- October 27, 2018
- Miscellaneous
- Michael
Not every summer resident has encountered karbysh. But those who have such misfortune will not soon forget about such contact. After all, a couple of these pests, finding themselves in a large area, may well leave a summer resident without the harvest he worked on all summer. Therefore, you have to fight the little carbysh animal, the photo of which is attached to the article, as decisively as possible, without the slightest compromise. Otherwise, instead of a rich harvest in the fall, you will get, at best, a mountain of cores.
Appearance
Description:
- The largest representative of the hamster subfamily. Body length in adult males is 27-34 cm, tail 3-8 cm, body weight on average 700 g.
- The tail is thick at the base , quickly becomes thinner towards the end, and is covered with short and stiff hair. The muzzle is of moderate length.
- The ears are rather short, covered with thin, darkish hair. The hand and foot are wide, and the fingers have well-developed claws.
- The hair is thick and soft. The color of the skin is bright and contrasting: the upper body is uniform, reddish-brown, the belly is black. On the front on the sides there are two large light spots, usually separated by a patch of black fur.
- light spots on the sides of the head and behind the ears, sometimes in the area of the shoulder blades. Entirely black specimens (melanists) or black specimens with white spots on the paws and throat are often found.
More than 10 subspecies have been described. The color of hamsters within their range brightens from north to south; body size increases from west to east and from north to south.
Tundra
Fauna of Australia
Only those birds that do not require lush vegetation live in the tundra zone. They also perfectly adapted to the cold, difficult climate. The natural conditions of the tundra are frequent hills, an abundance of swamps, small ponds, as well as many lichens and mosses. The tundra and arctic zones border each other, so the bird fauna has common features.
Tundra of Russia
polar owl
The polar or snowy owl is the largest inhabitant of the tundra among all owls. It is distinguished by its completely white color with small dark spots, although the chicks are born brown. Females are larger than males. The polar owl is a nomad and an active predator.
Polar Owl Interesting fact: the image of the polar owl is used in many industries. For example, in cinema and animation. This bird is also depicted on several coats of arms and is a symbol of the Canadian province of Quebec.
Bunochka
Representative of the order of Crows. The bunting weighs only about 30 g with a body length of 16.5 cm. Males and females differ in color, especially during the mating season. Males are usually black and females are white. Both have light bellies. Buntings feed on insects in summer and grains in winter.
Bunochka
Spreading
The common hamster is common in meadow and forest-steppes, as well as in the mixed-grass steppes of Eurasia from Belgium to Altai and Northern Xinjiang.
In Russia, the northern border of the range goes:
- from Smolensk north of Rzhev to Yaroslavl, Kirov and Perm;
- in the north of the Perm region it reaches 59°40′ N. sh.;
- in the Trans-Urals it goes through Yekaterinburg, crosses the Irtysh north of Tobolsk and the Ob in the Kolpashevo region, from where it goes to Krasnoyarsk.
The eastern border is formed by the Minusinsk steppe, where the hamster penetrated relatively recently.
The southern border runs:
- along the Azov and Black Sea coasts approximately to Gagra;
- covers the western Ciscaucasia, goes around the deserts and semi-deserts of the eastern Caspian region and the Volga-Ural interfluve from the north;
- crosses the Volga in the Astrakhan region.
Then it goes to Kazakhstan, where it goes approximately 47° N. w. to the lower reaches of the river Sarysu, covers the northern part of Betpak-Dala, the central and northeastern parts of the Kazakh hillocks, the valleys of the river. Ili and Karatal, the foothill areas of the northern and eastern Tien Shan, the Alakol and Zaisan basins and along the border of western Altai reaches the right bank of the Yenisei near the village. Beya.
Fauna of the Nizhny Novgorod region
The fauna of the Nizhny Novgorod region is also wide and diverse. A considerable number of representatives of different species live here.
Brown bears, lynxes, wolves and foxes live in forests and places far from humans. There are also moles, hares and squirrels, hedgehogs, muskrats and shrews.
Among the artiodactyls in the Nizhny Novgorod region you can find wild boars, deer, and moose.
Both in forests and in open spaces, there are martens, weasels, stoats and ferrets. Also representatives of small animals in the region are: badgers, otters and minks.
In the fields and meadows there are mice, voles, muskrats and hamsters.
The reservoirs and swamps of the Nizhny Novgorod region are full of inhabitants. Frogs, toads and newts find their refuge here, as well as lizards and snakes.
The region is home to many birds. Birds of prey include falcons, hawks and ospreys.
Herons and storks live in the floodplains, as well as ducks, geese and swans. The steppe zone is suitable for life of crane-like bird species.
The permanent and frequent inhabitants of the area are waders and gulls. Woodpeckers are irreplaceable inhabitants of both forests and steppes of these places.
It is also worth paying attention to the owl species; here you can find both tawny owls and owls. There is a bird here that is almost impossible to notice in everyday life - the black-throated and red-throated loon
There is a bird here that is almost impossible to notice in everyday life - the black-throated and red-throated loon.
Lifestyle
It is most numerous in the forest-steppe, forb and grass-forb steppe. It penetrates into the forest zone through floodplain and dry meadows, as well as forest fields (secondary deforested and plowed areas).
In the south of the range it adheres to wet areas: river valleys, depressions. It rises into the mountains to the lower border of the forest, and if there is no forest belt, to the mountain meadows inclusive.
It settles in cultivated areas - in rice systems, forest belts, parks, gardens, vegetable gardens and even in residential buildings. It settles less frequently on sandy and loose areas than on dense soils.
Twilight lifestyle. Spends the day in a hole, usually deep and complex, reaching 8 m in length and more than 1.5 m in depth.
Sometimes it occupies gopher burrows. A permanent burrow has 2-5, rarely up to 10 exits, a nesting chamber and several storage rooms.
Outside the breeding season, the common hamster leads a solitary lifestyle, is aggressive towards its relatives and is pugnacious.
Nutrition
The hamster is omnivorous, but its diet is dominated by plant foods. In addition to them, it eats insects and their larvae, small vertebrates (mice, reptiles and amphibians).
By autumn, it completely switches to feeding on seeds and tubers, which it stores in significant quantities: from 0.5 to 11-16 kg.
Hamster pantries are known to contain stocks of grain or potatoes up to 90 kg. The hamster feeds on them in the winter, when he temporarily wakes up from hibernation, and also in the spring before fresh food becomes available.
The hamster carries food in its cheek pouches, sometimes more than a kilometer away. Its cheek pouches can hold up to 46 g of wheat.
In the storerooms they found selected dried grains (rarely whole ears), peas, rice, millet, buckwheat, lupine, corn, lentils, and potatoes. The hamster stores different types of seeds separately.
Predator birds
There are many small predators in the forests and fields of the region. They are food for birds of prey, both diurnal and nocturnal.
You can recognize a buzzard hovering over a field by its short and rounded striped tail, as well as by the lighter color of its wings in the lower part. In flight, birds communicate with each other using a loud and drawn-out cry “kiya”. The main diet of the predator consists of rodents.
This formidable predator can be distinguished in flight by its forked tail. The bird's favorite food is fish, which it grabs with its claws. At the beginning of spring, the kite feeds on thawed carrion, protecting the forest from the spread of infectious diseases.
The owl’s “ears” are two tufts of feathers, which it can make invisible by pressing them to its head. The color of the bird is similar to the color of the bark of pine trees; a bird clinging to a tree can easily be mistaken for a branch. The owl is a nocturnal hunter whose main food is mouse-like rodents. Watch how ornithologists from the Nizhny Novgorod region ring birds.
What harm does it cause to the garden?
Throughout the warm season, karbysh actively feeds. Moreover, he happily eats cereals, gnaws beets, radishes and carrots, destroys crops of young peas, eating sprouts.
In general, he is not particularly picky, so the list of his “victims” may include cucumbers, tomatoes, pumpkins, onions, squash and much more.
The animal does not shine with intelligence, so it gnaws on almost everything that seems at least somewhat appetizing to it. Often he simply spits out the food he doesn’t like, but the vegetable is already spoiled!
Karbysh often sharpens its teeth on the bark of young fruit trees and shrubs, mercilessly tearing it off, which quite often leads to the death of the plant, which took several years to grow.
In the fall, he begins collecting supplies for the winter. Here he gives preference to cereals. Their karbysh, like all other hamsters, carries them around in cheek pouches.
In just a few weeks, a seemingly small animal can create a reserve of up to 15 kilograms in its burrow! And this is just one rodent.
But a couple of carbysh that appear on the site will quickly turn into several dozen. After all, if there is food, the female gives birth to cubs every month and a half.
Moreover, the litter can contain 10–12 cubs. Just imagine how many pests will end up in your area if you don’t take emergency measures.
If you leave everything to chance, hoping that the problem will be solved on its own, then in the fall you will definitely not see the harvest - it will be eaten or simply spoiled by harmful rodents.
Danger to humans
By the way, you shouldn’t be moved by looking at a photo of a karbysh. The animal is, of course, very beautiful. But it is not just a pest, but also poses a danger to humans.
Some people, having noticed this hamster on their site, decide to catch it. And as a result, they pay with their own health. A carbysh driven into a corner behaves no less cunningly and aggressively than a rat. Moreover, these rodents are often carriers of various infections. Therefore, a bite can cause a serious illness, the cure of which will take a lot of time and effort. Keep this in mind before you attack a rodent with your bare hands. No, this is a real war. And it must be carefully planned and thought out in order to achieve the desired result.
Reproduction
Among hamsters there is a complete absence of social organization. Pairs are formed only for a short mating period. Fertility is high.
The breeding season begins in March. The male searches for a partner, marking nearby territories with his scent. After mating, the pair separates and each returns to their own area.
From March to August, an adult female bears from 2 to 5 litters, each of which contains 4-12 cubs. Pregnancy lasts 21 days. The mother takes care of the newborns for about three weeks, and after 8 weeks the cubs begin independent life.
Young males are considered sexually mature at the age of 2 months, females - at 2.5-3 months.
If we take into account that a male covers several females during the period from March to August, then the population increases very significantly during the summer period. Despite this, the number of hamsters is unstable.
Rodents in the wild have many natural enemies. Years with increased birth rates are followed by periods of species extinction over large areas.
Until the mid-20th century, hamsters were caught for their skins, although rodent fur is not of great value. This led to a decline in the population.
To prevent complete extinction in five regions of Russia, the destruction of karbysh is prohibited by law.
Birds living near bodies of water
The reservoirs are rich in fish, insects, shellfish and reptiles, which become food for many species of birds.
gray heron
A beautiful and large bird that prefers shallow water. The back of the bird's head is decorated with a tuft of black feathers that bloom during the mating season. The nest of gray herons is built by the male; during the mating ritual, he drives away the female who has chosen him several times, after which they form a pair. Her favorite food is fish, which her excellent eyesight and sharp beak help her catch.
Bittern
Settles in swamps and lake shores overgrown with tall grasses (reeds, reeds). The bittern has a long and thick neck and a high and narrow beak. The feathers are yellow-brown, the body is covered with a pattern of brown spots and dashes. This bird is a master of camouflage; it pretends to be a snag or a stump and can stand in this position for a long time without moving.
The bittern has a loud and far-reaching cry, reminiscent of the roar of a bull.
Crake
A small and inconspicuous bird that lives in wetlands with standing water
He behaves very carefully, tries to avoid open spaces, runs quickly among tall grass. Mainly nocturnal
During the mating season, it makes sounds characteristic of this particular species of bird - a whistle similar to the sound of dripping water.
Lapwing
A distinctive feature of this bird is a black crest on its head and a wide black border decorating its white tail. Settle in damp meadows and swamps, using holes between hummocks for nests
The lapwing bravely protects its chicks; it even attacks dogs and people who approach the nest
Black swift
These birds form entire colonies on the banks of rivers. The swift's wing has a smooth curve, similar to a sickle. Swifts are the fastest birds in our country. However, they walk very poorly. To take off, they need to start falling down from the counter wall, sometimes they can’t even take off from level ground.
Snipe
A small bird with a very long and straight nose, variegated coloring and small stature allow it to remain unnoticed. During the flight it makes sharp and unexpected turns and can fall like a stone from a great height. The snipe performs its mating song with the help of its tail - having raised it and fluffed up the feathers, it sharply lowers it down. This produces a sound reminiscent of the bleating of a sheep.
What does the hole look like?
The karbysh digs a deep and complex hole. It reaches about eight meters in length and more than one and a half meters in depth. From time to time it settles in holes where gophers used to live.
A standard burrow of a common hamster can have up to 5 exits, numerous storage rooms and a nesting chamber.
The animal stores its supplies in the pantries. When the breeding season passes, the carbysh animal returns to a solitary lifestyle.
Flora of St. Petersburg
St. Petersburg is located at the southernmost tip of the taiga zone. Many thousands of years ago, a huge sea lay imposingly here, lazily rolling its blue waves under the influence of the wind. Then this area was covered by a glacier, which, crawling away, took with it the sea plain. All that was left of the sea was the Neva, a river in whose delta a huge number of islands formed. It was on them that Tsar Peter erected the first buildings of the future city. The swamps were urgently drained, and piles were pre-installed for the construction of many buildings. The piles were made from larch, which is known for the fact that it does not rot in water, and over time it becomes harder than stone.
Already 4 thousand years ago, the taiga encroached on these places. Its firs, spruces and pines approached the Gulf of Finland in a dense ring, interspersed only in the very south with tall bushes. Therefore, the flora of the city is presented in a very unique way. In the northern regions of the city, centuries-old pines and spruces still flourish, and in the south, ordinary people collect blueberries, lingonberries and sorrel.
Now St. Petersburg can be called one of the greenest cities in Russia. Vegetation covers up to 40% of the city's total area. Meticulous statisticians have calculated that until recently there was up to 65 sq.m. per St. Petersburg resident. green spaces. And no wonder, because the city has 68 parks, more than 150 gardens, over 700 public gardens and about 200 boulevards.
Natural forest vegetation has been preserved in many parks and gardens of the city: in Piskarevka, Sosnovka, near the Technical University and the Forestry Academy.
The vegetation of St. Petersburg is best represented in its parks. So in Central Park. S. Kirov, that on Elagin Island you can see 200-year-old oaks and elms, maples and birches, which coexist peacefully with centuries-old pines and firs. This is the northernmost park of the city, which very clearly demonstrates the proximity of taiga and deciduous forests.
The Summer Garden is the favorite brainchild of Peter I, who became one of the first parks in the capital of the empire, laid out according to all the rules of horticultural art. Over the centuries, the appearance of the garden has changed several times, but even now it remains one of the most visited parks in the city, where you can admire spreading linden and maple trees, numerous shrubs and a beautiful lawn.
Sosnovka Park, in the Vyborg region, is famous for its mighty pine trees. And Yuzhno-Primorsky Park, located in the Krasnoselsky district, delights visitors with slender chestnuts, weeping willows, mighty oaks and beautiful fir trees.
How to fight?
If a hamster has settled on your property, you should immediately take all possible measures to combat it. First of all, you can place traps on the animal and secure them properly.
Otherwise, the animal will go into the hole along with the trap.
You can drive away an “evil” hamster in the country with the help of water, which is used to flood the animal’s hole.
You need to pour a lot of water into the rodent’s home. Pour liquid until the animal begins to choke and crawls out. This method of pest control has its drawbacks.
A hamster's hole has more than one exit. In order to drive the animal out of the hole, the remaining exits should be closed.
The difficulty lies in the fact that the underground passages of a home can stretch for several meters, and the exit may be on someone else’s property.
One of the methods of pest control is rodent poisoning. An anti-carbysh remedy containing a toxic substance is placed next to the animal’s burrow. From time to time the poisonous “feeders” are replenished.
A dog can come to the rescue in the fight against carbysh. She is the enemy of the rodent. A rat-catcher cat is capable of catching an animal. She is specially trained for such hunting and, unlike a dog, will not cause much damage to the garden.
An ultrasonic repeller will help remove rodents from the area. The device emits specific mechanical and sound waves that are unpleasant for the animals, so when they hear them, they leave the area.
If there is a carbysh in the garden plot, then all fruit trees should be fenced with a metal mesh, since animals can damage the bark, and in some cases the tree is completely destroyed.
Chemical repellents for rodents
If a forest hamster has visited a summer cottage, you can remove it using rodent poison, which should be placed near the home.
The most popular chemicals are:
"Storm"
The poison acts quickly and effectively. Has mummifying properties. Prevents the animal's corpse from decomposing and eliminates the appearance of an unpleasant odor.
"Clairat"
Causes the death of the rodent within 24 hours. Reduces blood clotting and causes internal bleeding.
"Kilrath"
Effective on the pest for a week. It has a bitter taste, so experts advise mixing the drug with grain, porridge, mashed potatoes and other baits.
"Warat"
Bait in granules. Ensures 100% palatability by the animal. Valid for 3-6 days.
"Mortorath"
Mummifying bait. Produced in soft briquettes. Valid for 3-4 days. Contains the active ingredient brodifacoum. "The final". Produced in solid briquettes.
It is enriched with flavoring additives, which is why rodents eat it with pleasure. Has water-repellent properties. Convenient for use in damp places and at low temperatures.
"Rat Death"
Created on the basis of brodifacoum. Causes bleeding and suffocation. The death of the rodent occurs on days 5-8. The poison is placed near the karbysh burrows. Bait feeders are replenished from time to time.
Mechanical devices
In the fight against pests, mechanical devices will not be superfluous. A trap for carbysh should be taken with an arc one, designed for catching small fur-bearing animals. The charged device is placed at the horizontal entrance to the animal’s home.
Since the karbysh is capable of dragging away the trap, it should be securely fixed to the ground.
Some people fight rodents with traps, similar to mousetraps, only larger in size. This trap, like the previous one, should be secured.
To make the animal fall into the trap faster, you can add water to the hole. In this case, the hamster will jump out and immediately fall into the trap.
Homemade traps are used to catch the animal.
To make it, take a box with a lid that fits tightly. Two rubber bands are attached to the lid. They will press her. Place a spreader or stick under the lid. Bait is placed inside the box.
The rodent runs into the box and eats the bait. At this time the lid slams behind him. Instead of a box, it is more advisable to use a metal cage. Traps and traps are the best remedies for hamsters.
With them, the question of how to breed carbysh will be resolved within a short time.
Ultrasonic repellers
Another effective tool that helps remove carbys from the area is a rodent repeller. This method of pest control is the most humane and safe.
The device emits high-frequency ultrasonic waves, the frequency of which changes at a speed of 60 times per second.
For rodents, the sound produced becomes unbearable, and they try to move to another territory without a hostile sound signal.
The following devices are especially popular:
- "Typhoon". Can be used over an area of up to 220 m. Operates with a wide sound beam. Works in two modes: silent and sound. The first is used in residential premises, the second is more effective and is used where people do not live.
- "Grad". It works silently. Emits simultaneously sound and ultrasonic waves. There is a built-in flickering beam.
- "Electrocat" The rodent repeller acts not only with sound waves, but also with light flashes. There is a special irritating signal that has the most effective effect on rodents.
To achieve better results in the fight against underground pests, some gardeners bury an ultrasonic device in the ground and turn it on. According to them, karbysh leave the garden plot in a short time.
Fight against carbysh
The only bloodless and humane way to get rid of a rodent is to use special sound repellers. You can buy them in special stores. A person practically does not hear the sound they make, so all residents can calmly go about their business. But it has a more depressing effect on the carbysh, and as a result, after a few days the rodent leaves its usual habitat. The only negative is that this technique does not always work. The reason for this is unknown - either not all repellers are equally effective, or some animals are immune to them.
Therefore, we often have to resort to less humane methods - traps and poisons.
Traps (or large rat traps) are installed near the found exits from the holes. Be careful - one tunnel can have 4-5 exits. You can also place poisoned baits near the minks - poison can be easily purchased at any store for summer residents.
Yes, it's cruel. But in the battle for the harvest one cannot be too humane.
Prevention measures
If you do not want carbysh to start up on your site, you should get a dog or a rat-catcher cat.
These animals will do an excellent job of protecting against dangerous rodents. After all, they perceive them exclusively as tasty and desirable prey.
Of course, if you choose this method, then the use of poisons is out of the question - your pets may well be poisoned by them.
A new novel in the personal life of Dmitry Khrustalev
After breaking up with his common-law wife, Khrustalev began a new romance - with Ekaterina Varnava
Due to the fact that they worked together and communicated a lot on stage, few people paid attention to the beginning of a romantic relationship between the two colleagues; moreover, they diligently hid it. Katya admitted that she fell in love with Khrustalev when she did not yet know him personally, but only watched his performances as part of the KVN team
In the photo - Dmitry Khrustalev and Ekaterina Varnava
When they started working together at Comedy Woman, at first love was played out only on stage, and Varnava did not take Dmitry’s words seriously when he said that he could become an ideal husband for her. They became increasingly imbued with mutual sympathy, and after six months of relationship they began to live in the same apartment.
At that time, Khrustalev was already free, and nothing stopped him from changing something in his personal life.
However, Katya remained Dmitry Khrustalev’s common-law wife for no more than a year - living together turned out to be not so easy, quarrels began to break out more and more often between the lovers, and Varnava, tired of constant strife, went to live with a friend, and Mitya said that they would have a better life apart. Both claimed that the feelings between them had not passed, but they never managed to reunite again.
Conservation status
The number of the species has declined sharply over the past 20 years and continues to decline, but mainly only in the west and north of its range. Western European countries have adopted national programs for the conservation of this species.
The common hamster is protected in France, Belgium, the Netherlands, Germany, Poland, and Belarus.
In 2009, it was included in the Red Book of Ukraine, and by 2012, in the Autonomous Republic of Crimea, the animal was causing significant damage to the agriculture of the peninsula, including suburban farms.
On the territory of the Russian Federation it is protected in 5 constituent entities of the federation. A decrease in the number of the species has also been noted in other regions of the European part of Russia.
The hamster population is stable in Kazakhstan and Siberia, where during years of population growth it can cause harm to agriculture.
In recent years, the number has increased in the Azov district of the Rostov region, in the Krasnodar Territory, as well as in the Crimea, where the hamster also causes significant damage.
Habitat
The habitat of the carbysh animal, the photo of which you have already seen, is quite large. For example, in Europe it can be seen in Germany, France, Poland, Belgium, the Netherlands, Belarus - in all these countries it is protected, as it has been practically exterminated.
In our country, it lives from the northern border of the Perm Territory to Smolensk. Also, summer residents from Krasnoyarsk to Yekaterinburg often complain about it. There is quite a lot of it on the coast of the Black and Azov Seas. It is found in Kazakhstan - mainly in the east and north, where agriculture is most developed.
Where does the prairie dog live?
Photo: Prairie dogs
Prairie dogs have a permanent residence on the territory of the North American continent, or rather, on the vast expanses of its prairies. Rodents occupy an area stretching from the southern part of the province of Saskatchewan, which is located in Canada, and further covers a number of US states.
So, prairie dogs can be found in:
- Kansas;
- Wyoming;
- North and South Dakota;
- Texas;
- Nebraska;
- Utah;
- Montana;
- Oklahoma;
- Colorado;
- New Mexico;
- Arizona.
Prairie dogs have taken a liking to Northern and Central Mexico. They prefer semi-desert and steppe landscapes, where there is no tall vegetation; it is not for nothing that they are called meadow landscapes; the presence of short or medium-sized grass is enough for them. A grassy expanse of arid plains near some water source is an ideal habitat for these squirrels. Dogs try to avoid excessively wet soils and lowlands. Animals were also seen in mountain ranges at an altitude of more than three kilometers. Prairie dogs live collectively in dug burrows, the corridors of which underground form entire labyrinth cities, where there are rooms for various needs.
Interesting fact: The labyrinths of underground tunnels can reach up to 350 meters in length, and go down to 5 meters in depth.
Now you know where the prairie dog lives. Let's see what she eats.
Reptiles Edit
Unlike the common viper and grass snake, which are ubiquitous, the steppe viper and spotted snake are found only in the southern regions of Bashkiria. The godwit lives in forest and forest-steppe zones.
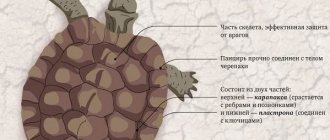
The European marsh turtle inhabits water bodies in the southern regions of the republic: Baymaksky, Kuyurgazinsky, Kugarchinsky, Meleuzovsky, Zianchurinsky, Zilairsky and Khaibullinsky districts. The marsh turtle lives in slow-flowing and stagnant bodies of water [17].
The Red Book of Bashkiria includes such rare species as the legless lizard - the spindle, the gray snake - the common copperhead, the water snake, the patterned snake, the steppe viper and the marsh turtle [18].
Karbyshi in the garden plot
The hamster causes great damage to garden plots. His activity in the garden begins during the seedling period. At this time, the karbysh (animal) cuts off the sprouts of cabbage, pumpkin, cucumber, carrot, and onion seedlings as if with scissors.
In the summer, the animal destroys the fruits of zucchini, carrots, pumpkins, and beets. The rodent loves onions and garlic. Doesn’t refuse squash and potatoes. Gnawing out tubers and roots from plants. At this time, the pest not only destroys crops, but also stores potatoes, carrots, and seeds for the winter.
Karbysh is very voracious, and it causes significant damage in the garden. Whatever he can't eat, he takes away with him. Gardeners are forced to constantly fight it.
Pros and cons of keeping rodents
pros
These include the following facts:
- inexpensive maintenance and minimum hassle;
- unpretentious care that any child can handle;
- these are very clean animals, so there will be no need for constant bathing;
- they do not make loud sounds and do not interfere with sleep;
- rodents are quite intelligent and easily amenable to simple training;
- There is nothing expensive that rodents eat: mainly special food, hay, vegetables, fruits, and various vitamins.
Minuses
The disadvantages include:
- many species do not live long - about 2-5 years, but the exceptions are chinchillas and rabbits, whose age can reach 12-15 years;
- the animal should not be allowed out of the cage if there is no one to look after it, otherwise the house will be a mess;
- the cage needs to be washed every day so that there is no strong smell in the apartment;
- small animals must be handled carefully, otherwise they may bite;
- can make sounds at night, since at this time of day they are most active.
This article talks about what types of domestic rodents are with photos and names.
Fauna of Bashkiria
Bashkir horses in the Abzelilovsky district
Fauna of Bashkiria
- a set of living organisms of all types of wild animals that permanently or temporarily inhabit the territory of the Republic of Bashkiria.
The diversity of landscapes and natural zones of the republic, geographical location and historical connections with the European part of Russia and Siberia determined the richness and diversity of its animal world. Bashkiria is home to 120 species of unicellular organisms, about 700 species of worms, 121 species of mollusks, about 5000 arthropods, 47 fish, 10 amphibians, 10 reptiles, about 300 birds, 76 mammals.
Karbysh animal: photo, description, habitat, harm and control methods
- October 27, 2018
- Miscellaneous
- Michael
Not every summer resident has encountered karbysh. But those who have such misfortune will not soon forget about such contact. After all, a couple of these pests, finding themselves in a large area, may well leave a summer resident without the harvest he worked on all summer. Therefore, you have to fight the little carbysh animal, the photo of which is attached to the article, as decisively as possible, without the slightest compromise. Otherwise, instead of a rich harvest in the fall, you will get, at best, a mountain of cores.