Many novice breeders, purchasing the following breeds of individuals of the hamster order - Djungarian and Syrian, begin to ask questions when they see that the hamster has black spots on the sides. There are a sufficient number of questions on the forums related to their presence on the body of animals. Many consider them “sores” and wonder whether they will harm humans and other pets. There is no need to sound the alarm, since these are peculiar anatomical features of the animals, explained by the protrusion of scent glands.
“Male” glands in individuals of the Syrian breed
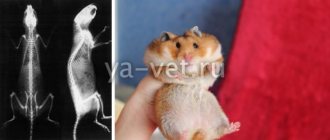
In individuals of the Syrian breed, black spots, which are scent gland tubules, may differ in appearance. There are cases when owners do not notice their presence, since they hardly stand out in the fur of their pets. In others, they can be large or soapy in size, in the form of bulges or flat, pale or dark in color. Sometimes the black spots are so small that they look like a cluster of small dots in one place.
The glands of males are more noticeable than those of females. They have the appearance of warts and are distinguished by their convexity and roughness. If you notice that your pet is rubbing its sides against the bars of the cage or some parts of its body are wet, do not worry. In this way, he marks a new territory or attracts the attention of a female during estrus.
Often the black spot a hamster has changes its appearance. In such situations, after an examination, veterinarians can identify the following conditions of the pet:
- being in a stressful situation;
- development of inflammatory processes;
- development of cancer.
Treatment in these cases can be prescribed either conservatively, using only medications, or surgically, requiring immediate surgical intervention.
LiveInternetLiveInternet
Thus, both Syrian and dwarf hamsters normally have scent glands. There is no need to treat these anatomical formations. However, it is important to keep track of their appearance, as it can reflect both the emotional state and health of the hamster. In addition, sometimes the scent glands become inflamed.
Questions of the following nature are often asked about the condition of Syrian hamsters: “... the hamster recently developed black sores on its back, symmetrically to each other. What could it be? How dangerous is this for animals and people?”; “... I noticed two black spots on the sides of the hamster’s back, similar to birthmarks. There are large round bald spots around the spots...”; “... what is the black spot (spots) on the back (on the barrel) of the Syrian hamster and how to treat it?”; “... our hamster began to itch on the sides, where her hind legs reach, she even developed scabs on both the right and left.
8. Males can “lick the glands” when they mark a new territory, when a female in heat is nearby, or in a state of severe stress. 9. The glands do not need to be “treated.” However, it is important to consider that a change in their appearance or the condition of the hair around them is a sign of severe stress in the hamster (he tries to smell as intensely as possible in order to scare enemies or secure territory).
Male dwarf hamsters (both Djungarian and Campbell's hamsters) have a scent gland on their abdomen. This is a natural anatomical formation and there is no need to worry about it. Dwarf hamsters (like Syrians) mark territory (it looks like the hamster is itching or scratching its belly). The gland usually looks like an oval-shaped spot or “crust”, red or brownish in color, often with yellow droplets of secretion. Females lack iron.
Scent glands of hamsters At home, they most often contain: Syrian hamster; Campbell's dwarf hamster; Dzungarian dwarf hamster. The last two types of hamsters are very similar in appearance and even interbreed. But, nevertheless, these are different hamsters.
Older pets may also develop a tumor of the scent gland. These conditions already require veterinary care (therapy or surgery). Veterinarian Artem Arkadievich Kazakov
It looks like small black dots on some parts of the body...” What should you know in this case? Syrian hamsters have scent glands on their sides, the secretions of which are used by hamsters to mark territory.
It happens that the glands simply look like a cluster of dark spots on the skin. 2. In males, the glands are more visible. They are large and dark, resembling moles or warts. 3. In females, the glands are not as convex and rough as in males. They are hardly noticeable on the body and (if there is no pigmentation) may not be detected at all.
9. Cases of the development of an inflammatory or oncological process in the glands are often noted. Such situations require conservative or surgical treatment by a veterinarian specializing in the treatment of rodents. Regarding dwarf hamsters, questions are also often asked: “... the dwarf hamster has a sore on its stomach, is it dangerous?”; “...my dwarf is itching and some kind of pimple has popped up on his stomach. Please tell me what to do?”; “... my jungarik (boy) has something appeared right in the middle of his abdomen, it looks like dry skin, or a dry sore (what it could be. " What is the situation for “dwarfs.”
YOU CAN ORDER ON THE OFFICIAL WEBSITE
The glands are located symmetrically on the sides, slightly in front of the hind legs. This is a normal anatomical formation for Syrian hamsters! What are the nuances? 1. The appearance of the glands may differ for each individual Syrian. For some they are practically invisible, for others they are pronounced. The glands can be large or small, convex or flat, light or brown.
4. The hamster can (and should) rub its sides (glands) against the bars of the cage when marking its territory. This is not a cause for concern. 5. Wool does not grow on glands. 6. In light-colored short-haired hamsters, the glands are often more visible than in other colors and hair types. 7. In young males of light colors, in place of the glands, the coat may be of a different, brighter color than the main color.
Scent glands in "jungarians"
Unlike the Syrian breed, individuals of the order of hamsters of the Djungarian breed have distinctive black spots on the stomach. By the way, they develop only in males and are absent in females. The animals mark their territory by scratching their bellies against various objects in the cage. For this reason, you should make sure that the accessories located in it do not have sharp corners.
As you can see, the black spots present on the hamster’s body are a common anatomical formation that should not be treated. However, if the black spot appears spontaneously, increases in size, and the animal’s condition begins to deteriorate, it is worth showing it to a specialist at a veterinary clinic. Spots that appear in large quantities on the body of animals can become a herald of the development of serious inflammatory and oncological processes.
Malocclusion and occlusion in rodents
Occlusion is the exact alignment of the upper and lower rows of teeth when chewing food. A slight displacement to the side is enough and the grinding of the surfaces will occur unevenly, the growth of the teeth will be excessive, and one incisor (or molar) may be smaller than the neighboring one. The appearance of sharp edges, shoots, and fragments is dangerous for the pet; they injure surrounding tissues, causing inflammation and suppuration.
Malocclusion is a disease that is characterized by improper formation of the dentition due to poor wear of teeth and the formation of pathological surfaces. Actually, malocclusion is the process of improper grinding of dental surfaces; at first glance, it is not dangerous, but as a result it can lead to the following problems in the oral cavity in rodents:
- wounds, ulcers on the oral mucosa;
- changes in tooth root growth;
- infection of periarticular tissues and organs. Bacterial microflora and purulent foci can spread to bone tissue, conjunctival sac, and postorbital space. As a result, abscesses, conjunctivitis, and osteomyelitis develop;
- deformation of the temporomandibular joint.
Any discomfort in a rodent's mouth does not allow it to eat normally, and apathy, exhaustion, dehydration, and disruption of the gastrointestinal tract develop. With purulent processes, there is a threat of blood poisoning (sepsis) and the development of secondary pathological processes, such as rhinitis, dermatitis, pododermatitis, etc.
Important! A veterinarian-ratologist, having identified the root cause of diseases that have developed in a rodent, makes a diagnosis and summarizes it with one name: “dental syndrome”.
The hamster has spots. What could it be?
Owners quite often notice black spots on their hamster’s body.
Don't rush to sound the alarm. These spots may not always be dangerous to the life and health of the animal. Black symmetrical spots on the sides are scent glands.
Syrian and Djungarian hamsters use scent glands to mark their territory. Their size and color may vary. Spots on hamsters
They can be large and convex, and in some they are very small and unnoticeable. Some owners do not notice these spots at all and this is quite normal.
In males, the scent glands are much more pronounced. They are convex and have a slight roughness. Sometimes rodents rub against the bars of the cage. At this point, you can notice that their sides are wet. In this way they mark their territory or try to attract the attention of the female. This is a natural phenomenon. There is no reason to worry.
If your hamster has black spots
change, you should consult a doctor. Changes may indicate stress, inflammation, or even cancer in the animal. Only a veterinarian can make a correct diagnosis after a full examination. Treatment can be either medication or surgery.
In Djungarian hamsters, the location of the scent glands is slightly different. Hamster has spots
are on the tummy. They are present only in males. They mark their territory by scratching their bellies. Try to remove all sharp objects from the cage so that the animal does not get hurt.
What to do if your hamster has spots?!
If you notice a red spot on your hamster,
then you should contact a veterinarian. These can be various skin diseases. They pose a great danger to small pets. Treatment of skin diseases should begin when the first symptoms appear. Weakness, partial refusal of food and water, bad mood, drowsiness. This can be lichen, dermatitis, damage by ticks, fleas and other parasites.
Parasitic diseases of hamsters: symptoms and treatment
Diseases caused by external (ectoparasites) and internal (endoparasites) agents.
If a hamster experiences itching, scratching, or loss of appetite, the owner may suspect the presence of external parasites in his pet; some types of parasites can be detected with the naked eye on the hamster’s fur, skin, and ears. These can be fleas, lice, lice, ticks and others. In this case, the ratologist prescribes contact insecticides in dosages that are safe for the health of the rodent.
If the hamster's stool is soft during defecation, there is mucus, blood, or even fragments of internal parasites in the stool, then you should suspect the presence of internal parasites in your pet (various types of helminths, coccidia, and others). You need to consult a ratologist to diagnose the type of parasite and prescribe antiparasitic drugs.
Lichen
This is a skin disease caused by a viral infection or microscopic fungi. Depending on the pathogen, there are two types of lichen: ringworm and pink lichen.
Rodents with weakened immune systems, mechanical trauma to the skin, and elderly animals are at risk of infection.
The following symptoms are typical for lichen:
- baldness;
- the appearance of inflamed areas;
- itching;
- loss of appetite.
If the disease is confirmed, the sick hamster is isolated from other pets, the cage, bowls, wheel and all objects that came into contact with the infected animal are disinfected. The most effective means for this will be a formaldehyde solution or a sulfur-carbolic mixture.
For treatment, antifungal drugs are used, which are prescribed by a specialist, who will also tell you the dosage and duration of the course. Hair is removed from damaged areas of the body as they are contaminated with fungal spores.
Dried crusts are softened and cut off, the area is treated with salicylic ointment, and the edges are treated with iodine. It is also recommended to support your pet’s body with immunostimulating drugs and probiotics during the treatment period.
Ringworm
A characteristic feature is rounded bald patches on the front of the body and muzzle.
Further, these bald spots become inflamed and form purulent ulcers, through which the fungus enters the body, poisoning it with toxins and causing itching throughout the body.
The disease is transmitted from humans to animals and vice versa.
Pityriasis rosea
The main difference from other skin diseases is the appearance of hairless pink areas of skin, more saturated at the edges than in the center.
It is not dangerous for humans - unlike trichophytosis (the scientific name for ringworm), it is not transmitted through household contact.
What is lichen?
This is a skin disease of viral origin, caused by fungi that can only be seen under a microscope.
It is believed that hamsters with weakened immune systems or those with a chronic disease are most susceptible to shingles.
The main signs of the disease are rashes on the skin in the form of pink, ringing or weeping spots, as well as the appearance of inflamed areas, in the place of which hairless spots appear, and the hairs themselves break off at the root. With lichen, there is constant itching, which is why the animal scratches the skin vigorously, resulting in the formation of crusts that begin to peel off. The pet’s appetite also worsens. The incubation period lasts from 10 to 30 days.
If your furry friend exhibits these symptoms, you should contact your veterinarian immediately, as shingles is often confused with a common allergic reaction. During the examination, the veterinarian uses a special device - a fluorescent lamp, with which you can clearly see fungal spores, which fluoresce when hit by a light beam. But an accurate diagnosis is established only after laboratory tests.
Scab
The causative agent is the fungus Achorion Schoenleini. Hamsters get the disease through contact with sick animals or humans, through insect bites and contaminated equipment.
It looks different depending on the stage of development.
- white scaly plaque on the ears, eyebrows and tip of the nose;
- formations are round in shape with a diameter of up to 1 cm;
- Over time, the affected areas become covered with blisters, which gradually increase in size and form crusts with hairs in the middle.
A sick animal must be isolated from other pets, the room and objects with which it has been in contact must be treated with disinfectants.
Establishing an accurate diagnosis will allow the veterinarian to select an antifungal drug, establish the dosage and course of treatment. It is also necessary to treat the affected areas of the skin - scales and scabs should be softened with oils and carefully removed.
Treat areas cleaned of crusts daily with iodine tincture mixed with alcohol solutions of glycerin, creolin or Lysol.
Treatment
Certain types of fungus are treated exclusively with antifungal drugs, which should be prescribed by a specialist . Having determined the type of fungus and the degree of infection, the required dosage of the drug and course of treatment are prescribed.
Antifungal drugs:
| Triderm | Complex antifungal drug that is applied externally | The course of treatment is 10-14 days. During this period, you need to apply a thin layer of ointment to the affected areas of the skin 2 times a day. |
| Fluconazole | An antifungal drug that suppresses the synthesis of fungal spores, which should be used once a day | Course of treatment 2–4 weeks |
| Griseofulvin | Antibiotic prevents fungal cell division | The course of taking the drug is prescribed by a veterinarian |
| Ketoconazole | A broad-spectrum drug that allows you to stop the synthesis of cell membrane substances, destroying the fungal membrane | Treatment course 10 days |
How to treat at home?
First of all, it is necessary to completely isolate the sick hamster from other pets. Next, disinfect all objects with which it came into contact; if it is an inexpensive item, then it is better, of course, to throw it away completely.
Fungal spores, especially ringworm, are very persistent and can remain on the hair throughout the animal's life.
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to remove the affected hairs in those areas of the body where the disease is observed, since they are infected with fungal spores. The scissors with which you cut the hairs must be boiled for 10 minutes and treated with disinfectant. means to destroy fungal spores.
If there are crusts, they need to be softened and removed; this procedure must be done until your furry animal has fully recovered.
In addition to medications, you also need to treat the lesions with iodine solution and salicylic ointment. Thanks to the components contained in iodine, the infected surface of the skin is well disinfected, and with the help of ointment, the affected areas can be quickly restored. Also, during the treatment period, it is necessary to give your hamster special medications that support the immune system and restore the microflora.
Dermatophytosis
A skin disease caused by dermatophyte fungi that feed on hair and dead cells. The infection is also known as ringworm because the red lesions appear in rings on the skin.
There is severe peeling along the edges of the spots, while the surface in the center is absolutely healthy.
Dermatophytosis poses a threat to households - it can be transmitted from animals to humans.
Treatment is selected by a specialist, usually using external agents such as Yam or Fungin ointment, Zoomekol aerosol, chlorhexidine, and sometimes oral medications. The duration of therapy is 1-2 months.
Don’t forget about disinfecting the premises – fungal spores are viable for up to 4 years.
Types and symptoms
Hamsters are susceptible to only two types of lichen: ringworm and pink lichen.
Reasons why hamsters get lichen:
- Low immunity;
- Mechanical injuries to the skin, in which pathogens penetrate into the wound;
- Age factor.
Ringworm, regardless of the type, most often occurs in the summer, but in winter this disease is observed less frequently due to the fact that cold weather prevents the active development of pathogenic fungi.
Shearer
It is divided into two infections - microscopy and trichophytosis. Characteristic signs of ringworm (or also called trichophytosis) are the appearance of a receding hairline on the face and front of the body. The pathogen is usually brought in from the street on clothes or shoes.
The disease may not be detected immediately ; the incubation period can reach several months or more. The first symptom is the appearance of a round bald spot on the hamster's body, then these areas of the skin become inflamed and purulent ulcers form, through which the fungus penetrates deep into the skin. It is the released toxins that cause itching, which is why the hamster begins to itch very much, resulting in baldness of the infected area of skin followed by the formation of a dense crust. The fungus penetrates deep into the tissues, releasing toxins inside the animal's body.
As a rule, the first areas to be affected are the muzzle, behind the ears and sides.
First of all, therapy should be aimed exclusively at increasing immunity.
Pink
The causative agent of this type of lichen is a viral infection. The main and most important symptom is the appearance of hairless areas of skin that are very itchy and flaky, causing discomfort to the hamster. In the center of the spot, reaching a diameter of up to two centimeters, a slightly pink color is observed, but at the edges it is more saturated. Pityriasis rosea, as a rule, occurs with a sharp decrease in immunity during the off-season, when hamsters may develop vitamin deficiency, as well as with a weakened immune system. It usually affects very young or elderly hamsters.
The main difference between pityriasis rosea and ringworm is that if your pet is infected with pityriasis rosea, you can be absolutely calm that this infection can be transmitted to you through contact and household contact.
Scab
A fungal disease caused by the fungus Achorion Schoenleini. If not properly treated in a timely manner, the infection can become chronic. The incubation period ranges from 3 to 12 days. The animal has a white scaly coating near the base of the ear, on the eyebrows or the tip of the nose. The diameter of the spots can reach up to 1 centimeter; small grayish bubbles form in the center of them, which gradually burst, forming a crust on the animal’s skin.
Dermatophytosis
A skin infectious disease that occurs when dermatophyte fungi enter the body and feed on dead skin cells and hair. This infection is also called “ringworm” because round, red spots appear on the infected area of skin in the form of rings. Peeling is observed along the edges of the spots, while the skin in the center of the spot itself is absolutely not affected and remains healthy. For treatment, antifungal drugs or ointments are prescribed, as well as chlorhexidine solution and zoomicol aerosol. The course of taking medications is 1-2 months.
Ticks
Ectoparasites on a hamster are quite common, but they do not bother the animal, since their number is usually small.
For a clear clinical picture of the disease to appear, they must be accompanied by vitamin deficiencies, weakened immunity, or poor hygienic conditions.
Causes and symptoms. Rodents are most often affected by Demodex mites, which are the causative agents of demodicosis.
With this disease, the pet experiences itching, dandruff, increased hair loss, dry and irritated skin.
Hamsters are often parasitized by Notoedres mites, the causative agents of notoedrosis.
This pathology is characterized by severe itching, hair loss, and the formation of dry crusts and dandruff on the face, ears, cheeks and limbs.
To get rid of itching, animals itch, the skin is damaged, and this leads to infection.
Rodents become irritable, refuse food - the result is exhaustion, which can be fatal.
Another type of scabies is caused by the scabies mite Sarcoptes anacanthos. With sarcoptic mange, pets itch severely, damaging the skin and infecting the wounds.
Pustules form throughout the body, which turn into scabs and scabs.
Without timely and effective help, a small pet may die 3-4 weeks after the first symptoms appear.
To get rid of ticks, use local preparations in the form of powders, sprays, ointments, shampoos with selenium sulfide or oral insecticides. Diagnosis and treatment should be carried out by a veterinarian.
The drugs metrifonate and cythioate showed good results. For sarcoptic mange, infected animals are bathed in a 0.5% bromocyclene solution.
To cure a hamster from notoerdrosis, the affected areas should be treated with a 3% solution of the drug SK-9, sulfur ointment, the course of recovery is 7-10 days.
In case of bream, the pet must be isolated from other individuals, and the cage and objects with which it has been in contact must be disinfected. This will prevent re-infection.
Demodectic mange in a hamster
Demodex spp are responsible for skin diseases in hamsters in 80% of cases. The causative agents of the pathology are Demodex criceti and D.aurati. The first type of ectoparasites have a short but thick body. They live in the keratin layer of the skin and can penetrate the surface of the epidermis. D.aurati has a cigar-shaped, elongated body shape.
They parasitize hair follicles and sebaceous glands.
The presence of mites in the layers of the skin does not guarantee the development of demodicosis. Symptoms of the disease appear under the following conditions:
- avitaminosis;
- weakened immune system;
- poor hygienic conditions;
- age from 6 months to 2 years.
Demodicosis is transmitted through contact of a healthy hamster with a sick animal through various objects, such as bedding, food, and the owner’s belongings.
Important! After reproducing under the skin, mites from the genus Demodecidae form colonies containing several thousand parasites.
The causative agents of demodicosis irritate the hair follicles and sebaceous glands. This leads to disruption of nutrition, innervation (conduction of nerve impulses), and skin functionality.
With demodicosis, the quality of hamsters' fur deteriorates, it becomes dull, and easily falls out, even in large clumps. Baldness of varying intensity and localization is observed. Itching is rare or absent. The skin in the foci of infection turns red, becomes covered with crusts, a dandruff-like coating, and thickens.
To diagnose demodicosis, a Wood's lamp examination is carried out, scrapings are taken from the affected areas for further microscopy. After identifying the type of tick, the ratologist draws up a treatment plan.
Important! If demodicosis is suspected in a hamster, a differential diagnosis is carried out. It will help distinguish the pathology that was caused by ticks from lichen, ectoparasites and allergies.
Treatment of demodicosis will be effective if the hamster eats properly. The diet should include proteins, vitamins, and minerals. If the immune system is weakened, the ratologist prescribes a vitamin-mineral complex for the pet.
Hamsters suffering from demodicosis are prescribed a course of injections using Ivermectin, Stromectol, Mectizan, Cydectin. The pet needs to receive from 2 to 6 injections with an interval of 10 days.
Also, for demodicosis, external treatment of the affected areas using local drugs (Ivermectin, Premetrin, Fipronil) is indicated. When treating lesions, it is important to capture a healthy border of skin (1 cm). External agents are used for 4 weeks. You also need to bathe your hamster using shampoo that contains benzoyl peroxide (0.25%).
Important! The life cycle of mites that cause demodicosis is about 15 days. Therefore, treatment with antiparasitic drugs should be repeated, otherwise relapse cannot be avoided.
Treatment of demodicosis in a hamster must be supplemented by regular disinfection of the cage, all its accessories, and cleaning of the room.
A skin disease that is similar to demodicosis can be caused by Notoedres cati, which affects the ears, muzzle, cheeks, limbs, and the area around the anus. Dry crusts with a gray coating appear in these places. The hair falls out, the hamster often itches and scratches the skin.
The skin disease is very contagious, progresses quickly, and if left untreated, the pet dies within 2–3 months. Hexochlorane can be used for treatment.
Sarcoptes scabiei, Trixacarus caviae and Liponyssus bacoti can also parasitize the skin of hamsters. When affected by these mites, the hamster is rarely bothered by itching and inflammation of the skin. During the treatment of skin diseases, Ivermectin, Selamectin or lime sulphide are used.
To avoid demodicosis, you need to limit the hamster from contact with other animals, keep its cage clean, make a balanced and varied diet, and be attentive to the pet’s health. If you suspect skin diseases, you should visit a ratologist.
Prevention measures
To avoid infection with skin diseases, as well as to prevent relapses, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- nutrition should be balanced;
- the water in the drinking bowl should be changed regularly so that it is always fresh;
- hygiene rules must be observed;
- periodically treat the premises with disinfectants;
- carry out vaccinations against major serious diseases.
These simple rules will support your pet’s immunity and prevent infection from developing.
Causes of hair loss
They can be divided into two categories: natural and pathological shedding.
The pet is healthy, active, eats well, but the fur is very loose.
Seasonal shedding - old wool is replaced by new. Occurs intensely on the abdomen and the inside of the legs, and almost imperceptibly on the back.
Age - on average, hamsters live three years, a two-year-old rodent is already considered old, and it is quite natural that he began to go bald.
Hormonal changes – during pregnancy, females can experience intense hair loss. Also, bald spots on the abdomen appear in hamsters that feed their young.
Sometimes hair loss can indicate health problems or improper care. The causes of baldness should be excluded and checked in order:
Filler - some of them can cause an allergic reaction in a rodent.
Nutrition - it must be balanced with all the necessary elements so as not to cause vitamin deficiency. Sometimes hamsters develop intolerance to some fruit or vegetable, it is worth finding out by elimination.
Stress – constant change of environment can lead to baldness.
Diseases are one of the most dangerous causes. Only a specialist can make a diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment.
Who is at risk?
The prerequisites for the development of pathologies are the structural features of the teeth. In rodents they are aradicular, characterized by lifelong growth, and do not have a true root or apex.
Pets – rodents and lagomorphs – are prone to dental problems. Oral diseases are usually associated with excessive growth of incisors and molars. If it is not possible to constantly sharpen them, then they injure the gums, adjacent teeth and periosteum. Often, with a severely advanced problem, the incisors can pierce right through the skull.