Breeds of decorative rats
Breeds of decorative rats
Standard are the most popular types of decorative rats with smooth and glossy fur. The standard rat is a rather massive animal with a long body. Body length is about 240 mm. It weighs 500 g. The tail is long, about 200 mm, thick at the base, gradually tapering towards the tip. The ears are wide, round in shape, squat, but not too large.
Rex are rats with dense and curly fur, which is less shiny than standard ones and coarser. Another peculiarity of the rex's coat is that the number of guard hairs in it is greatly reduced, and the animal's whiskers are slightly shorter and have a strongly curled appearance.
Tailless - rats that do not have a tail. This variety is the result of a mutation. The first tailless rat was bred by an amateur in 1983. Most of them do not suffer from the lack of a tail. The body shape of animals of this species is somewhat different. Tailless rats should have a pear-shaped body and no vestiges of a tail.
Hairless - hairless rats. The less hair a rat has and healthy, bright and soft skin, the better. It is quite acceptable to have fluff above the eyes, on the wrists and ankles, in the groin area and on the cheeks. But such fluff should not be excessive and disturb the picture of a naked animal.
Satin - the fur of this breed of decorative rats is thinner, shiny and elongated. This variety has the same body structure as individuals with regular hair. The hair of satin rats is somewhat elongated, smooth, with a deep shine. The wool is dense and very pleasant to the touch. The shine of the coat is the main distinguishing feature and advantage of this variety of decorative rats.
Dumbo - rats with large ears. This species was bred in California in 1991. This species of rat got its name from the elephant from the Disney cartoon. These rats are distinguished by their low-set and more rounded ears. The head of these animals is wider and smoother, compared to other breeds of decorative rats. The muzzle is relatively sharp. With its pear-shaped body shape, this species is similar to tailless rats, but has a shorter body and a long tail.
A unified standard for varieties (breeds) has not yet been developed for Russia, therefore, along with the generally accepted varieties, there are also other breeds of decorative rats:
Downy, Fuzz (Fuzz)
Fuzz is a rat with fine downy hair that forms a translucent coat. The hair is thin, sparse, short. There are no guard hairs. The mustache is curly and short. Disadvantages: lack of “fluff” on large areas of the skin, presence of spine.
Double Rex
The Double Rex is a rat with double hair. The coat is very short, so that the skin shows through, but like the Rex, it is twisted into a spiral. Hard guard hairs are distributed interspersed with soft, short and thin downy hairs throughout the body. Double Rex sheds regularly. As a result, some areas of the body are either temporarily devoid of hair or are covered only with a thin layer of downy hair. The color and color of the coat can be any, and the mustache is short and curly.
Sphinx - see Hairless hairless rats (AFRMA - Hairless)
The Sphinx is a rat that is completely hairless. In this case, the animal’s mustache is completely absent, and the skin is clean, smooth and folded. Rats can maintain different pigmentation until they reach the age of four months, in accordance with the standards of markings and colors. With age, the skin becomes completely pink as its pigmentation is lost. Male Sphynx rats have thicker skin than females.
After certain breeding work, some breeds were crossed with each other. As a result, various hybrids of decorative rats appeared: such as Dumbo Sphinx, Dumbo Double Rex and others.
The hair of a rat can be colored in a wide variety of colors: black, white, orange, gray, blue, dark blue, chocolate, brown, beige, red and others. Each coat color has its own eye color (one or more colors). Thus, blue rats have ruby-colored eyes, while rats with black fur can only have black eyes. White rats can have either red or black eyes.
In addition to colors (colors), you can note a variety of markings and markings - patterns: hood, husky, Himalayan, solid, Siamese and others.
So we found out what breeds of decorative rats exist in the world!
Read with this
Rat. Part 1, anatomical
Rats, like cats, can “stretch.” But the reason is somewhat different - in rats the spine is actually a couple of vertebrae longer. And the legs are shorter relative to the body, which is why the rat initially looks elongated.
The odontoid process of the second cervical vertebra (axial) has a conical shape. This allows the first vertebra (atlas) to rotate not only about the axis, but also in other directions. This skeletal feature provides rats with exceptional head mobility, which allows them to defeat even larger opponents.
Thanks to its powerful hind legs, the rat can jump up to a meter in height. The front legs are much smaller. To cushion them when jumping, rats have a structural feature: on the spinous process of the second thoracic vertebra there is a joint connecting it with a triangular bone plate directed forward. From below, tendon cords are attached to this plate, extending to the first thoracic and four posterior cervical vertebrae. When landing, this “structure” springs and absorbs the impact. Nutria has the same feature.
Rats have a visual angle of 160′ and are nearsighted. A rat can see clearly no further than a meter, so if you stand quietly in the opposite corner of the room and don’t move, you don’t exist for the rat. The animal does not see in the red spectrum, but distinguishes ultraviolet light; in general, the world for a rat is gray-blue-green, like for a dog.
How can one live with such vision? That's how. The rat constantly turns its head, and its eyes move independently of each other, and they always move in the opposite direction relative to the head: if the rat lowers its head, the eyes look towards the tail, when the rat raises its head, the eyes become “in a bunch”, when tilts his head - the lower eye looks up, and the upper eye looks down. The difference in the direction of the eyes is up to 40′ in the horizontal plane and up to 60′ in the vertical. Thus, the rat sees the surrounding space in fragments.
Rats have a unique hearing; they hear the slightest rustle, as well as ultrasound. But they do not distinguish pure tones. A rat may not hear a wailing siren, and ultrasonic rodent repellers do not work on them because their sound is quite acceptable to rats.
Rat noses have twice as many olfactory receptors as humans, and they smell through each nostril separately. In just fifty milliseconds, the source of the odor is identified and analyzed.
Rats make whistles in the ultrasonic range. Moreover, they whistle not with their lips, but with their throats and are able to suddenly change the frequency of the signals. Rats have a rich “vocabulary” of screams with special intonations and meanings. Scientists have found that rats are even capable of laughing: when “laughing,” the rat emits a series of identical ultrasounds.
Rats are the only living creatures that can sense X-rays. At the same time, they can withstand very high levels of radiation.
The tail is almost equal in length to the body, it is covered with fine bristles and scales, the tail is rough and hard to the touch. The tail has two functions - thermoregulation and balancing. Tendons run along the tail, thanks to them the rat can cling to its tail.
When a predator attacks a rat and grabs it by the tail, the skin is removed, exposing the spine bone. Over time, the bone dries out and falls off, after which the rat continues to live with the “stub.” A tailless rat, as a rule, does not live long. So do not grab or lift your pet rats by their tails, they may come off!))
The second part will be devoted to the “service” of the rat to man
source
Character of rats
Rats are pets that love to interact with people and develop strong bonds with their owners. They love to cuddle and climb on their owners, and if you socialize them properly, they enjoy being in the hands of their human. Rats often happily sit on their owners' shoulders or heads, or find them dozing on their owners' laps if given the opportunity. They have also been found to experience emotions in the same way as humans. They can feel loneliness and empathy, which helps guide their social behavior around people as well as other rats.
Rats can be trained to do all sorts of behaviors and tricks. If you like the idea of learning about animal behavior and training but don't have room for a dog, a rat is a great beginner pet. They quickly adapt to clicker training and can be home trained, learn their name, and learn to do almost anything that is physically possible for them.
Rats are relatively easy to care for compared to other pets. They keep themselves clean like cats, although they will rely on you to keep their cage free of contamination. You do not need to bathe or brush them except in special medical cases. You won't have to deal with shedding, and some rats are even hairless.
They also don't tend to bite. While this behavior is always a possibility, it occurs much less frequently in rats compared to other similar pets. If you are looking for a small pet that is suitable for children, a rat may be a better choice than other rodents that tend to bite and are less easy to handle.
Rats don't need large spaces, so you can easily keep your rat happy by living in a small space like an apartment. They do need time out of the cage, but they won't need a yard to roam, so they are much easier to keep than, say, a dog.
Hairline
Many people mistakenly believe that rats have a tail without hair, but upon closer inspection and touch it becomes clear that the tail is covered with many small hairs. The tail is warm and slightly rough to the touch.
The rat's tail became this way due to the process of evolution. Rats are excellent swimmers; they often live near bodies of water, and it is their smooth tail that allows them to easily and comfortably stay in the water. If a rat's tail were fluffy, it would cause many problems and inconveniences.
How to help a rat if it is panting, choking or grunting
Common causes of shortness of breath and breathing problems in rats are pneumonia and heart attack.
The most important thing to do is contact a veterinarian. Only a specialist can prescribe adequate treatment. If wheezing or other breathing problems occur, you can provide your pet with first aid and additional measures to the main treatment.
If wheezing or other breathing problems occur, you can provide your pet with first aid and additional measures to the main treatment.
To provide first aid to the animal, you need to drop a few drops of Corvalol into the rodent’s mouth and rush to the veterinarian as soon as possible. Try to handle your pet as little as possible during an attack. In this state, he is capable of injuring your hand with a bite. Because of this, the animal may fall, which will further aggravate the situation. You should remove all unnecessary and traumatic objects (tunnels, ladders) from the cage. During an attack, the rat does not control itself and can injure itself.
If your rat is sneezing more than usual, listen carefully to the animal's breathing. In the case when the breathing is even, there are no mucous discharges from the nose, you just need to observe the behavior of the animal. You should not start treatment until you are sure that the animal is actually sick. The cause of sneezing may be a simple allergy or dust.
If the animal makes unnatural, grunting sounds, your rat is sick! Contact your veterinarian immediately!
Grunting sounds in the sinuses indicate that they are full and breathing is difficult. The disease progresses very quickly, so it is worth taking steps to consult a veterinarian. Based on the diagnosis, he will prescribe a course of antibiotics.
Ratologist will help save the rat
Measures to restore animal health
In order to cure your pet as quickly as possible, in addition to a course of antibiotics, it is necessary to take measures to restore the animal.
— The rodent’s cage must be reliably protected from drafts. — The room in which the cage is located should have normal air humidity. It should not be overdried.
— The cage should be thoroughly cleaned daily: the ammonia smell irritates the animal’s nose and breath.
— A heating pad installed in the cage also promotes recovery.
— Echinacea decoction will help strengthen the rat’s immune system.
— If the pet is not alone, you need to seat the animals in different cages to prevent the spread of infection.
Functions of the tail
Why does a rat need a tail and why is it so important to it? It has two main functions thanks to which the rat can exist normally. One of the most important is thermoregulation. The tail is quite well adapted for these purposes: the bristles covering it are sparse and short, it itself has a decent area-to-volume ratio, and is penetrated by a fairly large number of blood vessels, especially in the middle and at the base of the tail.
Body temperature control
The tail helps in the following way: the rat regulates its body temperature by contracting and dilating blood vessels. If the ambient temperature rises by several degrees, the vessels dilate and allow more warm blood to pass through. Cooled by the environment, the already cold blood returns to the body, thereby cooling the rat’s entire body. If the temperature drops, the reverse process occurs. Therefore, the tail always saves the rat from overheating or hypothermia. In the figure below you can see how the structure of the tail changes with changes in air temperature: Changes in the tail of a rat at different temperatures
Balancing
The second important function of the tail is balancing. Everyone knows that a rat can crawl anywhere and anywhere. It can easily climb fences, wires, wires and branches, and in all cases its long tail helps the rodent maintain balance.
In this case, the tail can be compared to the pole of an acrobat who walks on a tightrope in the circus. When a rat walks along a rope, the latter acts as an axis. The tail of mice works similarly, since the body of a mouse is not particularly different from the body of a rat, except perhaps in size. Read more about the difference here.
In this case, the rat can rotate its tail around the indicated axis, while the center of gravity should always be strictly above the rope. Otherwise, gravity will force the rat to simply rotate around its axis. If it doesn't compensate for the rotation, it will fall. It follows from this that the moment of inertia increases, making rotation around the axis more difficult. The length of the tail also plays an important role: the longer it is, the higher the chance of maintaining balance.
The increased moment of inertia gives you time to adjust the position of your center of gravity. If there is no tail, then the rat will not be able to keep its body on an unstable surface and will fall down. The tail helps the rat maintain balance
Description of the breed
Dumbo rats have large ears on a small skull. The shape of the auricle differs in different species, they are:
- pointed;
- round and flat;
- slightly curled;
- resembling half-open petals with a pointed tip.
The animals have a short, pear-shaped body with greatly expanded pelvic bones. Males reach a length of 18-20 cm, body weight ranges from 250 to 500 mg. Females reach 15 cm and weigh about 250-400 g. Dumbo differ from other types of ornamental rats by a wide and flat skull with a blunt muzzle, and a longer tail.
On average, Dumbo rats live about 2-3 years. Life expectancy strictly depends on the quality of feeding and care of the pet. With timely treatment of diseases and a balanced diet, rodents can live to a ripe old age and delight their owners for 5 years.
Types of dumbo rats
There are several varieties of the Dumbo breed, differing in coat color.
Dumbo Rex Rat
A characteristic feature of the Rex is its strong, curly fur. There are rats of different colors: white, black and gray. In some cases, a baby may be born with variegated fur consisting of 3 or more colors. When removed over a considerable distance, the rodent without movement resembles a soft toy. In addition to fur, the rat has curled antennae. When you carefully examine the animal, you will notice thick and wavy fur, which will be rough when touched.
Dumbo Siamese rat
Rats of this species are distinguished by dark tails, paws and the front of the muzzle, which resemble Siamese cats. Areas of black or brown fur create a sharp contrast against the white body fur. Cubs rarely inherit this color. Siamese rodents are irritable and often show aggression towards their owners.
Dumbo sphinx rat
For people predisposed to allergies to wool, there is a special type of Dumbo - the Sphynx. Rats are completely hairless. Rodents are warm and soft to the touch, their skin is quite delicate and traumatic. The skin may not only have a pink color. There are animals with chocolate, white and bluish colors. These rats were specially bred through numerous crossings and genetic mutations.
Dumbo Husky Rat
Husky is rare. Such rats are often called chameleons due to the change in coat color throughout life. If a rodent baby is born with a white-gray, black or brown coat, it may later change to a new coat with white patterns.
Dumbo rat blue mink
The rarest variety of Dumbo rats is the blue mink, which is characterized by a purple-blue fur color. The texture of rodent fur can vary. The most common animals are those with straight, smooth hair. Rats with curly fur or long hairs on their faces are considered more expensive.
Dumbo Manx Rat
Features of behavior and character of the Dumbo rat
Smart rats quickly find a common language with people and get used to being picked up. They fearlessly climb over humans, displaying friendliness and sociability. Dumbo has a good sense of smell, so their activity increases when the owner approaches with various treats: sweet fruits, sugar or grains. At the same time, in everyday life, rats are not very mobile. They love to snooze at the bottom of the cage, basking in the sun's rays.
Rats are social animals, so without the attention of the owner or other relatives, they begin to get bored. Zoologists recommend purchasing rodents in quantities of several pieces.
Interesting and educational facts about the life of rats
In India there is a Karni Mata temple where rats are revered, cared for and protected. If the rules for caring for a sacred animal and killing it are violated, this person is obliged to bring a golden figurine in the form of a rat to the temple.
In some American states, it is illegal to hit a rat with a baseball bat and can result in a $1,000 fine.
In Asian and African countries, rats are considered a worthy delicacy for a festive dinner. Rat meat is considered a delicacy.
A gray rat eats up to 12 kg of various cereal products per year. Experts have calculated that every year about 6 kg of one farmer’s harvest is spent on feeding one rat.
Is it possible to pick up a rat by the tail?
This cute rodent's tail is a rather fragile part of its body, so picking up a rat by it is not recommended. This can lead to a fracture and damage to its soft tissues
This animal must be carefully grasped by the body in the chest and shoulder girdle.
Too nimble individuals can be carefully held at the base of the tail, but the animal itself should not be suspended, but stand on both legs.
Important! In case of damage, you should not use hydrogen peroxide, as this medication will cause severe pain in the animal.
If you inadvertently damaged this important organ of your pet, then you need to take the following actions:
If you inadvertently damaged this important organ of your pet, then you need to take the following actions:
- treat the area that began to bleed with Chlorhexidine or Miramistin;
- then a healing ointment such as “Terramycin-spray” (sold in veterinary pharmacies) or “Levomekol” should be applied to the damaged area;
- It would be a good idea to cover the damaged area with a bactericidal plaster.
If there is a suspicion of a fracture, the patient must be shown to a veterinarian.
A long, hairless tail is essential for the rat's agility and thermoregulation. Under no circumstances should you grab it, as the animal may get scared and shed the outer skin of this part of the body. After this, it is not restored, and the pet’s health is damaged.
Bone tissue injuries
The most common injury is a broken tail in a rat, which occurs as a result of being pinched by a cage door. It is not uncommon for owners or family members to unintentionally step on a rodent.
Veterinarians are confident that if a rat breaks its tail and is examined by a specialist in time, breeders can rest assured. Typically, the broken part must be amputated, but in rare cases the animal may chew it off. If a wound is found on the tail, the area is treated with a weak solution of potassium permanganate.
If the owner accidentally steps on a rat and the animal is injured, it is important to act quickly:
- place the animal on a flat surface;
- if a rodent has broken its spine, it will drag its hind legs;
- when an animal drags one paw, then we are talking about a fracture of the limb.
After initial measures, it is necessary to take an x-ray of the rat’s paw fracture so that the doctor can make an accurate diagnosis.
Behavior and lifestyle
Rats are usually nocturnal. At night they are active, going out hunting or looking for food. During the day, the rat chooses the safest possible shelter and sleeps, gaining strength. Rodents sleep very lightly, so how long their sleep lasts depends on environmental conditions. If the rat is disturbed by any sound or movement, it immediately wakes up.
One of the features of rat behavior is their ability to easily adapt to the proposed conditions. For example, decorative individuals living with people switch to the daily routine of the owner.
Rats are very mobile and hardy; during the day they can run 10–13 km, swim and hunt well in water, climb trees, overcome obstacles, jumping to a height of up to 1 m.
Rats usually live in large packs and hunt together. But there are individuals that live separately. Rat habits are largely explained by the aggressiveness of the animals. By the way, this is precisely what the education of the so-called rat-catcher rats is based on. A large number of rodents are placed in a closed space and given little to no food, forcing them to fight and eat each other. The surviving rat is tamed, and it protects the house from the invasion of its relatives.
A pack of rats
It is clear that in a battle against a mouse, the rat will always emerge victorious. An angry or cornered rodent can even attack a dog or person.
Tips and tricks for injuries
Even the most responsible and attentive owner is sometimes unable to keep track of the animal. If a rat has torn off its skin or your pet has fallen from a height, you should remember simple rules:
- Examine your pet carefully. If the skin is severely damaged or the animal has difficulty moving, you should immediately consult a doctor.
- Find out whether the animal could have been accidentally stepped on to rule out injuries to the spine and limbs.
- Do not forget that minor tissue damage is only visible on an x-ray.
If a rat breaks its leg after falling from a great height, carefully restrain the animal and apply a splint to prevent movement.
In case of fractures, it is important to ensure complete rest and limit movement as much as possible.
When an animal's limbs are broken, the recovery process largely depends on the prompt actions of the doctor and breeder. After being examined by a veterinarian and prescribing treatment procedures, strictly follow the recommendations and make sure that the rodent does not fall again or damage the skin.
They are indestructible
This quality unites many movie monsters, especially serial ones: you kill them, you kill them, and by the time the next part comes out they are as good as new again.
Well, what do rats have to do with it, you ask. Common rodents. No hint of immortality. They can be anything they want, but considering them invincible is too much.
However... What is the surest way to kill a rat? I? So here it is. When rats find food they aren't sure is safe, they taste (.pdf) it first—just a little. And if they feel somehow wrong, they don’t touch this food again. They are well aware of our insidious plans and know how to destroy them.
In addition, we are increasingly faced with a completely new variety of these creatures, which scientists have already nicknamed “super mutant rats”, which are no longer affected by practically any poison.
Why do animals need a tail?
Often, young children, just beginning to explore the world around them, ask their parents the same question: “Why do animals grow tails? “It should be noted that not every parent is able to give a clear and truthful answer to this simple question.
Usually the answer is banal phrases about how this is how it works. But inquisitive little minds are rarely satisfied with such a general answer and continue to look for more specific reasons.
Especially for these inquisitive kids, as well as for the peace of mind of their parents, we inform you: there really are such reasons.
Tails grow because without them, many animals would feel “as if they had no arms.” With the help of the tail, animals can communicate and express their emotions, find new friends and scare away opponents, defend and attack, keep warm, give danger signals, climb trees, steer their own body when running, jumping, flying or swimming, maintain balance or just have fun. Tails play a very important role in the lives of most animals.
How are the organs located inside the animal’s body?
The anatomy of the rat is well studied. The thoracic and abdominal regions of the animal are separated from each other by a diaphragm, under which a bright red liver is located. It partially obscures the pear-shaped stomach. To the left of the stomach is the oblong spleen.
Below these organs is a voluminous intestinal tract, covered with an omentum necessary for collecting animal fat. Behind the intestines, at the bottom of the abdominal cavity, there is a pair of bean-shaped kidneys. In rats they are asymmetrical - the left kidney is located deeper, as the stomach puts pressure on it.
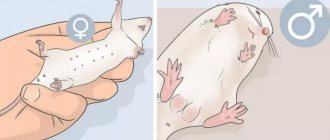
The bladder is located in the lower abdomen of the animal. The ureters lead to it. In the same part of the body are the genital viscera:
- Males have testes;
- females have complex reproductive organs.
A peculiarity of the internal structure of rats is that they do not have a gallbladder. Bile flows from the liver through the duct directly into the duodenum.
The animal’s vascular system is the inferior vena cava, through which blood flows from the abdominal organs to the heart. The aorta runs nearby.
The heart, surrounded by large vessels, is located in the chest cavity. There is also a pair of pink lungs (the right one consists of four lobes, and the left one - of one). They are not attached to the chest, but hang freely on the bronchi. The esophagus is located deep in the sternum, playing the role of a connecting link between the stomach and pharynx.
Interesting facts from physiology
Veterinarians and biologists, studying the anatomical and physiological structure of the rat, noted a number of interesting facts:
- numerous laboratory studies on rodents are explained by the similarities in physiology between rats and humans;
- the animals lack tonsils and thumbs;
- males have tissue for the formation of mammary glands, but there are no nipples even in their infancy;
- females have a vestigial penis that can be used for urination;
- In rats, the right and left lungs have different structures. The first has 4 beats, and the second has only one;
- rodents have an appendix, which is sometimes confused with a frolicking internal tumor;
- unlike humans and cats, albino rats do not suffer from hearing problems;
- ultrasonic exposure causes discomfort to rodents, but they can easily tolerate it;
- Rodents do not have lips around their mouths. Instead, a folded gap is formed above the lower jaw;
- The male spends 2 seconds on fertilization, so keeping different-sex individuals in the same cage guarantees the presence of offspring.
source
Rat King - truth or myth?
The Rat King is recognized as a rare phenomenon. The tails of several rodents become so tightly tangled that the rats cannot free themselves and untangle them.
Such rats quickly die because they cannot coordinate their actions to obtain food or simply direct movement. Such cases are very rare: throughout the world, over a long period of time, there are only a few dozen such remains. Often these discoveries were made by accident by ordinary people - on their farms, basements or near mills, but despite this, a huge number of myths about such monsters arose, especially in ancient times.
The most interesting thing in these stories is that no one has ever seen such kings live; only rat remains testified to this. To date, there is not a single photo, much less a video, to prove this phenomenon.
Of course, it is difficult to imagine that the tails were intertwined after death, i.e. It is logical that the knot arose during life - the constant bustle of rats could lead to this. A rat can live without food for a maximum of 4 days, i.e. Confused and unable to come to an agreement, such animals are doomed to death.
There is a version about the “fusion” of tails due to cramped circumstances: in a cramped and narrow space, sooner or later the tails will become connected. Or, according to another version, the tails may become tangled due to contamination, food debris, blood or sticky substances sticking the rats' tails together. Another theory is that the tails freeze together when rats try to stay warm in cold weather. In any case, after waking up, the rats try to run away in different directions, only tightening the knot more.
Here are some interesting facts about the common rat's tail. What fact was the most unexpected for you?
What I am a master at is talking incessantly about hamsters. I have three hamsters at home, and my husband has a pet rat. That’s how we live, the six of us eat, the six of us sleep :)
source
Posts 1 page 9 of 9
Share12013-04-19 01:33:41
- Author: runa
- Administrator
- From: Donetsk
- Registered: 2009-08-15
- Invitations: 0
- Posts: 20401
- Female gender
- ICQ: 41707184
- Time spent on the forum: 6 months 5 days
- Last seen: Yesterday 11:24:02
According to the NFRS, there are currently two such varieties - sphinxes and manxes.
The NFRS has a show regulation of which states;
'Any mutation that the society deems harmful to the health of the rat shall not be shown in any class, including New Varieties & pets'.
The NFRS currently has two varieties held under this regulation, the hairless or sphinx and the tailless or Manx. I have written this article to make it clear why these decisions where made and what they mean, as there appears to be some confusion about this.
Several mutations are responsible for hairless, most dominant but some are recessive. Some of these mutations are very harmful and produce rats with persistent skin infections etc while most only appear to affect the coat. The commonest one in the UK is the double or homozygous rex, which you get when you cross two rexes together. In this case approx 25% of the kittens will have a very weak coat, which grows through and then breaks off. Most hairless mutations are like this. Another recessive mutation turned up via imported stock. The hairless mutations I have seen all had whiskers (curly ones) but at least one mutation does not have them. Some are prone to growing eyelashes.
This variety is showable in the US (especially in the warmer states) but not in the UK at shows with NFRS support. These rats are much more sensitive to cold than normal rats and are more prone to injuries due to their lack of a protective coat. Both of these things makes them unsuitable for showing.
tailless rats are due to the interaction of several genes and possibly environmental factors as well. Some strains are prone to produce them. For instance the Siamese which went to the US in the '80s, but in my experience they are just as likely to appear from the crossing of two unrelated strains. Some tailless have a small stub of tail but most that I have seen have none at all or perhaps a very tiny finger-like projection. Most tailless are perfectly healthy, however some have problems with nerve impairment to the bowels and the bladder and a few lack hip sockets and are missing some pelvic bones.
Moustache wiggling
Rat whiskers are sensitive antennas that help animals navigate in space. The information that rodents receive with the help of such a navigator is so detailed that the animals not only move confidently in the dark, but also receive an almost complete understanding of the surrounding objects, including the features of their dynamic trajectory.
When a rat moves its whiskers, it not only explores odors, collects information about the world around it, but also maintains the balance of movement. It is with its sensitive whiskers that the animal first of all checks unfamiliar objects, including the palms of people.
Balancer
Another interesting fact about the rat and its tail is its ability to balance. After all, it will not be difficult for a rat to climb a vertical surface or crawl along a branch or wire. And in all these situations, her tail comes to her aid. It is he who allows the animal not to fall and maintain its balance, performing the function of an invisible hand. The length of the rat’s tail is of particular importance in this case: the longer it is, the more confident the animal feels.
Now you know about the value of this rat’s dignity, which not only adorns the animal, but also saves the animal from danger.
Fun Features
If your rat is making a loud noise, he is likely unhappy. She may protest your treatment of her or show her displeasure at being taken out of her crate.
Night noise
Don't expect your rat to sleep on the same schedule as you. They are nocturnal, which means their normal sleep cycle is to play at night and sleep during the day.
Scavenger hunt
Rats take whatever they can get and then bring it back to their lair. They are especially prone to stealing items that they can chew, such as things made of wood, plastic, or rubber. Rats also hoard food; so don't be surprised to find a little edible stash hidden in your rat's cage.
Boxing
Rats do not box for fun or play. They box to show who is the alpha rat. They have a natural social hierarchy with the dominant rat emerging from the pack.
Bites
If your rat is chewing or licking you, it may be showing affection by grooming you. They also have a great sense of smell, so a rat may chew, lick your hand, or smell you after you have eaten or cooked food. Your pet may bite you if it finds leftover food, such as crumbs or sauce, on your hands.
Digging
In the wild, rats live in underground burrows. Pet rats will also dig burrows or the ground, especially if they are offered bedding or a pile of shredded paper, to create a safe and comfortable place to sleep.
wiggling mustache
We have GPS to get from point A to point B. Rats have whiskers which they use to navigate objects and also to maintain balance. The rodent moves its whiskers to literally get a better sense of its surroundings, such as to see whether an object is moving or static and to gather other spatial information.
Tail movements
If you suddenly grab your rat, he may flick his tail, trying to feel his way through what is happening. The rat also uses its tail for balance, which it holds straight while running. They even use their tail to support themselves in a standing position.
Bulging eyes
Eye bulging occurs when a rat's eyes move in and out of their sockets. Don't worry, the animal isn't completely crazy yet. In fact, the rat may be quite relaxed and happy at this point.
Teeth grinding
Protruding eyes usually occur along with teeth grinding, also called bruxism. Rats' teeth are constantly growing, so teeth grinding helps keep them under control. A rat is more likely to grind its teeth when it is relaxed and content, similar to how a cat purrs. The sounds made by her jaw moving back and forth and her teeth grinding create vibrations and cause the rat's eyes to bulge.
What does a black rat look like (photo)
Black rat.
Name: Black rat Lat.:
Rattus rattusClass: Mammals - Mammalia Order: Rodents - Rodentia Family: Mouse - Muridae
| Habitats: | fields and arable lands |
| Nutrition: | everything that comes across |
| Peculiarities: | their incisors require constant sharpening, so they eat and spoil everything |
Is it possible to pick up a rat by the tail?
The rat's tail is quite fragile. Under no circumstances should you lift an animal by it, as there is a high risk of simply tearing off its skin or breaking it. The animal is lifted by the body, carefully grasped by the chest and shoulders.
Particularly mobile decorative pets can be carefully held by the base of the tail, but the animal itself must have support on its paws. If you accidentally damage your pet's long tail, give him first aid: Stop the bleeding by treating the injury site with Chlorhexidine. It can be replaced with Miramistin
It is better not to use hydrogen peroxide, as treatment with this drug causes severe pain.
It can be replaced with Miramistin. It is better not to use hydrogen peroxide, as treatment with this drug causes severe pain.
If you accidentally damage your pet's long tail, give him first aid: Stop the bleeding by treating the injury site with Chlorhexidine. It can be replaced with Miramistin. It is better not to use hydrogen peroxide, as treatment with this drug causes severe pain.
Apply a drug to the tail that accelerates healing: Terramycin spray (veterinary product), Levomekol.
Apply a bactericidal patch to the affected area.
For both domestic and wild rats, the tail is vital. Thanks to it, animals regulate body temperature, move quickly and deftly on any surface, and overcome various obstacles. This part of the body is covered with small hairs and scales, which gives it a rough appearance.
Previous Features and habits of rats Why does a domestic rat lick your hands Next Features and habits of rats Skeleton and anatomy of a rat, internal structure and location of organs
Thermostat
People have often wondered why rats have a tail. This process has two purposes, which ensures the normal functioning of the animal. The first purpose is to regulate body temperature. The blood vessels inside the rat's appendix are able to expand and allow a larger volume of warm blood to pass through them. The liquid is returned to the rodent’s body already cooled, which helps lower the animal’s body temperature.
Article on the topic: How many years do decorative rats live at home?
The cycle in the opposite direction occurs when body temperature drops. Therefore, the rat’s tail serves as a kind of thermostat.
Caring for dysocactus at home
Lighting for disocacti
“Rat tails” are today considered one of the most light-loving representatives of succulents. But unlike many other cacti, these ampelous beauties with climbing shoots do not tolerate direct sunlight very well. For dysocacti, it is necessary to provide bright, diffused lighting. Window sills of eastern and western orientation or southern windows with appropriate shading at noon are considered ideal for them.
Since the plant develops buds during winter, the lighting regime during this period is very important for it. For aporocacti, during the cold season, the lighting is increased by moving the containers to brighter places. If correction is not carried out, abundant flowering will not be achieved.
Bright lighting is also critical during warm winters
The vast majority of disocacti do not like artificial lighting and need a naturally bright location.
Comfortable temperature conditions
Unfortunately, magnificent dysocacti cannot be counted among those subspecies of the main indoor succulents that are able to bloom under any conditions. The easiest way to achieve flowering is to winterize it in a warm room. To produce flowers, “rat tails” need to be kept cool or carefully monitor the lighting and dramatically adjust their care.
During the period of active development, this not the most heat-loving cactus is best kept at a temperature of 20 to 25 degrees. Disocactus will tolerate hotter conditions only outdoors. But during the dormant period, it is better to provide aporocacti with a cool temperature of 7 to 10 degrees. Warmer wintering will lead to a reduction in the number of buds, and if the lighting is not corrected, there will be no flowering at all.
Unlike many cacti, disocactus can be taken out into the fresh air, placed on balconies and terraces (and even in the garden), provided it is protected from direct sunlight and precipitation.
Disocactus flagelliformis is better known as Aporocactus flagelliformis. Olgapro
Watering and air humidity
The intensity of watering for this cactus directly depends on the stage of development. Regular procedures will only be needed in spring and summer. In this case, as for all other representatives of the cactus family, it is necessary to carefully avoid any waterlogging and only keep the substrate slightly moist. Stagnation of water in the pan, too much and frequent watering can lead to the death of the plant. The following procedure is carried out only after the top layer of soil has completely dried and the substrate in the middle part of the pot has partially dried.
During the dormant stage, dysocacti require much more limited watering. Regardless of the temperature, the following procedure in winter should be carried out only when the substrate is completely dry. If disocacti are kept in cool conditions, then watering is carried out extremely rarely in accordance with the low rate of soil drying. When wintering in warm conditions, the cactus needs almost dry conditions.
In their preferences for air humidity, “rat tails” are somewhat different from their other counterparts. Disocactus does not need conditions of high humidity at all, but at the same time it really likes spraying during the summer if the air temperature rises above 24-25 degrees Celsius. Spraying is usually carried out with warm water, slightly moistening the plant. During autumn and winter, spraying is strictly prohibited.
Ackermann's disocactus (Disocactus ackermannii). John C.Disocactus biformis. Universität GöttingenDisocactus speciosus. Universität Göttingen
Fertilizers for disocacti
Fertilizers for this type of cacti are applied exclusively during the period of active development. Typically, plant fertilizers are added to irrigation water from March to mid-summer. The easiest way to navigate is by the timing of stopping fertilizing at the end of flowering. As soon as the cactus sheds its last flowers, you must stop applying fertilizer in any form. During the active period of development, special mixtures of fertilizers intended for representatives of the Cactus family are used for dysocacti. The optimal frequency of procedures is 1 feeding per month.
How to get rid of black rats
Black rats are cunning and intelligent. They avoid traps and traps, have a good sense of smell and smell poison. Therefore, it is necessary to approach the issue of their destruction or expulsion from the site in a comprehensive manner.
| Destruction method | Action |
| Chemicals. | All kinds of poisons that act quickly and effectively, but require caution. |
| Lures and traps. | These are traps, special rat traps or glue traps into which the pest will fall and remain unharmed. |
| Folk remedies. | Mixtures with a pleasant aroma that will stop the animal's stomach, leading to death. |
| Prevention measures. | Repellers, animals with hunting instincts and maintaining order in the area. |
Follow the links to articles with detailed instructions on how to get rid of rats on your property and in your barn.
Range and specific habitats
Rats live all over the globe, with the possible exception of the Arctic and Antarctic. They adapt quite easily to even the harshest conditions, so you can find rat tracks in the snow even in the cold winter. Under natural conditions, rodents live in forests, fields, and along the banks of reservoirs. Rats dig holes underground, occupy natural shelters, hollow trees or nests on branches.
But still, rodents prefer to settle closer to people. In rural areas, they can live in cowsheds and poultry houses, in outbuildings, in underground floors, and construction waste. In cities, rats live in garbage dumps, warehouses, and often even in apartment buildings. Residents of the lower floors, wondering where rats suddenly come from in the apartment, should know that animals can come from the basement, garbage chute, or technical corridor.
Being extremely cautious, rats try to settle in the safest places and act without leaving traces.
Natural enemies
Danger awaits both rats living in the wild and those who live next to humans. Despite the fact that rodents are very intelligent and careful, they regularly become victims of birds and animals of prey. Depending on the region where they live in nature, rats are threatened by:
- representatives of the mustelid family (ferrets, martens);
- hedgehogs (can attack a small rat);
- some types of snakes;
- foxes;
- beavers;
- birds (for example, eagle owls).
As for rats living in populated areas, their main enemies are dogs. But cats also contribute to reducing the rodent population by hunting them.