarf hamsters reach no more than 10 cm in length. It seems that the maintenance and care of both dwarf and regular hamsters will be the same, but in fact this is not the case. Dwarf hamsters, due to their small height and weight, require a slightly different approach.
All dwarf hamsters are much more active than their regular counterparts. Most pet dwarf hamsters are normal colored, just like in nature. Gray-brown back, light gray belly and dark longitudinal stripe on the back. This is what Djungarian and Campbell's hamsters look like, and it is very difficult to determine the species if the hamster is of normal color without the appropriate experience.
The most popular representative of dwarf hamsters is the Djungarian hamster or, as it is also called, Djungarian, and scientifically - Phodopus sungorus. The gray color, black stripe on the back and small stature of the hamster are very popular with many rodent lovers. But in addition, there are other breeds of dwarf hamsters. So, Taylor's dwarf hamsters
very similar to gray mice.
dwarf hamster
has a brownish coat.
And the Roborovsky hamster
has sandy-golden hair on its back and head, and white on its belly. All these hamsters reach a length of 4.5 to 5.5 cm. And they weigh no more than 50 g.
The Djungarian hamster captivates with its surprisingly cute appearance of a fluffy, good-natured hulk. The muzzle is pointed, the ears are small, the back is brownish-gray or ocher-gray, sometimes darker on the sides, the belly is light, the border between the color of the back and belly is clearly expressed. The soles of the paws are covered with thick hairs that hide the digital tubercles. A narrow black stripe runs along the ridge, the paws are white, the ears are blackish, white on the inside. In summer, these animals are grayish. Their fur changes color at prolonged temperatures below 16 degrees. Celsius. In this case, the wool becomes lighter in places. In winter, especially when kept in cool rooms, the hamster becomes almost white, with a silver-gray ridge. Two types of Djungarian hamsters have been bred: with light gray fur (sapphire) and a variant with snow-white fur. In the second case, hamsters were even obtained almost completely without stripes on the back and sides.
Djungarian hamsters are active at dusk and at night. The burrows have several entrances, holes and a nesting chamber. The basis of nutrition consists of seeds and green parts of plants, as well as insects. The animal prepares reserves of seeds for the winter. Does not hibernate. Apparently, often in winter, it comes out of the hole outside, since in places with snow cover the animals turn almost completely white by November-December.
From March to September, the female brings 6-8 (sometimes up to 12) cubs 3-4 times. The offspring of the Djungarian hamster quickly matures, and young ones from the first brood can reproduce in the first year of life, at the age of about 4 months.
These animals are very pleasant and live well in captivity. Of all the dwarf hamsters, the Djungarian hamster (Phodopus sungorus) is the most suitable for domestication. He is not as biting as Campbell's hamster, and not as nervous as Roborovsky's hamster. But still, like all dwarf hamsters, he is more suitable as an object for observation. Even animals that are not used to being handled hardly bite.
The animals are well tamed and reproduce at home. When kept on sawdust (a layer of sawdust about 3 cm) and at least weekly cleaning, there is no smell from them. Djungarian hamsters can be kept in a cage, the base of which measures at least 30x70 cm. Sometimes smaller cages are available for sale. They are not suitable for long-term keeping of hamsters. Like all types of hamsters, Djungarian hamsters have a pronounced desire for movement, the absence of which can lead to disturbances in behavior and health. The Djungarian hamster (like all other hamsters) loves to run long distances, along which there is a lot of interesting things to do.
The manner of stuffing the cheek pouches and storing food, as well as using the front paws as hands, is similar to the golden hamster. But Djungarian hamsters are much livelier and more active. It is not recommended to let these small crepuscular animals into the room: the risk that they will run wild, get lost, or be crushed is too great.
To breed "jungarians" it is better to keep them in pairs, accustoming them to each other, preferably from an early age. The animals become sexually mature at 18-23 days, but young females should be mated no earlier than three months of age. The gestation period is 16-20 days. The cubs develop fur on the fifth day after birth, and by the tenth day it is already well developed. The eyes open at the age of 10 days. Twenty-day olds can already be separated from their parents. It happened that the second litter appeared when the babies of the previous one were still with their parents. This did not affect their cultivation. When the expanded family remained unseated until the appearance of the third litter, the newborns were apparently eaten by the grown animals from the first litter. Usually the number of cubs in a litter is 4-6, less often up to 9. Life expectancy is usually 2-3 years, in rare cases it reaches 4. Tiny fidgets seem to be created to give joy and are able to significantly improve the mood of their adult and little owners.
Hamsters do not like noise and loud, sharp sounds. They have very acute hearing. Their vision is poor, they see better in soft, dim light, not more than four steps away. Hamsters recognize objects by smell. The hamster's sense of touch is its whiskers, with the help of which it can determine the distance to objects or the width of a hole - whether it can crawl through or not. The hamster washes itself quickly and vigorously. First, he licks the front paws several times with his tongue and then wipes the wet face and entire body. Where the hamster cannot reach with its front paws, it washes itself with its hind paws. The fur is combed with claws. Keeps the fur clean and tidy, because neat fur is warmer than tangled and disheveled fur. Hamsters build their bed depending on the ambient temperature. If the hamster is cold, he collects the bedding in a pile and buries himself in it. If he is hot, he scatters the bedding.
If the hamster is very frightened, he freezes in place or begins to quickly wash himself. A frightened hamster may rush from side to side, pressing its belly to the ground and lifting its tail up, or stand on its hind legs and bare its teeth. When a hamster hears or sees something interesting, it will raise its front paw or stand on its hind legs, ready to explore what caught its attention. He listens intently and sniffs the air. If a hamster chews on its cage, it means it is bored and wants to go out for a walk around the apartment. Or he simply grinds his teeth down so they don’t grow too long.
An X hamster living at home eats dry food, which is sold in pet stores. This is a mixture of various seeds and grains, which is exactly the diet of hamsters in the wild. Hamsters can also be fed fresh fruits and vegetables: tomatoes, cucumbers, carrots, melon, grapes, apples, cabbage. But do not give your hamster a lot of fresh fruits and vegetables, otherwise he will get a stomach ache. 10 - 20 grams of fresh food will be enough for him.
Remove everything he hasn't eaten - fresh food spoils quickly. A hamster needs one teaspoon of milk or yogurt per day. Your hamster needs fresh water every day. Don't worry if he doesn't drink enough, he'll get the water he needs from vegetables and fruits. Mineral vitamins are sold in pet stores for older hamsters. Never give your hamster onions, garlic, oranges and other citrus fruits, sweets, chocolate, salted nuts and cucumbers, or any spicy food.
When buying a hamster for a child, immediately warn him that he should not pick up the new resident in the first days, let him be patient, offering treats from his palm. Do not leave the hamster unattended outside the cage, otherwise he may get lost. Let the child choose a name for the animal, call out to him affectionately, and bring him a treat. Teach your child to love and care for a pet, and the furry will reward you with devotion and affection. A tamed hamster loves to be picked up, stroked, and can fall asleep in the palm of your hand.