Modern meat rabbit breeding is unthinkable without the use of special mixtures consisting of grain, grass granules and special additives. Compound feed for rabbits allows you to provide them with all the elements they need: nutrients, vitamins, microelements. For animals at different periods of life (pregnancy, fattening, resting state) there are different compositions of mixtures.
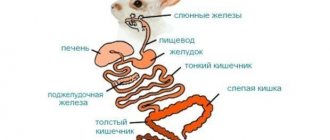
Features of digestion in rabbits
Proper feeding of rabbits is impossible without knowledge of the peculiarities of their digestion. Rabbits have a fairly developed gastrointestinal tract, the length of which is 9-10 times greater than the length of the body. Moreover, only the thin section has a length of 3-4 m. Rabbits have a well-developed cecum, and its volume is 7-8 times larger than the stomach.
Digestion of nutrients in rabbits begins in the oral cavity, where the food is mechanically ground and moistened with saliva containing the enzyme diastase. Under its action, the starch of the feed turns into sugar. From the mouth, food enters the stomach. In it, under the action of the enzyme pepsin and hydrochloric acid, feed proteins are broken down into albumoses and peptones. It should be noted that the enzymatic activity of gastric juice in rabbits is significantly higher than in other herbivorous domestic animals.
From the stomach, the food mass is pushed into the duodenum, where further digestion of nutrients occurs. Under the influence of pancreatic enzymes, intestinal juice and bile, all nutrients in the feed are broken down - proteins, fats and carbohydrates. In the small intestine, breakdown occurs to amino acids, monosaccharides, glycerol, and fatty acids. Then they are absorbed into the blood and distributed throughout the body. Water and microelements are also absorbed in the small intestine. The digestion of food nutrients is completed in the large intestine (cecum, colon and rectum). In the cecum of rabbits, the digestion of nutrients ends, and fiber is also fermented.
The digestion of rabbits differs from other domestic animals by the presence of the act of coprophagy - eating their own soft feces. As a result, the rabbit’s body receives some of the nutrients that were not absorbed during their passage through the gastrointestinal tract. This feature is an important biological adaptation of the species to the harsh environmental conditions in which rabbits were before domestication (severe frosty winters, dry summers, etc.). However, the large intestine in rabbits is underdeveloped, so they do not effectively use high-fiber feeds.
How to make compound feed with your own hands
If you want to cook food for rabbits at home, you need to purchase machines and devices that automate the process. Without them, the mixtures are not homogeneous enough, so it will be more difficult to achieve the optimal ratio of ingredients.
The costs will pay off quickly enough, and the pet owner will be able to independently regulate the quality of the mixtures. It is impossible not to take into account that those who decide to make home production save time and money on transporting bags, and the time spent on servicing pets is also reduced.
Equipment needed to make compound feed with your own hands:
- Scales (error – 0.1 g). They help determine the exact dosage of ingredients included in feed mixtures for rabbits.
- A trimmer or a device similar in operating principle, thanks to which you can process plant materials.
- Industrial crusher for grain. Purpose – bringing grain to a fine structure and grinding all ingredients.
- Mixer. A device that ensures the homogeneity of the grain mixture and the required degree of nutritional value.
- Granulator (meat grinder). Processes loaded components to prepare both loose and pelleted feed. In the second case, the ingredients are pre-moistened before granulation.
- Dryer. Eliminates excess moisture from hot mixtures and helps avoid excessive steaming of components when creating mixed feed.
Raw materials that appear to be spoiled should not be placed into equipment. It is enough to soak one component with a flaw for the work to go down the drain. Experts advise producing dry feed in quantities that will last for the next month. Otherwise, a fungus may develop, causing poisoning of animals with a fatal outcome.
Rabbit food
To properly feed rabbits, you need to know the nutritional value of feed and its digestibility. Here it is also necessary to take into account that the digestibility of feed depends on its quality and the physiological state of the animals. In livestock farming practice, all feed is conventionally divided into four groups: coarse, juicy, green and concentrated. In addition, mineral and vitamin supplements and industrial waste (dry pulp, cakes, meal) are used in rabbit farming.
Green food is the main food for rabbits in the summer, both when kept in cages and when kept in shad. In terms of biological value, green feed has no equal, as it contains the entire range of essential nutrients. Chlorophyll from green feed also takes part in hematopoietic processes. Such feeds differ greatly in chemical composition and nutritional value, and contain 60-80% or more moisture. The dry matter of green mass, mowed in the optimal phase of the growing season, is close in nutritional value to concentrated feed, but its biological value is significantly higher. On average, the dry matter of such green feeds includes 20-25% digestible protein, 10-15% fiber, 4-5% fat, 30-60% nitrogen-free extractives and 9-11% minerals.
Of the sown grasses, the most valuable food for rabbits are legumes (clover, alfalfa, sainfoin, peas, vetch-oat and vetch-pea mixtures). Rabbits are also good at eating cereal plants (winter wheat, rye, oats, corn) that are mowed before the heading stage. The green conveyor is designed in such a way that during the spring-summer and autumn periods of the year, green feed is constantly supplied to the rabbit farm in the required quantity.
Succulent feeds (root tubers, melons and silage) with a combined type of feeding rabbits in terms of nutritional value occupy up to 30-50% of the diet in the late autumn, winter and spring periods of the year. Among them, rabbits are fed carrots, potatoes, sugar beets, turnips, rutabaga, and melons - zucchini, pumpkin, and watermelons. Root tubers contain a lot of water and little protein, minerals, fat and fiber. The dry matter of these feeds consists of easily digestible carbohydrates, mainly sugar.
The best succulent food for rabbits is red carrots, 1 kg of which contains up to 250 mg of carotene, 0.62 g of calcium and 0.5 g of phosphorus. Sugar beet tops are unsuitable for feeding rabbits because they contain a number of organic acids (oxalic, malic, etc.). They can cause digestive disorders in rabbits, especially young ones. Potatoes are usually given to rabbits steamed, but the water must be drained to prevent solanine poisoning. Silage is fed to rabbits only of the highest quality, without signs of mold.
Among the roughage for feeding rabbits, hay is used, which is an important source of protein, vitamins and minerals. Small-stemmed, leafy hay from forbs collected at optimal times during the growing season contains 15-18% water, 8-9% digestible protein, 1-2.5% fat, 40% nitrogen-free extractives and 25-28% fiber. Straw, both cereals and legumes, are not used to feed rabbits.
The above-mentioned feeds (green, rough and juicy) form the basis of diets, but do not provide high growth rates for rabbits, because there is an insufficient amount of energy and nutrients per unit of their natural mass. In this regard, it is impossible to properly balance the diets of rabbits without concentrated feed . The level of use of this type of feed in the technological process directly determines the intensity of the rabbit breeding industry. Depending on the chemical composition, grain concentrates are divided into two types - carbohydrate and protein. Carbohydrate concentrates include cereal grains (oats, barley, corn), protein concentrates include legume grain feeds (vetch, soybeans), as well as cakes, meal and bran, animal feed, and feed yeast. Grass meal is of great importance in feeding rabbits, especially when switching rabbit farming to dry feeding. Herbal meal contains 10-12% water, 17-20% digestible protein, 2-3% fat, 35-40% nitrogen-free extractives and 20-22% fiber.
As part of animal feed for feeding rabbits, dry skimmed skim milk, meat and bone meal and fish meal are used. The main feature of animal feed is that it contains no fiber at all. They consist mainly of protein, a small amount of fat, sugar (in milk) and minerals. It is advisable to introduce such feeds into the diets of nursery and suckling females, replacement and fattening young animals. Feeder yeast contains biologically complete protein, a complex of vitamins B, and, when exposed to ultraviolet irradiation, vitamin D.
A special place in the group of concentrated feeds is occupied by compound feeds, the components of which include ground or crushed grain of cereals and legumes, animal feed, grass flour, industrial waste (cakes, meal, etc.), as well as vitamins. mineral premixes.
Formulated feed recipes for rabbits are developed based on data on the rationing of their feeding depending on the physiological state, age and type of feeding.
What is feed made from?
Main components included:
- grain of wheat, barley, oats, corn;
- sunflower cake;
- legume grains: beans, peas, soybeans, lupine;
- oilseed grains: sunflower, rapeseed, rapeseed;
- roughage as a source of fiber;
- bran;
- bone flour;
- mineral, vitamin supplements, biostimulants.
In addition, to improve digestion, high-quality industrially produced feed includes:
You may be interested in: Industrial cages for rabbits at home: drawings How to make drinking bowls for rabbits with your own hands Cages for rabbits with your own hands: photos, original ideas
- acetic, ascorbic, benzoic and sorbic acids;
- ammonium hydroxide as a mold inhibitor;
- beet pulp – sugar production waste;
- source of calcium – limestone or calcium carbonate;
- source of protein – rapeseed flour, made from rapeseed after pressing the oil;
- B4 or choline chloride;
- preservative – citric acid. The use of citric acid helps to enhance growth and increase immunity in animals;
- flavoring additive – corn gluten;
- magnesium oxide;
- binding component and source of magnesium – black or cane molasses;
- source of phosphorus – monosodium phosphate;
- papaya to improve digestion;
- soybean hulls as a source of fiber;
- safflower flour as a source of protein;
- rosemary extract – a perfect natural antioxidant;
- safflower oil to improve taste;
- soybean meal is a source of protein;
- yucca to normalize the animal's gastrointestinal tract.
Energy requirement
The energy requirement of rabbits, per unit of live weight, in comparison with other domestic animals, is significantly higher. When rationing the feeding of rabbits using a factorial method, energy costs for maintaining life and energy costs associated with various physiological states (lactation, pregnancy, growth, development, etc.) are distinguished. For example, during the mating period, the diet of males in terms of energy indicators must be increased, in comparison with the supporting feeding background, by 40%. The diets of females at the beginning of pregnancy according to this indicator are increased by 30%, and in the second half they are increased to two norms of maintenance energy. During lactation, the need for energy increases sharply. During 2, 3-4, 5-6, 7-8 weeks of lactation, the rabbits’ energy requirement is respectively 200, 300, 400 and 600% of the maintenance level of the diet.
According to foreign experts, the norm of maintenance energy for adult rabbits with a live weight of 3 kg is 280 kcal (1.15 MJ), 3.5 kg - 320 kcal (1.32 MJ), 4 kg - 350 kcal (1.44 MJ), 4.5 kg – 380 kcal (1.56 MJ). At the same time, 100 g of feed for adult rabbits should contain at least 250 kcal (1.05 MJ), but not more than 270 kcal (1.13 MJ) of metabolic energy, and for young animals - accordingly, at least 280 kcal (1.17 MJ) ), but not more than 320 kcal (1.34 MJ).
Production of feed at home
Self-preparing mixed feed will not only save the annual costs of purchasing ready-made feed, but will also allow you to control the quality of the components of the diet. To start home production, you will need a machine called an extruder. With its help, the feed takes the form of granules. This occurs due to heat treatment and compression of the ingredients poured into the unit. Thanks to different attachments, you can get feed of different diameters. Larger pellets are used for large livestock. For rabbits, smaller feed is usually made.
Extruder
Feed granulator prices
Feed granulator
What you need to make feed at home
In order to mechanize the work of preparing mixed feed as much as possible, some costs will be required. However, they will pay for themselves very quickly if you prepare feed not only for yourself, but also for sale. The production of concentrated feed requires the following equipment:
- A brushcutter can easily help you make hay even on an industrial scale.
- A hay dryer allows you to reduce the time spent waiting for results. During the process of turning grass into hay, the product may not dry well due to rain and adverse weather conditions. The dryer reduces risks to a minimum.
- A hay chopper helps quickly achieve the ingredients needed for the mixture.
- A grain crusher grinds coarse ingredients into flour or a homogeneous product.
- An oil press is necessary for grinding seeds. It can also be used to obtain oil. The purchase of such a unit is important, but not mandatory in the first stages of home production.
- The extruder turns the products, crushed to dust, into compressed granules. This process is necessary because crushed feed into dust can clog the animals' lungs and lead to the death of rabbits.
Harvesting grass using a brush cutter
Solar dryer for hay and fodder grass
Protein requirement
During the period of sexual quiescence, adult rabbits need about 12% of digestible protein in the dry matter of their diets. Replacement young stock also have a similar need for digestible protein. For females during lactation, males during mating, and young animals for fattening, protein nutrition standards are increased by 30-35%.
When rationing protein for rabbits, special attention must be paid to their amino acid nutrition. The role of amino acids in rabbit nutrition is very important. Lysine is used for the synthesis of tissue proteins. Arginine promotes the synthesis of urea and takes part in the formation of sperm, muscle creatinine, and insulin. Histidine is needed for the formation of hemoglobin and red blood cells. Tyrosine – for the formation of thyroxine and adrenaline. Cystine activates insulin and methionine and takes part in fat metabolism processes. Tryptophan – in the renewal of blood plasma proteins. In the body of rabbits, essential amino acids are not synthesized, and therefore, for normal life, animals must receive them with food. This applies to the greatest extent to rabbits raised for meat.
What foods are toxic?
Although rabbits are herbivores, there are greens that are dangerous to their health and life. The most dangerous and toxic:
- Celandine and wild radish. Lead to bloating, colic, and diarrhea. Death is possible, especially from celandine.
- Foxglove and milestones. Cause severe disorders of the cardiovascular system.
- Hemlock and dog parsley. They have a detrimental effect on the nervous system.
- Larkspur. Leads to disruption of the respiratory, nervous, cardiovascular and gastrointestinal systems of the animal.
The following can have a very negative effect on a rabbit's health:
- lily of the valley;
- milkweed;
- belladonna;
- Datura;
- hellebores.
Among the trees that are poisonous to rabbits are the branches of bird cherry, apricot, wild rosemary, elderberry, buckthorn, and wolf's bast.
Carbohydrate needs
Carbohydrates are divided into two groups: fiber and nitrogen-free extractives (NFEs). In this case, fiber includes cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin, and non-fuel materials include sugar, starch, part of hemicelluloses, organic acids, etc. These easily digestible carbohydrates (especially sugar and starch) are sources of energy and play an important role in regulating metabolism in rabbits. When they are deficient in rabbits’ diets, protein-fat metabolism is disrupted, and acidosis occurs due to an increase in the level of ketone bodies in the blood and a decrease in its reserve alkalinity.
Fiber is the main source of indigestible organic matter. Both low and high levels of its content in the dry matter of rabbit feeds negatively affect the nutritional value of diets. At a low content (<6%), rabbits experience gastrointestinal upset, and at a high content (>20%), the level of digestibility of the main nutrients of feed sharply decreases. Experts believe that the optimal level of fiber in the diets of females is 12-15% of the dry matter of feed, and in the diets of young animals for fattening - 8-10%.
Determining the usefulness of purchased feed
Before purchasing feed, you must carefully study the label attached to it. The packaging must indicate what components the concentrate consists of, as well as the percentage of nutrients. In veterinary medicine, the following nutritional standards have been adopted for adult rabbits:
- raw fiber: more than 18%;
- indigestible elements: more than 12.5%;
- crude protein: 10 to 16%;
- fat: from 1 to 4%;
- calcium: from 0.6 to 1%;
- phosphorus: from 0.4 to 0.8%.
Food should contain vitamins:
- vitamin A: from 6,000 to 10,000 IU per kilogram;
- vitamin D: from 800 to 1200 IU per kilogram;
- vitamin E: from 40 to 70 mg per kilogram;
- trace elements: magnesium 0.3%, zinc 0.5%, potassium 0.6%.
Dr. Dana Krempels recommends the following ratio:
- fiber at least 22%;
- protein no more than 14%;
- fat 1%;
- calcium 1%.
On a note!
Young rabbits require food high in protein and fat.
Finding a feed composition that satisfies all the requirements is quite problematic, so when purchasing, pay attention to the most important factors. For an obese animal, the best choice would be a feed with a high amount of fiber and a reduced amount of fat, for an animal suffering from kidney problems - with a minimal amount of calcium.
Fat requirement
In adult rabbits and young animals, the standard requirement for fat is almost completely satisfied by its intake with food. Rabbit milk has a very high fat content (15-18%), which is 4-4.5 times higher than the fat content of cow's milk. In this regard, it is necessary to control the fat content in the diets of rabbits, especially young animals reared at an early age. It has been established that young rabbits develop poorly if the dry matter of the diet contains less than 5% crude fat.
Tips and tricks
Some rabbit breeders claim that rabbits should have plenty of food for up to six months. However, the nutrition of ornamental breeds will be somewhat different from animals in natural conditions. Pets are virtually stress-free and activity-free. This means that their metabolic processes are much slower. Therefore, food in unlimited quantities is the main cause of obesity.
To organize proper nutrition for domestic rabbits, it is recommended to adhere to a number of rules:
- In the morning add 2 tbsp. l. feed mixture. If by evening the bowl is empty, you need to add the same amount.
- If the morning portion remains by the evening, you can slightly adjust your diet. Give 1 spoon of feed in the morning, and 3 in the evening.
- It is not recommended to increase the feed rate. Its constant excess negatively affects the condition of the body.
- The basis of a rabbit's diet is hay. It must be available all the time. Such food promotes proper digestion.
- For older rabbits, feed mixtures can be given once a day (4–5 tbsp.) By evening, the animals usually eat everything. Hay is added to the feeder regularly.
Proper and balanced feeding is the key to the health of pets. Errors in diet planning have a negative impact on the functioning of the body. Rabbits themselves are susceptible to obesity, indigestion and other gastrointestinal problems. Dietary recommendations are aimed at preventing them.
Requirement for minerals
Minerals play an important role in all metabolic processes in the body of rabbits. Females excrete a significant amount of them in milk. In particular, calcium - 1.32 g, magnesium - 0.7 g, phosphorus - 0.9 g, potassium - 0.43 g and sodium - 0.3 g per day. It should be taken into account that lactating rabbits produce twice as much milk per unit of live weight as cows and goats. As a rule, in feeding rabbits, the mineral saturation of the dry matter of feed is usually able to meet the needs of animals (with the exception of table salt). However, depending on the characteristics of the soil conditions of certain geochemical zones in which forage plants grow, a deficiency of mineral elements often occurs, which must be compensated in the diet. That is why, in feeding rabbits, as well as other species of animals, the correct determination of the chemical composition of feed is of great importance. It is better when such a determination is carried out on each individual feed sample in a laboratory setting.
Calcium and phosphorus are the main minerals in the body of rabbits, which account for 65-70% of the mass of feed ash. Calcium here is the main material for the formation of bone tissue. It is also part of the body's cells. Calcium metabolism is closely related to the functions of the endocrine glands. With its deficiency, the development of embryos, clouding of the crystals of the eyes, tetany, and osteomalacia are disrupted. These phenomena can be prevented by daily calcium supplementation at a level of 30-60 mg. Feeds rich in calcium include clover, alfalfa, vetch, as well as animal feed - meat and bone meal and fish meal. Phosphorus also forms the basis of bone tissue in rabbits. There is quite a lot of phosphorus in glandular tissues, muscles, nervous tissue, and phosphoric acid takes part in the metabolism of carbohydrates and fats. Lack of phosphorus in the body of rabbits leads to rickets, osteomalacia and other problems. Its optimal level in the dry matter of the rabbit diet is 0.144-0.164%. A lot of phosphorus is contained in bran and cakes.
Iron and copper . A special feature of rabbit milk is the almost complete absence of iron in its composition. There is a reserve of iron in the liver of newborn rabbits, but it decreases very quickly over time. Therefore, during the suckling period, rabbits may already be in an anemic state. The normal level of hemoglobin in the baby rabbit’s body is restored by daily feeding 2 mg of iron and 0.2 mg of copper. A lack of copper in the diets of rabbits is accompanied by hair loss, peeling skin and growth retardation. Feeds rich in iron and copper include meat and bone meal and blood meal.
Potassium and magnesium . Insufficient amount (0.3% or less) of potassium in the diet of rabbits is the cause of muscular dystrophy. The norm of potassium content in diets, which ensures intensive growth of rabbits, is 0.6-0.9% of the dry matter of the feed. At the same time, with a low (less than 30 mg per 100 g of feed) level of magnesium in diets, growth retardation, convulsions and death of rabbits occur. A preventative measure for magnesium deficiency can be the administration of 30-40 mg of this element as part of magnesium sulfate.
Manganese and sulfur . It is believed that 1 mg of manganese provides the daily requirement for rabbits, and 8 mg is already a toxic dose. Rabbits can use inorganic sulfur from sulfates.
Cobalt and iodine . The need of rabbits for iodine is ensured by its intake with food; however, this statement requires mandatory verification taking into account the geochemical zone where feed crops grow. Cobalt is found in willow and aspen leaves, legumes (clover, alfalfa, vetch) and root vegetables.
Salt . Table salt, which is part of the blood, cells and tissues of their body, is of great importance for the normal functioning of the body of rabbits. A lack of salt in diets causes loss of body water, a decrease in the growth energy of animals and their milk production, as well as the efficiency of feed use. In the practice of rabbit breeding, it is accepted that young animals need 0.5 g of table salt per day, adult rabbits - 1-1.5 g, and females during pregnancy - 1.5-2.0 g. Complete granulated food for rabbits contains salt. include in the amount of 0.5-1.0%.
Self-production of feed
A prerequisite for this is the presence of a grain crusher. For complete mixing, all components must be ground to a homogeneous mass. To mix small volumes, you can use an electric drill with an attachment; for continuous feed production, it is easier to purchase a concrete mixer.
Full ration food recipe
- In a grain crusher, grain is ground into flour. 20% barley, 10% wheat, 10% corn, 5.5% soybeans are poured into the container.
- Add 40% of the volume of the container of chopped hay to the resulting mixture.
- Next, the sunflower cake is finely crushed and added in the amount of 10% of the volume.
- The total mass is filled with 2% feed yeast, 0.3% salt, 2.2% meat and bone meal.
The mixture is thoroughly mixed.
Need for vitamins
Vitamin A is essential for normal growth, development and reproduction in rabbits. A lack of this vitamin in the body leads to a decrease in its resistance to diseases. At the same time, diseases of the eyes, skin, and respiratory tract develop, the fertility of females and the viability of offspring decreases. In summer, the main source of this vitamin in rabbits' diets is green food, and in winter - roughage and succulent food. Young animals receive vitamin A mainly from rabbits' milk. Green grass, carrots, cabbage leaves and grass meal are especially rich in vitamin A. In spring, the reserves of vitamin A in the body of rabbits sharply decrease, which may be the cause of A-vitaminosis. During this period, it is advisable to introduce high-quality bean hay, carrots, grass or hay flour into the diet.
Vitamin D is contained in feed in small quantities. Its active form (calciferol - vitamin D3) is already synthesized in the body of rabbits under the influence of the ultraviolet spectrum. The main function of this vitamin is to regulate the metabolism of calcium and phosphorus, and its insufficient amount leads to rickets in young rabbits and osteomalacia in adults. Most often, short-haired rabbits - rexes, as well as young animals of all breeds from numerous and late litters - suffer from rickets. As a rule, when rabbits are kept in open cages, there is no need for additional feeding of this vitamin, however, with intensive rabbit breeding (indoors), vitamin D in the diet should be in quantities of 20-25 IU per 1 kg of live weight.
Vitamin E is also called the reproduction vitamin. Its insufficient amount in the diets of rabbits negatively affects spermatogenesis and the process of fertilization of females, leading to the death and resorption of embryos. Vitamin E deficiency in rabbit diets causes muscular dystrophy and myocarditis (heart disease). Experts believe that the introduction of 0.2-0.5 mg of tocopherol per 1 kg of live weight into feed eliminates the consequences of E-vitaminosis.
Vitamins C and K. Unlike other animal species, rabbits do not require significant amounts of vitamin C in their diets for normal development. Research has found that rabbits grow normally on diets that cause scurvy in guinea pigs. A lack of vitamin K in rabbit feeds can lead to abortion, but the need for it is usually met through natural content in the feed.
B vitamins are synthesized in the body of rabbits. There are quite a lot of them in the soft feces eaten by rabbits (coprophagia). A number of experiments have established that adding 0.1-0.3 mg of nicotinic acid (vitamin B3) to the basic diet increases the growth rate of young rabbits. The need for choline (vitamin B4) for them is approximately 0.13% of the dry matter of the diet. Adult rabbits without satisfying their need for choline quickly lose weight and die from liver degeneration (cirrhosis) and muscular dystrophy.
Types of feed
The industry produces two types of combined feeds for rabbits:
- PC – fully rationed feed. Their composition fully satisfies all the needs of the animal body for nutrients, vitamins and microelements. When using this feed there is no need for additional feeding.
- Concentrated feeds are sold under the designation K or KK. This feed supplements the basic diet of animals with protein, fiber and minerals.
Different feed options are available for different ages of animals:
- for fattening young animals aged from one to five months, PK 90, PK 91, K91 are used;
- for feeding adult rabbits use K 92-1 and K 92-2;
- For final fattening of animals for meat, K93-1 compound feed is used.
Compound feed goes on sale in two states:
- granulated. An excellent option for complete feeding. Excellent storage, easy to dose, convenient for animals to eat;
- bulk mixtures. All components in them are ground into powder. It is most convenient to use them in mash.
On a note!
Feeding feed intended for other animals or birds can be harmful to rabbits due to the specific additives included in it.
Automation of feed accounting and ration calculations
Large farms have long been using specialized software for automating feeding accounting and calculating rations. The development of modern technologies and the reduction in the cost of computers and software have led to the fact that now even medium and small farms can also afford such automation.
As one example of software where you can conveniently and quickly keep track of feeding and calculate rations, as well as production accounting and reporting for rabbit breeding, you can cite the “MATRIX” program. Rabbit breeding”, developed by specialists from the MATRITSA company from Belgorod.
Conclusion
In organizing the technological process on a rabbit breeding farm, of particular importance is the creation of a system of adequate feeding for them, capable of ensuring high growth rates of young animals and good reproductive abilities of adult livestock. In this case, it is necessary to pay attention not only to providing rabbits’ diets with energy and protein, but also to take into account the content of different fractions of carbohydrates, fat, macro- and microelements, and vitamins of various groups. Only such an approach to rationing rabbit feeding with an economically sound choice of different types of feed can ensure sustainable and highly profitable development of the industry. It is almost impossible to do this without the introduction of automated systems for calculating rations and recording feeding in rabbit breeding.
Advantages of using compound feed for feeding rabbits
Loose and granulated feed contains elements that influence the pet's weight gain and promote harmonious development. There are universal products suitable for feeding pregnant women, newborns, sick rabbits, meat, meat and wool, and skin processing. Different products are combined to achieve the best result. When choosing a product, you should pay attention to the composition and recommendations for feeding rodents.
Advantages of rabbit feed:
- Optimizing the animal's diet.
- Simplifying your pet's feeding.
- The likelihood of contracting intestinal infections is reduced.
- The daily norm is easy to calculate.
- The amount of independently prepared feed is decreasing.
- Allows you to quickly gain weight.
In winter, herbs, vegetables, and fruits are sold in insufficient quantities. The quality of succulent feed is also not always suitable for feeding animals. Pelleted food helps replenish the missing substances. The average price of concentrate is higher than self-produced products. You should pay attention to the quality of the product, since unscrupulous manufacturers sell stale products containing harmful impurities that negatively affect the health of rodents.
Supplementing the diet is recommended to increase the rodent’s immunity. The body's resistance to disease is especially important for young animals. So that the pet grows quickly and fully develops. You should choose vitamin supplements for young adults that contain elements for weight gain, or generic products. Raw materials can be mixed to achieve a better effect.
conclusions
- Proper nutrition is the key to the health and long life of rabbits. These animals are very sensitive and picky about food.
- Rabbits are herbivores. However, not all herbs can benefit them. Consumption of some plants can cause serious illness or death.
- You need to carefully monitor what your rabbit eats. There are herbs, tree branches, tops and root vegetables that can harm the animal.
- Rabbits should not be overfed, because... this can also harm their health.
- You can prepare dry food yourself at home. This saves money on maintenance, and you know what your pet is eating.